- Miscellaneous
- Corrigendum: Correction of Acknowledgments. Active Surveillance as an Effective Management Option for Low-Risk Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma
-
Min Ji Jeon, Won Gu Kim, Tae Yong Kim, Young Kee Shong, Won Bae Kim
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(1):180. Published online February 28, 2022
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.103
-
Corrects: Endocrinol Metab 2021;36(4):717
-
2,608
View
-
107
Download
-
1
Web of Science
-
1
Crossref
-
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader  ePub ePub
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Lateral Involvement in Different Sized Papillary Thyroid Carcinomas Patients with Central Lymph Node Metastasis: A Multi-Center Analysis
Yu Heng, Zheyu Yang, Pengyu Cao, Xi Cheng, Lei Tao
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(17): 4975. CrossRef
- Thyroid
- Clinical Characteristics and Prognosis of Coexisting Thyroid Cancer in Patients with Graves’ Disease: A Retrospective Multicenter Study
-
Jee Hee Yoon, Meihua Jin, Mijin Kim, A Ram Hong, Hee Kyung Kim, Bo Hyun Kim, Won Bae Kim, Young Kee Shong, Min Ji Jeon, Ho-Cheol Kang
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(6):1268-1276. Published online November 26, 2021
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1227
-
-
4,891
View
-
187
Download
-
10
Web of Science
-
11
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF Supplementary Material Supplementary Material PubReader PubReader  ePub ePub
- Background
The association between Graves’ disease (GD) and co-existing thyroid cancer is still controversial and most of the previously reported data have been based on surgically treated GD patients. This study investigated the clinicopathological findings and prognosis of concomitant thyroid cancer in GD patients in the era of widespread application of ultrasonography.
Methods
Data of GD patients who underwent thyroidectomy for thyroid cancer between 2010 and 2019 in three tertiary hospitals in South Korea (Asan Medical Center, Chonnam National University Hwasun Hospital, and Pusan National University Hospital) were collected and analyzed retrospectively. In the subgroup analysis, aggressiveness and clinical outcomes of thyroid cancer were compared nodular GD and non-nodular GD groups according to the presence or absence of the thyroid nodules other than thyroid cancer (index nodules).
Results
Of the 15,159 GD patients treated at the hospitals during the study period, 262 (1.7%) underwent thyroidectomy for coexisting thyroid cancer. Eleven patients (4.2%) were diagnosed with occult thyroid cancer and 182 patients (69.5%) had microcarcinomas. No differences in thyroid cancer aggressiveness, ultrasonographic findings, or prognosis were observed between the nodular GD and non-nodular GD groups except the cancer subtype. In the multivariate analysis, only lymph node (LN) metastasis was an independent prognostic factor for recurrent/persistent disease of thyroid cancer arising in GD (P=0.020).
Conclusion
The prevalence of concomitant thyroid cancer in GD patients was considerably lower than in previous reports. The clinical outcomes of thyroid cancer in GD patients were also excellent but, more cautious follow-up is necessary for patients with LN metastasis in the same way as for thyroid cancer in non-GD patients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Comparison of Surgical Outcomes of Transoral Versus Open Thyroidectomy for Graves Disease
Suo-Hsien Wang, Wu-Po Chao, Ta-You Lo, Soh-Ching Ng, Yu-Hsien Chen
Surgical Laparoscopy, Endoscopy & Percutaneous Techniques.2024; 34(2): 150. CrossRef - Outcomes of Surgical Treatment for Graves’ Disease: A Single-Center Experience of 216 Cases
Hanxing Sun, Hui Tong, Xiaohui Shen, Haoji Gao, Jie Kuang, Xi Chen, Qinyu Li, Weihua Qiu, Zhuoran Liu, Jiqi Yan
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(4): 1308. CrossRef - Cancer and Mortality Risks of Graves’ Disease in South Korea Based on National Data from 2010 to 2019
Young Ju Choi, Kyungdo Han, Won Kyoung Cho, Min Ho Jung, Byung-Kyu Suh
Clinical Epidemiology.2023; Volume 15: 535. CrossRef - Risk and Prognosis of Thyroid Cancer in Patients with Graves’ Disease: An Umbrella Review
Marco Palella, Francesca Maria Giustolisi, Adriana Modica Fiascaro, Martina Fichera, Antonella Palmieri, Rossella Cannarella, Aldo E. Calogero, Margherita Ferrante, Maria Fiore
Cancers.2023; 15(10): 2724. CrossRef - Characteristics, staging and outcomes of differentiated thyroid cancer in patients with and without Graves’ disease
Chaitra Gopinath, Hanna Crow, Sujata Panthi, Leonidas Bantis, Kenneth D. Burman, Chitra Choudhary
Journal of Clinical & Translational Endocrinology.2023; 33: 100321. CrossRef - Prevalence, Treatment Status, and Comorbidities of Hyperthyroidism in Korea from 2003 to 2018: A Nationwide Population Study
Hwa Young Ahn, Sun Wook Cho, Mi Young Lee, Young Joo Park, Bon Seok Koo, Hang-Seok Chang, Ka Hee Yi
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(4): 436. CrossRef - Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis and Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma: A Follow-Up Study in Patients with Absence of Aggressive Risk Factors at the Surgery of the Primary Tumor
Andrea Marongiu, Susanna Nuvoli, Andrea De Vito, Sonia Vargiu, Angela Spanu, Giuseppe Madeddu
Diagnostics.2023; 13(19): 3068. CrossRef - Table of Contents
Clinical Thyroidology.2022; 34(2): 48. CrossRef - Predisposition to and Prognosis of Thyroid Cancer May Not Be Affected by Graves’ Disease, But Some Questions Still Remain
Yanrui Huang, Haixia Guan
Clinical Thyroidology.2022; 34(2): 59. CrossRef - A Comparative Follow-Up Study of Patients with Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Associated or Not with Graves’ Disease
Andrea Marongiu, Susanna Nuvoli, Andrea De Vito, Maria Rondini, Angela Spanu, Giuseppe Madeddu
Diagnostics.2022; 12(11): 2801. CrossRef - An unusual case of papillary thyroid carcinoma presenting as Graves’ disease
Pooja Tiwari, Uma Kaimal Saikia, Abhamoni Baro, Ashok Krishna Bhuyan
Thyroid Research and Practice.2022; 19(1): 47. CrossRef
- Thyroid
- Clinicopathological Characteristics and Disease-Free Survival in Patients with Hürthle Cell Carcinoma: A Multicenter Cohort Study in South Korea
-
Meihua Jin, Eun Sook Kim, Bo Hyun Kim, Hee Kyung Kim, Yea Eun Kang, Min Ji Jeon, Tae Yong Kim, Ho-Cheol Kang, Won Bae Kim, Young Kee Shong, Mijin Kim, Won Gu Kim
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(5):1078-1085. Published online October 28, 2021
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1151
-
-
3,929
View
-
110
Download
-
4
Web of Science
-
4
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF Supplementary Material Supplementary Material PubReader PubReader  ePub ePub
- Background
Hürthle cell carcinoma (HCC), a type of thyroid carcinoma, is rare in South Korea, and few studies have investigated its prognosis.
Methods
This long-term multicenter retrospective cohort study evaluated the clinicopathological features and clinical outcomes in patients with HCC who underwent thyroid surgery between 1996 and 2009.
Results
The mean age of the 97 patients included in the study was 50.3 years, and 26.8% were male. The mean size of the primary tumor was 3.2±1.8 cm, and three (3.1%) patients had distant metastasis at initial diagnosis. Ultrasonographic findings were available for 73 patients; the number of nodules with low-, intermediate-, and high suspicion was 28 (38.4%), 27 (37.0%), and 18 (24.7%), respectively, based on the Korean-Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data System. Preoperatively, follicular neoplasm (FN) or suspicion for FN accounted for 65.2% of the cases according to the Bethesda category, and 13% had malignancy or suspicious for malignancy. During a median follow-up of 8.5 years, eight (8.2%) patients had persistent/recurrent disease, and none died of HCC. Older age, gross extrathyroidal extension (ETE), and widely invasive types of tumors were significantly associated with distant metastasis (all P<0.01). Gross ETE (hazard ratio [HR], 27.7; 95% confidence interval [CI], 2.2 to 346.4; P=0.01) and widely invasive classification (HR, 6.5; 95% CI, 1.1 to 39.4; P=0.04) were independent risk factors for poor disease-free survival (DFS).
Conclusion
The long-term prognosis of HCC is relatively favorable in South Korea from this study, although this is not a nation-wide data, and gross ETE and widely invasive cancer are significant prognostic factors for DFS. The diagnosis of HCC by ultrasonography and cytopathology remains challenging.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Molecular Alterations and Comprehensive Clinical Management of Oncocytic Thyroid Carcinoma
Lindsay A. Bischoff, Ian Ganly, Laura Fugazzola, Erin Buczek, William C. Faquin, Bryan R. Haugen, Bryan McIver, Caitlin P. McMullen, Kate Newbold, Daniel J. Rocke, Marika D. Russell, Mabel Ryder, Peter M. Sadow, Eric Sherman, Maisie Shindo, David C. Shonk
JAMA Otolaryngology–Head & Neck Surgery.2024; 150(3): 265. CrossRef - Oncocytic carcinoma of the thyroid: Conclusions from a 20‐year patient cohort
Nelson R. Gruszczynski, Shahzeb S. Hasan, Ana G. Brennan, Julian De La Chapa, Adithya S. Reddy, David N. Martin, Prem P. Batchala, Edward B. Stelow, Eric M. Dowling, Katherine L. Fedder, Jonathan C. Garneau, David C. Shonka
Head & Neck.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Hurthle cell carcinoma: a rare variant of thyroid malignancy – a case report
Yuvraj Adhikari, Anupama Marasini, Nawaraj Adhikari, Laxman D. Paneru, Binit Upadhaya Regmi, Manita Raut
Annals of Medicine & Surgery.2023; 85(5): 1940. CrossRef - Hürthle Cell Carcinoma: Single Center Analysis and Considerations for Surgical Management Based on the Recent Literature
Costanza Chiapponi, Milan J.M. Hartmann, Matthias Schmidt, Michael Faust, Christiane J. Bruns, Anne M. Schultheis, Hakan Alakus
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Thyroid
- Active Surveillance as an Effective Management Option for Low-Risk Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma
-
Min Ji Jeon, Won Gu Kim, Tae Yong Kim, Young Kee Shong, Won Bae Kim
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(4):717-724. Published online August 11, 2021
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1042
-
Correction in: Endocrinol Metab 2022;37(1):180
-
4,736
View
-
181
Download
-
4
Web of Science
-
3
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader  ePub ePub
- Active surveillance (AS) for low-risk papillary thyroid microcarcinoma (PTMC) has been accepted worldwide as safe and effective. Despite the growing acceptance of AS in the management of low-risk PTMCs, there are barriers to AS in real clinical settings, and it is important to understand and establish appropriate AS protocol from initial evaluation to follow-up. PTMC management strategies should be decided upon after careful consideration of patient and tumor characteristics by a multidisciplinary team of thyroid cancer specialists. Patients should understand the risks and benefits of AS, participate in decision-making and follow structured monitoring strategies. In this review, we discuss clinical outcomes of AS from previous studies, optimal indications and follow-up strategies for AS, and unresolved questions about AS.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Serum thyroglobulin testing after thyroid lobectomy in patients with 1–4 cm papillary thyroid carcinoma
Ahreum Jang, Meihua Jin, Chae A Kim, Min Ji Jeon, Yu-Mi Lee, Tae-Yon Sung, Tae Yong Kim, Won Bae Kim, Young Kee Shong, Won Gu Kim
Endocrine.2023; 81(2): 290. CrossRef - Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma: Active Surveillance Against Surgery. Considerations of an Italian Working Group From a Systematic Review
Giuseppina Orlando, Gregorio Scerrino, Alessandro Corigliano, Irene Vitale, Roberta Tutino, Stefano Radellini, Francesco Cupido, Giuseppa Graceffa, Gianfranco Cocorullo, Giuseppe Salamone, Giuseppina Melfa
Frontiers in Oncology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Prognosis of Patients with 1–4 cm Papillary Thyroid Cancer Who Underwent Lobectomy: Focus on Gross Extrathyroidal Extension Invading Only the Strap Muscles
Ahreum Jang, Meihua Jin, Won Woong Kim, Min Ji Jeon, Tae-Yon Sung, Dong Eun Song, Tae Yong Kim, Ki-Wook Chung, Won Bae Kim, Young Kee Shong, Yu-Mi Lee, Won Gu Kim
Annals of Surgical Oncology.2022; 29(12): 7835. CrossRef
- Clinical Study
- Gender-Dependent Reference Range of Serum Calcitonin Levels in Healthy Korean Adults
-
Eyun Song, Min Ji Jeon, Hye Jin Yoo, Sung Jin Bae, Tae Yong Kim, Won Bae Kim, Young Kee Shong, Hong-Kyu Kim, Won Gu Kim
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(2):365-373. Published online April 7, 2021
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.939
-
-
5,071
View
-
152
Download
-
4
Web of Science
-
5
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF Supplementary Material Supplementary Material PubReader PubReader  ePub ePub
- Background
Serum calcitonin measurement contains various clinical and methodological aspects. Its reference level is wide and unclear despite sensitive calcitonin kits are available. This study aimed to identify the specific reference range in the healthy Korean adults.
Methods
Subjects were ≥20 years with available calcitonin (measured by a two-site immunoradiometric assay) data by a routine health checkup. Three groups were defined as all eligible subjects (group 1, n=10,566); subjects without self or family history of thyroid disease (group 2, n=5,152); and subjects without chronic kidney disease, autoimmune thyroid disease, medication of proton pump inhibitor/H2 blocker/steroid, or other malignancies (group 3, n=4,638).
Results
This study included 6,341 male and 4,225 female subjects. Males had higher mean calcitonin than females (2.3 pg/mL vs. 1.9 pg/mL, P<0.001) in group 1. This gender difference remained similar in groups 2 and 3. Calcitonin according to age or body mass index was not significant in both genders. Higher calcitonin in smoking than nonsmoking men was observed but not in women. Sixty-nine subjects had calcitonin higher than the upper reference limit (10 pg/mL) and 64 of them had factors associated with hypercalcitoninemia besides medullary thyroid cancer. Our study suggests the reference intervals for men who were non, ex-, current smokers, and women (irrespective of smoking status) as <5.7, <7.1, <7.9, and <3.6 pg/mL, respectively.
Conclusion
Specific calcitonin reference range should be provided considering for sex and smoking status. Taking account for several factors known to induce hypercalcitoninemia can help interpret the gray zone of moderately elevated calcitonin.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Determinants of circulating calcitonin value: analysis of thyroid features, demographic data, anthropometric characteristics, comorbidities, medications, and smoking habits in a population with histological full exclusion of medullary thyroid carcinoma
Pierpaolo Trimboli, Giuseppe Peloni, Dorotea Confalonieri, Elena Gamarra, Tommaso Piticchio, Francesco Frasca, Petra Makovac, Arnoldo Piccardo, Lorenzo Ruinelli
Frontiers in Oncology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Surgical treatment of solid variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma: Fifteen-year experience of a tertiary center
Katarina Tausanović, Marina Stojanović, Milan Jovanović, Boban Stepanović, Jovan Ilić, Sara Ivaniš, Vladan Živaljević
Medicinska istrazivanja.2024; 57(1): 121. CrossRef - Some genetic differences in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
Hosam M. Ahmad, Zaki M. Zaki, Asmaa S. Mohamed, Amr E. Ahmed
BMC Research Notes.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Presence or severity of Hashimoto’s thyroiditis does not influence basal calcitonin levels: observations from CROHT biobank
M. Cvek, A. Punda, M. Brekalo, M. Plosnić, A. Barić, D. Kaličanin, L. Brčić, M. Vuletić, I. Gunjača, V. Torlak Lovrić, V. Škrabić, V. Boraska Perica
Journal of Endocrinological Investigation.2022; 45(3): 597. CrossRef - Environmental Factors That Affect Parathyroid Hormone and Calcitonin Levels
Mirjana Babić Leko, Nikolina Pleić, Ivana Gunjača, Tatijana Zemunik
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 23(1): 44. CrossRef
- Clinical Study
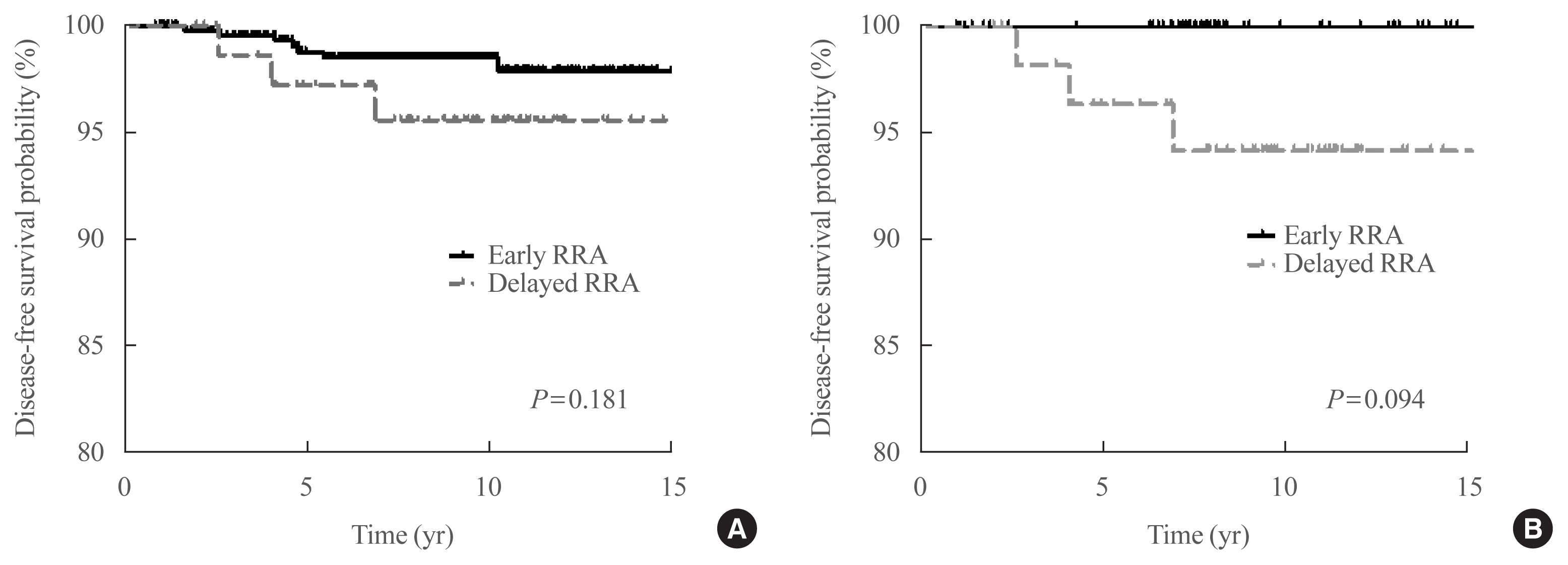
- Clinical Outcomes after Early and Delayed Radioiodine Remnant Ablation in Patients with Low-Risk Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma: Propensity Score Matching Analysis
-
Jonghwa Ahn, Meihua Jin, Eyun Song, Min Ji Jeon, Tae Yong Kim, Jin-Sook Ryu, Won Bae Kim, Young Kee Shong, Ji Min Han, Won Gu Kim
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(4):830-837. Published online November 18, 2020
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.747
-
-
4,279
View
-
132
Download
-
3
Web of Science
-
6
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF Supplementary Material Supplementary Material PubReader PubReader  ePub ePub
- Background
The clinical outcomes of delayed radioiodine remnant ablation (RRA) therapy in patients with low-risk papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) are unclear. We aimed to evaluate the clinical impact of the interval between total thyroidectomy (TT) and RRA therapy in patients with low-risk PTC.
Methods
We included 526 patients who underwent TT and RRA for low-risk PTC with a primary tumor size of >1 cm between 2000 and 2012. Patients were divided into the early (<90 days) and the delayed (≥90 days) RRA groups based on the interval between TT and RRA. The results of diagnostic whole-body scan (DxWBS), ongoing risk stratification (ORS; response to therapy), and disease-free survival (DFS) were evaluated before and after propensity score matching (PSM).
Results
Among the 526 patients, 75 (14.3%) patients underwent delayed RRA; they had more cervical lymph node metastasis and received a higher RRA dose than those who underwent early RRA. The median follow-up period was 9.1 years after initial therapy, and the structural recurrence rate was 1.9%. In DxWBS, 60 patients had focal iodine uptake limited in operative bed, with no significant difference between groups. According to ORS, 78%, 20%, 1%, and 1% patients were classified into excellent, indeterminate, biochemical incomplete, and structural incomplete response groups, respectively. There was no significant difference in ORS or DFS between groups before and after PSM.
Conclusion
The timing of the first RRA had no clinical impact in patients with low-risk PTC. Thus, the clinical decision for RRA can be determined >3 months after TT considering other prognostic factors.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Dynamic risk assessment in patients with differentiated thyroid cancer
Erika Abelleira, Fernando Jerkovich
Reviews in Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders.2024; 25(1): 79. CrossRef - Ablation Rates and Long-Term Outcome Following Low-Dose Radioiodine for Differentiated Thyroid Cancer in the West of Scotland: A Retrospective Analysis
Kathryn Graham, Fay Tough, Helena Belikova, Irene Wotherspoon, David Colville, Nicholas Reed
Endocrine Practice.2024; 30(4): 327. CrossRef - Radioiodine ablation after thyroidectomy could be safely abandoned or postponed in selected stage I papillary thyroid carcinoma patients of low-risk group: an observational prospective study
S.M. Cherenko, A.Yu. Glagolieva, D.E. Makhmudov
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENDOCRINOLOGY (Ukraine).2024; 20(1): 7. CrossRef - Patient Preparation and Radiation Protection Guidance for Adult Patients Undergoing Radioiodine Treatment for Thyroid Cancer in the UK
J. Wadsley, N. Armstrong, V. Bassett-Smith, M. Beasley, R. Chandler, L. Cluny, A.J. Craig, K. Farnell, K. Garcez, N. Garnham, K. Graham, A. Hallam, S. Hill, H. Hobrough, F. McKiddie, M.W.J. Strachan
Clinical Oncology.2023; 35(1): 42. CrossRef - Delay of initial radioactive iodine therapy beyond 3 months has no effect on clinical responses and overall survival in patients with thyroid carcinoma: A cohort study and a meta‐analysis
Fang Cheng, Juan Xiao, Fengyan Huang, Chunchun Shao, Shouluan Ding, Canhua Yun, Hongying Jia
Cancer Medicine.2022; 11(12): 2386. CrossRef - Delayed (>3 Months) Postoperative Radioactive Iodine Ablation Does Not Impact Clinical Response or Survival in Differentiated Thyroid Cancers
Tatiana Fedorova, Lilah F. Morris-Wiseman
Clinical Thyroidology.2022; 34(10): 456. CrossRef
- Clinical Study
- Vandetanib for the Management of Advanced Medullary Thyroid Cancer: A Real-World Multicenter Experience
-
Mijin Kim, Jee Hee Yoon, Jonghwa Ahn, Min Ji Jeon, Hee Kyung Kim, Dong Jun Lim, Ho-Cheol Kang, In Joo Kim, Young Kee Shong, Tae Yong Kim, Bo Hyun Kim
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(3):587-594. Published online September 22, 2020
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.687
-
-
5,703
View
-
148
Download
-
12
Web of Science
-
12
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader  ePub ePub
- Background
Vandetanib is the most widely used tyrosine kinase inhibitor for the treatment of patients with advanced medullary thyroid cancer (MTC). However, only limited data regarding its use outside clinical trials are available. We aimed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of vandetanib in patients with advanced MTC in routine clinical practice.
Methods
In this multicenter retrospective study, 12 patients with locally advanced or metastatic MTC treated with vandetanib at four tertiary hospitals were included. The primary outcome was the objective response rate (ORR) based on the Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors. The progression-free survival (PFS), overall survival (OS), and toxicities were also evaluated.
Results
Eleven patients (92%) had distant metastasis and 10 (83%) had disease progression at enrollment. Partial response was observed in five patients (ORR, 42%) and stable disease lasting ≥24 weeks was reported in an additional five patients (83%). During the median 31.7 months of follow-up, disease progression was seen in five patients (42%); of these, two died due to disease progression. The median PFS was 25.9 months, while the median OS was not reached. All patients experienced adverse events (AEs) which were generally consistent with the known safety profile of vandetanib. Vandetanib was discontinued in two patients due to skin toxicity.
Conclusion
Consistent with the phase III trial, this study confirmed the efficacy of vandetanib for advanced MTC in terms of both ORR and PFS in the real-world setting. Vandetanib was well tolerated in the majority of patients, and there were no fatal AEs.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Metastatic medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC): disease course, treatment modalities and factors predisposing for drug resistance
Katerina Saltiki, George Simeakis, Olga Karapanou, Stavroula A. Paschou, Maria Alevizaki
Endocrine.2023; 80(3): 570. CrossRef - Initial Experiences of Selective RET Inhibitor Selpercatinib in Adults with Metastatic Differentiated Thyroid Carcinoma and Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma: Real-World Case Series in Korea
Han-Sang Baek, Jeonghoon Ha, Seunggyun Ha, Ja Seong Bae, Chan Kwon Jung, Dong-Jun Lim
Current Oncology.2023; 30(3): 3020. CrossRef - Molecular Basis and Natural History of Medullary Thyroid Cancer: It is (Almost) All in the RET
Nicolas Sahakian, Frédéric Castinetti, Pauline Romanet
Cancers.2023; 15(19): 4865. CrossRef - Sporadic Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma: Towards a Precision Medicine
Antonio Matrone, Carla Gambale, Alessandro Prete, Rossella Elisei
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Targeted therapy and drug resistance in thyroid cancer
Yujie Zhang, Zhichao Xing, Tianyou Liu, Minghai Tang, Li Mi, Jingqiang Zhu, Wenshuang Wu, Tao Wei
European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry.2022; 238: 114500. CrossRef - Daily Management of Patients on Multikinase Inhibitors’ Treatment
Carla Colombo, Simone De Leo, Matteo Trevisan, Noemi Giancola, Anna Scaltrito, Laura Fugazzola
Frontiers in Oncology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Angiogenic Balance and Its Implications in Cancer and Cardiovascular Diseases: An Overview
Cătălina Ionescu, Bogdan Oprea, Georgeta Ciobanu, Milena Georgescu, Ramona Bică, Garofiţa-Olivia Mateescu, Fidan Huseynova, Veronique Barragan-Montero
Medicina.2022; 58(7): 903. CrossRef - Reassessing vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in anti-angiogenic cancer therapy
Tobiloba C. Elebiyo, Damilare Rotimi, Ikponmwosa O. Evbuomwan, Rotdelmwa Filibus Maimako, Matthew Iyobhebhe, Oluwafemi Adeleke Ojo, Olarewaju M. Oluba, Oluyomi S. Adeyemi
Cancer Treatment and Research Communications.2022; 32: 100620. CrossRef - Current Guidelines for Management of Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma
Mijin Kim, Bo Hyun Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(3): 514. CrossRef - Recent advances in precision medicine for the treatment of medullary thyroid cancer
Jolanta Krajewska, Aleksandra Kukulska, Malgorzata Oczko-Wojciechowska, Barbara Jarzab
Expert Review of Precision Medicine and Drug Development.2021; 6(5): 307. CrossRef - Functional evaluation of vandetanib metabolism by CYP3A4 variants and potential drug interactions in vitro
Mingming Han, Xiaodan Zhang, Zhize Ye, Jing Wang, Jianchang Qian, Guoxin Hu, Jianping Cai
Chemico-Biological Interactions.2021; 350: 109700. CrossRef - Nephrotoxicity in advanced thyroid cancer treated with tyrosine kinase inhibitors: An update
Alice Nervo, Francesca Retta, Alberto Ragni, Alessandro Piovesan, Alberto Mella, Luigi Biancone, Marco Manganaro, Marco Gallo, Emanuela Arvat
Critical Reviews in Oncology/Hematology.2021; 168: 103533. CrossRef
- Clinical Study
- Clinical Outcomes of N1b Papillary Thyroid Cancer Patients Treated with Two Different Doses of Radioiodine Ablation Therapy
-
Meihua Jin, Jonghwa Ahn, Yu-Mi Lee, Tae-Yon Sung, Won Gu Kim, Tae Yong Kim, Jin-Sook Ryu, Won Bae Kim, Young Kee Shong, Min Ji Jeon
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(3):602-609. Published online September 22, 2020
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.741
-
-
5,425
View
-
121
Download
-
1
Web of Science
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader  ePub ePub
- Background
The optimal dose of radioactive iodine (RAI) therapy for N1b papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) is controversial. We evaluated the clinical outcome of N1b PTC patients treated with either 100 or 150 mCi of RAI.
Methods
We retrospectively analyzed N1b PTC patients who underwent total thyroidectomy and postoperative RAI therapy at a tertiary referral center between 2012 and 2017. As the baseline characteristics differed between treatment groups, we performed exact matching for various pathological factors according to RAI dose. We evaluated the response to therapy and recurrence-free survival (RFS) in the matched patients. Structural recurrent/persistent disease was defined as new structural disease detected after initial therapy, which was confirmed by cytology or pathology.
Results
Of the total 436 patients, 37 (8.5%) received 100 mCi of RAI and 399 (91.5%) received 150 mCi of RAI. After an exact 1:3 matching, 34 patients in the 100 mCi group and 100 patients in the 150 mCi group remained. There was no significant difference in response to therapy between the groups in the matched population (P=0.63). An excellent response was achieved in 70.6% (n=24) of patients in the 100 mCi group and 76.0% (n=76) in the 150 mCi group. Two (5.9%) patients in the 100 mCi group and four (4.0%) in the 150 mCi group had recurrence and there was no significant difference in RFS between the groups in the matched population (P=0.351).
Conclusion
There were no differences in response to therapy and RFS in N1b PTC patients according to RAI dose.
- Clinical Study
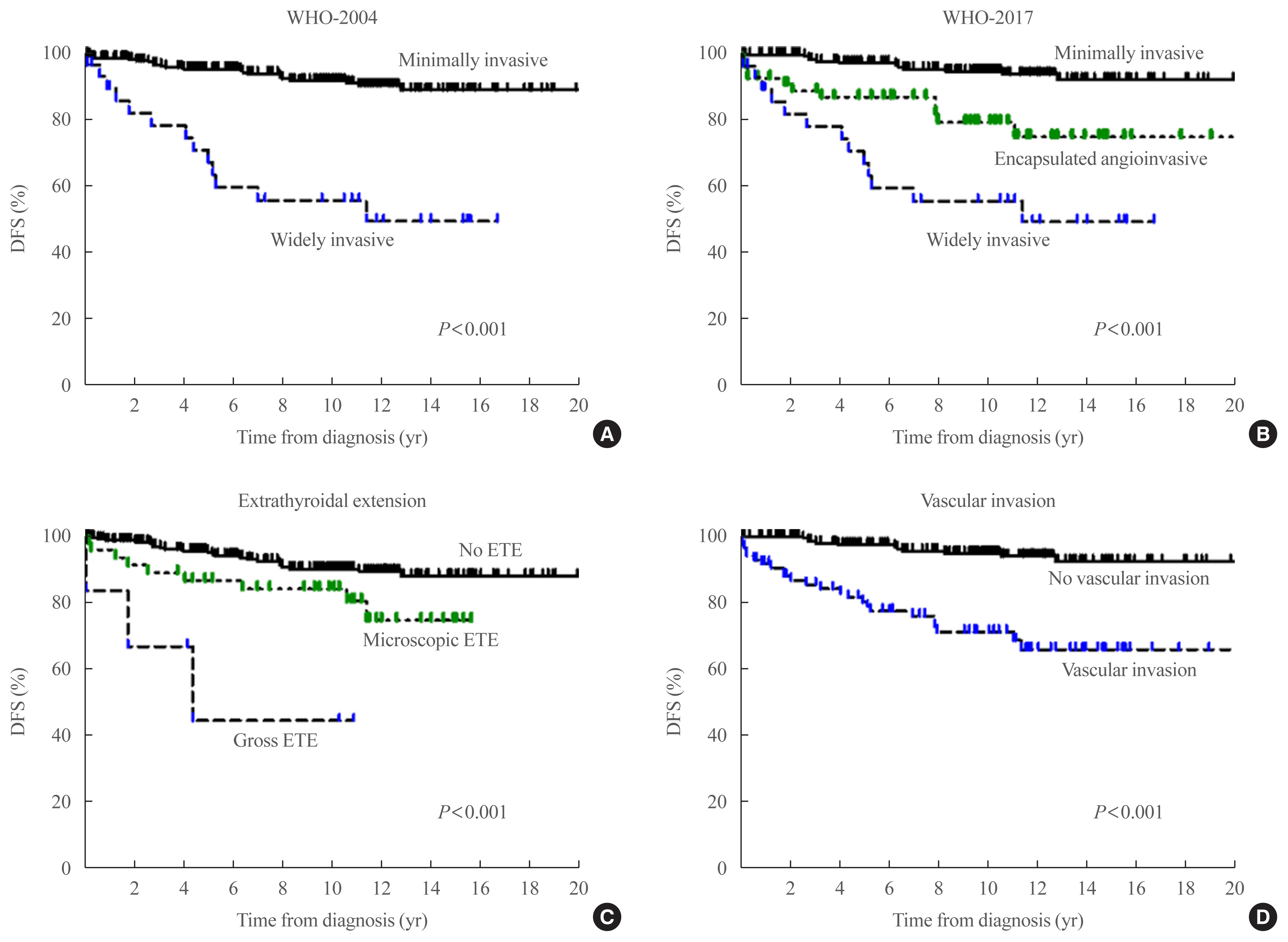
- Clinical Implication of World Health Organization Classification in Patients with Follicular Thyroid Carcinoma in South Korea: A Multicenter Cohort Study
-
Meihua Jin, Eun Sook Kim, Bo Hyun Kim, Hee Kyung Kim, Hyon-Seung Yi, Min Ji Jeon, Tae Yong Kim, Ho-Cheol Kang, Won Bae Kim, Young Kee Shong, Mijin Kim, Won Gu Kim
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(3):618-627. Published online September 22, 2020
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.742
-
-
5,456
View
-
121
Download
-
8
Web of Science
-
9
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader  ePub ePub
- Background
The study aimed to compare the prognostic value of the 4th edition of World Health Organization classification (WHO-2017) with the previous WHO classification (WHO-2004) for follicular thyroid carcinoma (FTC).
Methods
This multicenter retrospective cohort study included 318 patients with FTC from five tertiary centers who underwent thyroid surgery between 1996 and 2009. We evaluated the prognosis of patients with minimally invasive (MI), encapsulated angioinvasive (EA), and widely invasive (WI) FTC according to WHO-2017. Further, we evaluated the proportion of variation explained (PVE) and Harrell’s C-index to compare the predictability of disease-free survival (DFS) and disease-specific survival (DSS).
Results
In total, 227, 58, and 33 patients had MI-, EA-, and WI-FTC, respectively. During a median follow-up of 10.6 years, 46 (14.5%) patients had disease recurrence and 20 (6.3%) patients died from FTC. The 10-year DFS rates of patients with MI-, EA-, and WI-FTC were 91.1%, 78.2%, and 54.9%, respectively (P<0.001, PVE=7.1%, C-index=0.649). The corresponding 10-year DSS rates were 95.9%, 93.5%, and 73.5%, respectively (P<0.001, PVE=2.6%, C-index=0.624). The PVE and C-index values were higher using WHO-2017 than using WHO-2004 for the prediction of DFS, but not for DSS. In multivariate analysis, older age (P=0.02), gross extrathyroidal extension (ETE) (P=0.003), and distant metastasis (P<0.001) were independent risk factors for DSS.
Conclusion
WHO-2017 improves the predictability of DFS, but not DSS, in patients with FTC. Distant metastasis, gross ETE and older age (≥55 years) were independent risk factors for DSS.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Association of Ultrasonography Features of Follicular Thyroid Carcinoma With Tumor Invasiveness and Prognosis Based on WHO Classification and TERT Promoter Mutation
Myoung Kyoung Kim, Hyunju Park, Young Lyun Oh, Jung Hee Shin, Tae Hyuk Kim, Soo Yeon Hahn
Korean Journal of Radiology.2024; 25(1): 103. CrossRef - Clinical Outcomes and Implications of Radioactive Iodine Therapy on Cancer-specific Survival in WHO Classification of FTC
Genpeng Li, Ziyang Ye, Tao Wei, Jingqiang Zhu, Zhihui Li, Jianyong Lei
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Radioiodine whole body scan pitfalls in differentiated thyroid cancer
Cristina Basso, Alessandra Colapinto, Valentina Vicennati, Alessandra Gambineri, Carla Pelusi, Guido Di Dalmazi, Elisa Lodi Rizzini, Elena Tabacchi, Arber Golemi, Letizia Calderoni, Stefano Fanti, Uberto Pagotto, Andrea Repaci
Endocrine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The Prognostic Impact of Extent of Vascular Invasion in Follicular Thyroid Carcinoma
David Leong, Anthony J. Gill, John Turchini, Michael Waller, Roderick Clifton‐Bligh, Anthony Glover, Mark Sywak, Stan Sidhu
World Journal of Surgery.2023; 47(2): 412. CrossRef - TERT Promoter Mutation as a Prognostic Marker in Encapsulated Angioinvasive and Widely Invasive Follicular Thyroid Carcinomas
Yasuhiro Ito, Takashi Akamizu
Clinical Thyroidology.2023; 35(5): 202. CrossRef - Risk factors for death of follicular thyroid carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Ting Zhang, Liang He, Zhihong Wang, Wenwu Dong, Wei Sun, Ping Zhang, Hao Zhang
Endocrine.2023; 82(3): 457. CrossRef - Molecular classification of follicular thyroid carcinoma based on TERT promoter mutations
Hyunju Park, Hyeong Chan Shin, Heera Yang, Jung Heo, Chang-Seok Ki, Hye Seung Kim, Jung-Han Kim, Soo Yeon Hahn, Yun Jae Chung, Sun Wook Kim, Jae Hoon Chung, Young Lyun Oh, Tae Hyuk Kim
Modern Pathology.2022; 35(2): 186. CrossRef - Whole-genome Sequencing of Follicular Thyroid Carcinomas Reveal Recurrent Mutations in MicroRNA Processing Subunit DGCR8
Johan O Paulsson, Nima Rafati, Sebastian DiLorenzo, Yi Chen, Felix Haglund, Jan Zedenius, C Christofer Juhlin
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2021; 106(11): 3265. CrossRef - Clinicopathological Characteristics and Disease-Free Survival in Patients with Hürthle Cell Carcinoma: A Multicenter Cohort Study in South Korea
Meihua Jin, Eun Sook Kim, Bo Hyun Kim, Hee Kyung Kim, Yea Eun Kang, Min Ji Jeon, Tae Yong Kim, Ho-Cheol Kang, Won Bae Kim, Young Kee Shong, Mijin Kim, Won Gu Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(5): 1078. CrossRef
- Clinical Study
- Quality of Life in Patients with Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma According to Treatment: Total Thyroidectomy with or without Radioactive Iodine Ablation
-
Jonghwa Ahn, Min Ji Jeon, Eyun Song, Tae Yong Kim, Won Bae Kim, Young Kee Shong, Won Gu Kim
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(1):115-121. Published online March 19, 2020
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.35.1.115
-
-
5,542
View
-
110
Download
-
8
Web of Science
-
12
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader  ePub ePub
- Background
Recently, there has been some controversy regarding the role of radioactive iodine (RAI) ablation in the treatment of low-risk differentiated thyroid carcinoma (DTC), especially papillary thyroid microcarcinoma (PTMC). This study aimed to compare quality of life (QoL) parameters between patients with PTMC who underwent total thyroidectomy (TT) alone and those who underwent TT with RAI ablation. MethodsIn this cross-sectional study, patients with PTMC who underwent TT with/without RAI remnant ablation were prospectively enrolled between June 2016 and October 2017. All patients completed three questionnaires: the 12-item short-form health survey (SF-12), thyroid cancer-specific quality of life (THYCA-QoL) questionnaire, and fear of progression (FoP) questionnaire. ResultsThe TT and TT with RAI groups comprised 107 and 182 patients, respectively. The TT with RAI group had significantly lower serum thyrotropin (TSH) levels than the TT group. However, after matching for TSH levels between the groups (n=100 in both groups), there were no significant differences in baseline characteristics. According to the SF-12, the score for general health was significantly lower in the TT with RAI group than in the TT group (P=0.047). The THYCA-QoL also showed a significant difference in the “felt chilly” score between groups (P=0.023). No significant differences in FoP scores were observed between the groups. ConclusionPatients with PTMC who underwent TT with RAI ablation experienced more health-related problems than those managed with TT alone. These findings support the idea that RAI ablation should be carefully considered in patients with low-risk DTCs.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Quality of life of patients with thyroid cancer in Colombia
Oscar Gómez, Alvaro Sanabria
Endocrinología, Diabetes y Nutrición.2024; 71(2): 61. CrossRef - Quality of life of patients with thyroid cancer in Colombia
Oscar Gómez, Alvaro Sanabria
Endocrinología, Diabetes y Nutrición (English ed.).2024; 71(2): 61. CrossRef - Fear of Cancer Recurrence in Differentiated Thyroid Cancer Survivors: A Systematic Review
Jacob Hampton, Ahmad Alam, Nicholas Zdenkowski, Christopher Rowe, Elizabeth Fradgley, Christine J. O'Neill
Thyroid®.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Review: Improving quality of life in patients with differentiated thyroid cancer
Pia Pace-Asciak, Jonathon O. Russell, Ralph P. Tufano
Frontiers in Oncology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Health-Related Quality of Life and Thyroid Cancer-Specific Symptoms in Patients Treated for Differentiated Thyroid Cancer: A Single-Center Cross-Sectional Survey from Mainland China
Changlian Chen, Jiayan Cao, Yueyang Wang, Xuya Han, Yaju Zhang, Shumei Zhuang
Thyroid.2023; 33(4): 474. CrossRef - The "not so good" thyroid cancer: a scoping review on risk factors associated with anxiety, depression and quality of life
Kyle Alexander, Sum-Yu Christina Lee, Stelios Georgiades, Constantina Constantinou
Journal of Medicine and Life.2023; 16(3): 348. CrossRef - Comparison of health‐related quality of life and cosmetic outcome between traditional gasless trans‐axillary endoscopic thyroidectomy and modified gasless trans‐axillary endoscopic thyroidectomy for patients with papillary thyroid microcarcinoma
Deenraj Kush Dhoomun, HuiLan Cai, Ning Li, YanHuan Qiu, XingRui Li, XiaoPeng Hu, WenZhuang Shen
Cancer Medicine.2023; 12(15): 16604. CrossRef - Risk of Adverse Pregnancy Outcomes in Young Women with Thyroid Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Shinje Moon, Ka Hee Yi, Young Joo Park
Cancers.2022; 14(10): 2382. CrossRef - Health-related quality of life following FDG-PET/CT for cytological indeterminate thyroid nodules
Elizabeth J de Koster, Olga Husson, Eveline W C M van Dam, G Sophie Mijnhout, Romana T Netea-Maier, Wim J G Oyen, Marieke Snel, Lioe-Fee de Geus-Oei, Dennis Vriens, _ _
Endocrine Connections.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Is a four-week hormone suspension necessary for thyroid remnant ablation in low and intermediate risk patients? A pilot study with quality-of-life assessment
Poliane A.L. Santos, Maria E.D.M. Flamini, Felipe A. Mourato, Fernando R.A. Lima, Joelan A.L. Santos, Fabiana F. Lima, Estelita T.B. Albuquerque, Alexandra C. De Freitas, Simone C.S. Brandão
Brazilian Journal of Radiation Sciences.2022; 10(4): 1. CrossRef - Health-related quality of life after transoral robotic thyroidectomy in papillary thyroid carcinoma
Chang Myeon Song, Hyang Sook Bang, Hyung Gu Kim, Hae Jin Park, Kyung Tae
Surgery.2021; 170(1): 99. CrossRef - Protocol for a Korean Multicenter Prospective Cohort Study of Active Surveillance or Surgery (KoMPASS) in Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma
Min Ji Jeon, Yea Eun Kang, Jae Hoon Moon, Dong Jun Lim, Chang Yoon Lee, Yong Sang Lee, Sun Wook Kim, Min-Hee Kim, Bo Hyun Kim, Ho-Cheol Kang, Minho Shong, Sun Wook Cho, Won Bae Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(2): 359. CrossRef
- Thyroid
- Unmet Clinical Needs in the Treatment of Patients with Thyroid Cancer
-
Won Bae Kim, Min Ji Jeon, Won Gu Kim, Tae Yong Kim, Young Kee Shong
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(1):14-25. Published online March 19, 2020
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.35.1.14
-
-
7,113
View
-
135
Download
-
14
Web of Science
-
10
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader  ePub ePub
The increased incidence of thyroid cancer is a worldwide phenomenon; however, the issue of overdiagnosis has been most prominent in South Korea. The age-standardized mortality rate of thyroid cancer in Korea steeply increased from 1985 to 2004 (from 0.17 per 100,000 to 0.85 per 100,000), and then decreased until 2015 to 0.42 per 100,000, suggesting that early detection reduced mortality. However, early detection of thyroid cancer may be cost-ineffective, considering its very high prevalence and indolent course. Therefore, risk stratification and tailored management are vitally important, but many prognostic markers can only be evaluated postoperatively. Discovery of preoperative marker(s), especially for small cancers, is the most important unmet clinical need for thyroid cancer. Herein, we discuss some such factors that we recently discovered. Another unmet clinical need is better treatment of radioiodine-refractory (RAIR) differentiated thyroid cancer (DTC) and undifferentiated cancers. Although sorafenib and lenvatinib are available, better drugs are needed. We found that phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase, a critical enzyme for serine biosynthesis, could be a novel therapeutic target, and that the lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratio is a prognostic marker of survival in patients with anaplastic thyroid carcinoma or RAIR DTC. Deeper insights are needed into tumor-host interactions in thyroid cancer to improve treatment. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Lenvatinib Compared with Sorafenib as a First-Line Treatment for Radioactive Iodine-Refractory, Progressive, Differentiated Thyroid Carcinoma: Real-World Outcomes in a Multicenter Retrospective Cohort Study
Mijin Kim, Meihua Jin, Min Ji Jeon, Eui Young Kim, Dong Yeob Shin, Dong Jun Lim, Bo Hyun Kim, Ho-Cheol Kang, Won Bae Kim, Young Kee Shong, Hee Kyung Kim, Won Gu Kim
Thyroid.2023; 33(1): 91. CrossRef - Serum thyroglobulin testing after thyroid lobectomy in patients with 1–4 cm papillary thyroid carcinoma
Ahreum Jang, Meihua Jin, Chae A Kim, Min Ji Jeon, Yu-Mi Lee, Tae-Yon Sung, Tae Yong Kim, Won Bae Kim, Young Kee Shong, Won Gu Kim
Endocrine.2023; 81(2): 290. CrossRef - Integration of ultrasound-based radiomics with clinical features for predicting cervical lymph node metastasis in postoperative patients with differentiated thyroid carcinoma
Fengjing Fan, Fei Li, Yixuan Wang, Zhengjun Dai, Yuyang Lin, Lin Liao, Bei Wang, Hongjun Sun
Endocrine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Transcriptomic Analysis of Papillary Thyroid Cancer: A Focus on Immune-Subtyping, Oncogenic Fusion, and Recurrence
Seung-Jin Park, Yea Eun Kang, Jeong-Hwan Kim, Jong-Lyul Park, Seon-Kyu Kim, Seung-Woo Baek, In Sun Chu, Shinae Yi, Seong Eun Lee, Young Joo Park, Eun-Jae Chung, Jin Man Kim, Hye Mi Ko, Je-Ryong Kim, Seung-Nam Jung, Ho-Ryun Won, Jae Won Chang, Bon Seok Koo
Clinical and Experimental Otorhinolaryngology.2022; 15(2): 183. CrossRef - Prognosis of Patients with 1–4 cm Papillary Thyroid Cancer Who Underwent Lobectomy: Focus on Gross Extrathyroidal Extension Invading Only the Strap Muscles
Ahreum Jang, Meihua Jin, Won Woong Kim, Min Ji Jeon, Tae-Yon Sung, Dong Eun Song, Tae Yong Kim, Ki-Wook Chung, Won Bae Kim, Young Kee Shong, Yu-Mi Lee, Won Gu Kim
Annals of Surgical Oncology.2022; 29(12): 7835. CrossRef - Carboxy terminus of HSP70‐interacting protein (CHIP) attenuates the stemness of thyroid cancer cells through decreasing OCT4 protein stability
Ying Xu, Gang Xu, Huimin Dang, Wei Qu, Dan Chang, Xin He, Minmin Li, Qian Wang
Environmental Toxicology.2021; 36(4): 686. CrossRef - Lactate Dehydrogenase A as a Potential New Biomarker for Thyroid Cancer
Eun Jeong Ban, Daham Kim, Jin Kyong Kim, Sang-Wook Kang, Jandee Lee, Jong Ju Jeong, Kee-Hyun Nam, Woong Youn Chung, Kunhong Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(1): 96. CrossRef - Clinical implications of age and excellent response to therapy in patients with high‐risk differentiated thyroid carcinoma
Meihua Jin, Jonghwa Ahn, Yu‐Mi Lee, Tae‐Yon Sung, Dong Eun Song, Tae Yong Kim, Ki‐Wook Chung, Jin‐Sook Ryu, Won Bae Kim, Young Kee Shong, Min Ji Jeon, Won Gu Kim
Clinical Endocrinology.2021; 95(6): 882. CrossRef - CD73 Overexpression Promotes Progression and Recurrence of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
Young Mun Jeong, Haejin Cho, Tae-Min Kim, Yourha Kim, Sora Jeon, Andrey Bychkov, Chan Kwon Jung
Cancers.2020; 12(10): 3042. CrossRef - The Role of Exosomes in Thyroid Cancer and Their Potential Clinical Application
Kaixiang Feng, Runsheng Ma, Lele Zhang, Hongqiang Li, Yifeng Tang, Gongbo Du, Dongpeng Niu, Detao Yin
Frontiers in Oncology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef
- Clinical Study
- Modification of the Tumor-Node-Metastasis Staging System for Differentiated Thyroid Carcinoma by Considering Extra-Thyroidal Extension and Lateral Cervical Lymph Node Metastasis
-
Mijin Kim, Won Gu Kim, Min Ji Jeon, Hee Kyung Kim, Hyon-Seung Yi, Eun Sook Kim, Bo Hyun Kim, Won Bae Kim, Young Kee Shong, Ho-Cheol Kang, Tae Yong Kim
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(1):149-156. Published online March 19, 2020
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.35.1.149
-
-
5,279
View
-
82
Download
-
6
Web of Science
-
5
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader  ePub ePub
- Background
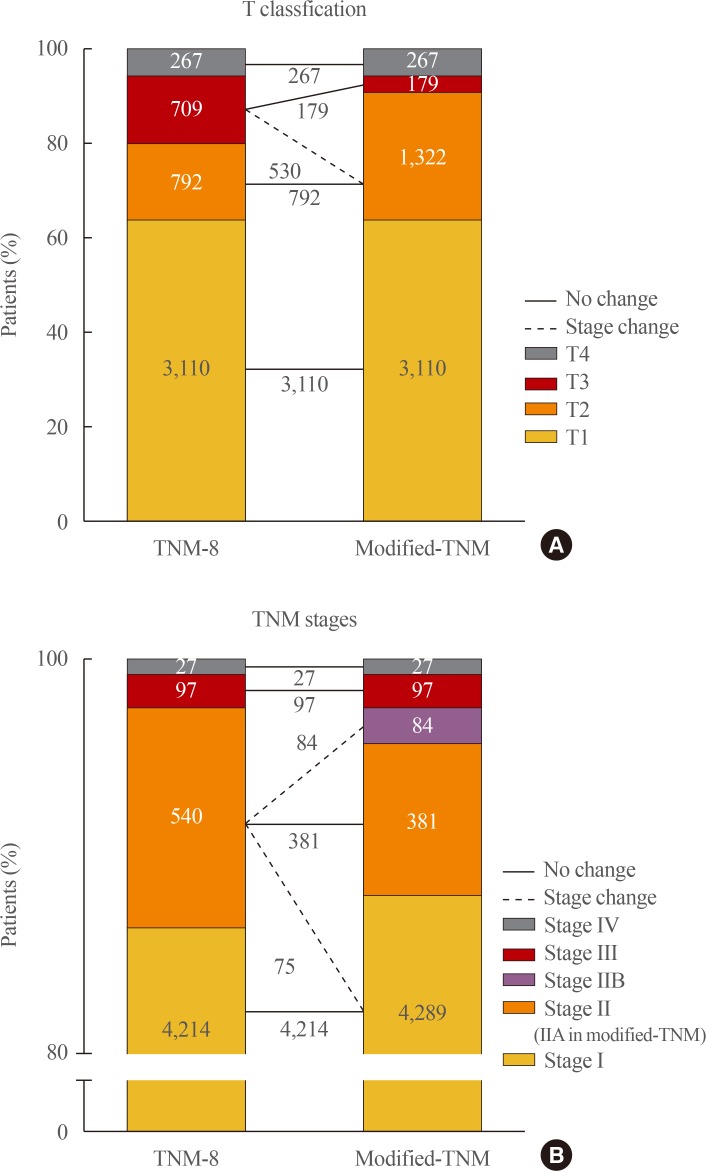
Concerns have arisen about the classification of extra-thyroidal extension (ETE) and lateral cervical lymph node metastasis (N1b) in the 8th edition of the tumor-node-metastasis staging system (TNM-8). This study evaluated the prognostic validity of a modified-TNM staging system, focusing on ETE and N1b, in differentiated thyroid carcinoma (DTC) patients. MethodsThis multicenter retrospective cohort study included 4,878 DTC patients from five tertiary hospitals. In the modified-TNM, T3b in TNM-8 was down-staged to T2, and stage II was subdivided into stages IIA and IIB. Older patients with N1b were reclassified as stage IIB. ResultsThe modified-TNM resulted in staging migration in 540 patients (11%) classified as stage II according to the TNM-8, with 75 (14%), 381 (71%), and 84 patients (16%) classified as stages I, IIA, and IIB, respectively. The 10-year disease-specific survival (DSS) rates in patients classified as stages I, II, III, and IV by TNM-8 were 99.8%, 95.9%, 81.0%, and 41.6%, respectively. The DSS rates of patients classified as stages I, IIA, IIB, III, and IV according to the modified-TNM were 99.8%, 96.4%, 93.3%, 81.0%, and 41.6%, respectively. DSS curves between stages on TNM-8 (P<0.001) and modified-TNM (P<0.001) differed significantly, but the modified-TNM discriminated better than TNM-8. The proportions of variation explained values of TNM-8 and modified-TNM were 6.3% and 6.5%, respectively. ConclusionModification of the TNM staging system focusing on ETE and N1b could improve the prediction of DSS in patients with DTC. Further researches are needed to validate the prognostic accuracy of this modified-TNM staging system.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Clinicopathological features of differentiated thyroid carcinoma as predictors of the effects of radioactive iodine therapy
Wen Liu, Beibei Jiang, Jingli Xue, Ruijing Liu, Yuqing Wei, Peifeng Li
Annals of Diagnostic Pathology.2024; 69: 152243. CrossRef - Thyroid Collision Tumors: The Presence of the Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma Component Negatively Influences the Prognosis
Ion Negura, Victor Ianole, Mihai Danciu, Cristina Preda, Diana Gabriela Iosep, Radu Dănilă, Alexandru Grigorovici, Delia Gabriela Ciobanu Apostol
Diagnostics.2023; 13(2): 285. CrossRef - Serum thyroglobulin testing after thyroid lobectomy in patients with 1–4 cm papillary thyroid carcinoma
Ahreum Jang, Meihua Jin, Chae A Kim, Min Ji Jeon, Yu-Mi Lee, Tae-Yon Sung, Tae Yong Kim, Won Bae Kim, Young Kee Shong, Won Gu Kim
Endocrine.2023; 81(2): 290. CrossRef - Prognostic Impact of Microscopic Extra-Thyroidal Extension (mETE) on Disease Free Survival in Patients with Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma (PTC)
Nadia Bouzehouane, Pascal Roy, Myriam Decaussin-Petrucci, Mireille Bertholon-Grégoire, Chantal Bully, Agnès Perrin, Helene Lasolle, Jean-Christophe Lifante, Françoise Borson-Chazot, Claire Bournaud
Cancers.2022; 14(11): 2591. CrossRef - Impacts of the American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) 8th edition tumor, node, metastasis (TNM) staging system on outcomes of differentiated thyroid cancer in Thai patients
Yotsapon Thewjitcharoen, Waralee Chatchomchuan, Krittadhee Karndumri, Sriurai Porramatikul, Sirinate Krittiyawong, Ekgaluck Wanothayaroj, Siriwan Butadej, Soontaree Nakasatien, Veekij Veerasomboonsin, Auchai Kanchanapituk, Rajata Rajatanavin, Thep Himatho
Heliyon.2021; 7(3): e06624. CrossRef
- Endocrine Research
- Expression of NF2 Modulates the Progression of BRAFV600E Mutated Thyroid Cancer Cells
-
Mi-Hyeon You, Min Ji Jeon, Tae Yong Kim, Won Bae Kim, Young Kee Shong, Won Gu Kim
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2019;34(2):203-212. Published online June 24, 2019
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2019.34.2.203
-
-
5,091
View
-
66
Download
-
7
Web of Science
-
5
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF Supplementary Material Supplementary Material PubReader PubReader  ePub ePub
- Background
We previously reported the frequent neurofibromatosis 2 (NF2) gene mutations in anaplastic thyroid cancers in association with the BRAFV600E mutation. We aimed to investigate the role of NF2 in thyroid cancer with BRAF mutation. MethodsTo identify the function of NF2 in thyroid cancers, we investigated the changes in cell proliferation, colon formation, migration and invasion of thyroid cancer cells (8505C, BHT101, and KTC-1) with BRAFV600E mutation after overexpression and knock-down of NF2. We also examined how cell proliferation changed when NF2 was mutagenized. Human NF2 expression in papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) was analyzed using the The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) data. ResultsFirst, NF2 was overexpressed in 8505C and KTC-1 cells. Compared to control, NF2 overexpressed group of both thyroid cancer cells showed significant inhibition in cell proliferation and colony formation. These results were also confirmed by cell migration and invasion assay. After knock-down of NF2 in 8505C cells, there were no significant changes in cell proliferation and colony formation, compared with the control group. However, after mutagenized S288* and Q470* sites of NF2 gene, the cell proliferation increased compared to NF2 overexpression group. In the analysis of TCGA data, the mRNA expression of NF2 was significantly decreased in PTCs with lateral cervical lymph node (LN) metastasis compared with PTCs without LN metastasis. ConclusionOur study suggests that NF2 might play a role as a tumor suppressor in thyroid cancer with BRAF mutation. More studies are needed to elucidate the mechanism how NF2 acts in thyroid cancer with BRAF mutation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Mechanistic Insights of Thyroid Cancer Progression
Luis Javier Leandro-García, Iñigo Landa
Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Gene Editing with CRISPR/Cas Methodology and Thyroid Cancer: Where Are We?
Cesar Seigi Fuziwara, Diego Claro de Mello, Edna Teruko Kimura
Cancers.2022; 14(3): 844. CrossRef - Extracellular Vesicles as Signal Carriers in Malignant Thyroid Tumors?
Małgorzata Grzanka, Anna Stachurska-Skrodzka, Anna Adamiok-Ostrowska, Ewa Gajda, Barbara Czarnocka
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(6): 3262. CrossRef - Mitofusin-2 modulates the epithelial to mesenchymal transition in thyroid cancer progression
Mi-Hyeon You, Min Ji Jeon, Seong ryeong Kim, Woo Kyung Lee, Sheue-yann Cheng, Goo Jang, Tae Yong Kim, Won Bae Kim, Young Kee Shong, Won Gu Kim
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - High Phosphoglycerate Dehydrogenase Expression Induces Stemness and Aggressiveness in Thyroid Cancer
Min Ji Jeon, Mi-Hyeon You, Ji Min Han, Soyoung Sim, Hyun Ju Yoo, Woo Kyung Lee, Tae Yong Kim, Dong Eun Song, Young Kee Shong, Won Gu Kim, Won Bae Kim
Thyroid.2020; 30(11): 1625. CrossRef
- Thyroid
- Clinical Outcomes of Differentiated Thyroid Cancer Patients with Local Recurrence or Distant Metastasis Detected in Old Age
-
Ji Min Han, Ji Cheol Bae, Hye In Kim, Sam Kwon, Min Ji Jeon, Won Gu Kim, Tae Yong Kim, Young Kee Shong, Won Bae Kim
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2018;33(4):459-465. Published online November 30, 2018
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2018.33.4.459
-
-
4,797
View
-
54
Download
-
5
Web of Science
-
4
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader  ePub ePub
- Background
Differentiated thyroid carcinoma (DTC) shows a very good prognosis, but older patients have a higher recurrence rate and those show poor prognosis than younger patients. The aim of this study was to determine the clinical outcomes of thyroid cancer patients who experienced recurrence in old age according to the treatment strategy used. MethodsThis retrospective observational cohort study was conducted at Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. Among DTC patients with no evidence of disease after initial treatment, we enrolled 86 patients who experienced recurrence at an age >65 years from 1994 to 2012. Sixty-nine patients had local recurrence and 17 patients showed distant metastasis. ResultsThe mean age of patients at recurrence was 72 years. Patients were followed up for a median of 4.1 years after recurrence. Sixty-three of the 69 patients with local recurrence received additional treatment, while the other six received conservative care. The cancer-specific mortality rate was 15.5% in the local recurrence group. Airway problems were the main cause of death in patients who did not receive further treatment for local recurrence. Among the 17 patients with distant metastasis, 10 underwent specific treatment for metastasis and seven received only supportive management. Seven of those 17 patients died, and the cancer-specific mortality rate was 35% in the distant metastasis group. ConclusionThe overall cancer-specific mortality rate was 20% in DTC patients in whom recurrence was first detected at an age >65 years. Mortality due to uncontrolled local disease occurred frequently in patients who did not receive definitive management for recurrence.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Identification of Circulating Tumor Cell Phenotype in Differentiated Thyroid Carcinoma
Huiling Wang, Mian Lv, Yonghong Huang, Xiaoming Pan, Changyuan Wei
Journal of Biomaterials and Tissue Engineering.2022; 12(4): 813. CrossRef - Long-Term Outcomes and Prognoses of Elderly Patients (≥65-Years-Old) With Distant Metastases From Well-Differentiated Thyroid Cancer During Radioiodine Therapy and Follow-Up
Zhong-Ling Qiu, Chen-Tian Shen, Zhen-Kui Sun, Hong-Jun Song, Chuang Xi, Guo-Qiang Zhang, Yang Wang, Quan-Yong Luo
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Head-to-Head Comparison of Neck 18F-FDG PET/MR and PET/CT in the Diagnosis of Differentiated Thyroid Carcinoma Patients after Comprehensive Treatment
Yangmeihui Song, Fang Liu, Weiwei Ruan, Fan Hu, Muhsin H. Younis, Zairong Gao, Jie Ming, Tao Huang, Weibo Cai, Xiaoli Lan
Cancers.2021; 13(14): 3436. CrossRef - Highly sensitive electrochemical immunosensor using a protein-polyvinylidene fluoride nanocomposite for human thyroglobulin
Maria Oneide Silva de Moraes, João de Deus Pereira de Moraes Segundo, Marcos Marques da Silva Paula, Maria Goreti Ferreira Sales, Walter Ricardo Brito
Bioelectrochemistry.2021; 142: 107888. CrossRef
- Thyroid
- Comparison of Immunohistochemistry and Direct Sanger Sequencing for Detection of the BRAFV600E Mutation in Thyroid Neoplasm
-
Hye-Seon Oh, Hyemi Kwon, Suyeon Park, Mijin Kim, Min Ji Jeon, Tae Yong Kim, Young Kee Shong, Won Bae Kim, Jene Choi, Won Gu Kim, Dong Eun Song
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2018;33(1):62-69. Published online January 30, 2018
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2018.33.1.62
-
-
5,847
View
-
69
Download
-
17
Web of Science
-
19
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF Supplementary Material Supplementary Material PubReader PubReader  ePub ePub
- Background
The BRAFV600E mutation is the most common genetic alteration identified in papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC). Because of its costs effectiveness and sensitivity, direct Sanger sequencing has several limitations. The aim of this study was to evaluate the efficiency of immunohistochemistry (IHC) as an alternative method to detect the BRAFV600E mutation in preoperative and postoperative tissue samples. MethodsWe evaluated 71 patients who underwent thyroid surgery with the result of direct sequencing of the BRAFV600E mutation. IHC staining of the BRAFV600E mutation was performed in 49 preoperative and 23 postoperative thyroid specimens. ResultsSixty-two patients (87.3%) had PTC, and of these, BRAFV600E was confirmed by direct sequencing in 57 patients (91.9%). In 23 postoperative tissue samples, the BRAFV600E mutation was detected in 16 samples (70%) by direct sequencing and 18 samples (78%) by IHC. In 24 fine needle aspiration (FNA) samples, BRAFV600E was detected in 18 samples (75%) by direct sequencing and 16 samples (67%) by IHC. In 25 core needle biopsy (CNB) samples, the BRAFV600E mutation was detected in 15 samples (60%) by direct sequencing and 16 samples (64%) by IHC. The sensitivity and specificity of IHC for detecting the BRAFV600E mutation were 77.8% and 66.7% in FNA samples and 99.3% and 80.0% in CNB samples. ConclusionIHC could be an alternative method to direct Sanger sequencing for BRAFV600E mutation detection both in postoperative and preoperative samples. However, application of IHC to detect the BRAFV600E mutation in FNA samples is of limited value compared with direct sequencing.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Circulating Nucleic Acids in Colorectal Cancer: Diagnostic and Prognostic Value
Somayeh Igder, Mozhdeh Zamani, Shima Fakher, Morvarid Siri, Hassan Ashktorab, Negar Azarpira, Pooneh Mokarram, Sowjanya Thatikonda
Disease Markers.2024; 2024: 1. CrossRef - The Accurate Interpretation and Clinical Significance of Morphological Features of Fine Needle Aspiration Cells in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
Xue-Jiao Xiong, Ming-Ming Xiao, Yi-Xia Zhang, Dong-Ge Liu, Mu-Lan Jin, Jian Wang, Hong-Tao Xu, Qing-Chang Li, Guang-Ping Wu, Giovanni Tuccari
Analytical Cellular Pathology.2023; 2023: 1. CrossRef - An effective approach for BRAF V600E mutation analysis of routine thyroid fine needle aspirates
Tanupriya Agrawal, Liqiang Xi, Winnifred Navarro, Mark Raffeld, Snehal B. Patel, Mark J. Roth, Joanna Klubo‐Gwiezdzinska, Armando C. Filie
Cytopathology.2022; 33(3): 344. CrossRef - A dual identification strategy based on padlock ligation and CRISPR/Cas14a for highly specific detection of BRAF V600E mutation in clinical samples
Weicheng Shi, Yao Gong, Decai Zhang, Tiantian Yang, Ming Yi, Jingyi Tan, Shijia Ding, Wei Cheng
Analytical Methods.2022; 14(19): 1913. CrossRef - Research Progress of BRAF V600E Gene Mutation in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
延泽 刘
Advances in Clinical Medicine.2022; 12(09): 8499. CrossRef - VE1 immunohistochemistry is an adjunct tool for detection of BRAFV600E mutation: Validation in thyroid cancer patients
Faiza A. Rashid, Sobia Tabassum, Mosin S. Khan, Hifzur R. Ansari, Muhammad Asif, Ahmareen K. Sheikh, Syed Sameer Aga
Journal of Clinical Laboratory Analysis.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - BRAF testing in a South African cohort of MLH1 deficient endometrial carcinomas: lessons learnt
Reubina Wadee, Wayne Grayson
Southern African Journal of Gynaecological Oncology.2021; 13(1): 1. CrossRef - Association between mutation profiles and clinicopathological features in Chinese patients with thyroid cancer
Changwen Jing, Haixia Cao, Rong Ma, Jianzhong Wu, Zhuo Wang
Precision Medical Sciences.2021; 10(3): 113. CrossRef - Development of a Molecular Assay for Detection and Quantification of theBRAFVariation in Residual Tissue From Thyroid Nodule Fine-Needle Aspiration Biopsy Specimens
Guodong Fu, Ronald S. Chazen, Christina MacMillan, Ian J. Witterick
JAMA Network Open.2021; 4(10): e2127243. CrossRef - Variations in MAP kinase gladiators and risk of differentiated thyroid carcinoma
Faiza Rashid, Ghulam Bhat, Mosin Khan, Sobia Tabassum, Mohammad Bhat
Molecular and Clinical Oncology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Порівняльне імуногістохімічне дослідження BRAFV600E-позитивних і BRAFV600E-негативних радіогенних і спорадичних папілярних тиреоїдних карцином
L. Yu. Zurnadzhy, T.I. Rogounovitch, V.O. Saenko, M.Yu. Bolgov, S.V. Masiuk, S.V. Burko, T.L. Degtyaryova, S.V. Chernyshov, S.V. Gulevatyi, N. Mitsutake, M.D. Tronko, T.I. Bogdanova
Endokrynologia.2021; 26(2): 105. CrossRef - Evaluation of the expression levels of BRAFV600E mRNA in primary tumors of thyroid cancer using an ultrasensitive mutation assay
Tien Viet Tran, Kien Xuan Dang, Quynh Huong Pham, Ung Dinh Nguyen, Nhung Thi Trang Trinh, Luong Van Hoang, Son Anh Ho, Ba Van Nguyen, Duc Trong Nguyen, Dung Tuan Trinh, Dung Ngoc Tran, Arto Orpana, Ulf-Håkan Stenman, Jakob Stenman, Tho Huu Ho
BMC Cancer.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - VE1 Immunohistochemistry Improves the Limit of Genotyping for Detecting BRAFV600E Mutation in Papillary Thyroid Cancer
Sonam Choden, Somboon Keelawat, Chan Kwon Jung, Andrey Bychkov
Cancers.2020; 12(3): 596. CrossRef - Comparison of Molecular Methods and BRAF Immunohistochemistry (VE1 Clone) for the Detection of BRAF V600E Mutation in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma: A Meta-Analysis
Kyle G. Parker, Michael G. White, Nicole A. Cipriani
Head and Neck Pathology.2020; 14(4): 1067. CrossRef - Next generation sequencing based detection of 15 target genes mutations in papillary thyroid carcinoma
Zhuo Wang, Changwen Jing, Haixia Cao, SiWen Liu, Jianzhong Wu, Rong Ma
Precision Medical Sciences.2020; 9(2): 90. CrossRef - A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Diagnostic Performance of BRAF V600E Immunohistochemistry in Thyroid Histopathology
Ranjit Singarayer, Ozgur Mete, Laure Perrier, Lehana Thabane, Sylvia L. Asa, Stan Van Uum, Shereen Ezzat, David P. Goldstein, Anna M. Sawka
Endocrine Pathology.2019; 30(3): 201. CrossRef - Comparison of droplet digital PCR and direct Sanger sequencing for the detection of the BRAFV600E mutation in papillary thyroid carcinoma
Zhuo Wang, Kejing Sun, Changwen Jing, Haixia Cao, Rong Ma, Jianzhong Wu
Journal of Clinical Laboratory Analysis.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Immunohistochemistry Innovations for Diagnosis and Tissue-Based Biomarker Detection
Narittee Sukswai, Joseph D. Khoury
Current Hematologic Malignancy Reports.2019; 14(5): 368. CrossRef - Immunohistochemistry is a feasible method to screen BRAF V600E mutation in colorectal and papillary thyroid carcinoma
Xiangyan Zhang, Lili Wang, Jigang Wang, Han Zhao, Jie Wu, Shuhong Liu, Lu Zhang, Yujun Li, Xiaoming Xing
Experimental and Molecular Pathology.2018; 105(1): 153. CrossRef
- Active Surveillance of Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma: A Mini-Review from Korea
-
Tae Yong Kim, Young Kee Shong
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2017;32(4):399-406. Published online December 14, 2017
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2017.32.4.399
-
-
4,802
View
-
65
Download
-
32
Web of Science
-
33
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader
In Korea, the incidence of thyroid cancer increased explosively in the early 2000s, and reached a plateau in the early 2010s. Most cases of newly diagnosed thyroid cancer are small indolent microcarcinoma and could be good candidates for active surveillance (AS) instead of immediate surgery. Many considerations must be taken into account for establishing selection criteria for candidates for AS of papillary thyroid microcarcinoma (PTMC), including the characteristics of the tumor, the patient, and the medical team. If possible, AS of PTMC should be a part of a prospective clinical trial to ensure long-term safety and to identify clinical and/or molecular markers of the progression of PTMC. In this review, we discuss lessons regarding surgical interventions for PTMC, and then describe the concept, application, caveats, unanswered questions, and future perspectives of AS of PTMC. For appropriately selected patients with PTMC, AS can be a good alternative to immediate surgery. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Incidental thyroid carcinoma in an endemic goiter area in Italy: histopathological features and predictors of a common finding
Eusebio Chiefari, Nadia Innaro, Rita Gervasi, Maria Mirabelli, Stefania Giuliano, Alessandra Donnici, Stefania Obiso, Francesco S. Brunetti, Daniela Patrizia Foti, Antonio Brunetti
Endocrine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Study on diagnosis of thyroid nodules based on convolutional neural network
AiTao Yin, YongPing Lu, Fei Xu, YiFan Zhao, Yue Sun, Miao Huang, XiangBi Li
Die Radiologie.2023; 63(S2): 64. CrossRef - Mortality rate and causes of death in papillary thyroid microcarcinoma
Jung Heo, Hyun Jin Ryu, Hyunju Park, Tae Hyuk Kim, Sun Wook Kim, Young Lyun Oh, Jae Hoon Chung
Endocrine.2023; 83(3): 671. CrossRef - Thyroid Papillary Microcarcinoma - Carcinoma with Clinically Benign Behaviour
Hitesh R Singhavi, Manish Mair, Burhanuddin Qayyumi, Arjun Singh, Pankaj Chaturvedi
Journal of Head & Neck Physicians and Surgeons.2023; 11(2): 95. CrossRef - Clinicopathological Findings Associated With Cervical Lymph Node Metastasis in Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma: A Retrospective Study in China
Yimeng Shi, Zheyu Yang, Yu Heng, Huijun Ju, Yu Pan, Yifan Zhang
Cancer Control.2022; 29: 107327482210849. CrossRef - Nomograms Based on Serum N-glycome for Diagnosis of Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma and Prediction of Lymph Node Metastasis
Zejian Zhang, Zhen Cao, Rui Liu, Zepeng Li, Jianqiang Wu, Xiaoli Liu, Mengwei Wu, Xiequn Xu, Ziwen Liu
Current Oncology.2022; 29(9): 6018. CrossRef - Meta-Analysis of the Application Effect of Different Modalities of Thermal Ablation and Surgical Treatment in Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma
Tao Li, Bin Lu, Yuanpeng Zhang, Yong Sun, Tian jiao Wang
Disease Markers.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Impact of Molecular Testing on the Management of Indeterminate Thyroid Nodules Among Western and Asian Countries: a Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Hanh Thi Tuyet Ngo, Truong Phan Xuan Nguyen, Trang Huyen Vu, Chan Kwon Jung, Lewis Hassell, Kennichi Kakudo, Huy Gia Vuong
Endocrine Pathology.2021; 32(2): 269. CrossRef - Unnecessary thyroid nodule biopsy rates under four ultrasound risk stratification systems: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Pyeong Hwa Kim, Chong Hyun Suh, Jung Hwan Baek, Sae Rom Chung, Young Jun Choi, Jeong Hyun Lee
European Radiology.2021; 31(5): 2877. CrossRef - Current surgical treatment of intermediate risk differentiated thyroid cancer: a systematic review
Michael Y. Guo, Jacob J. Wiseman, Sam M. Wiseman
Expert Review of Anticancer Therapy.2021; 21(2): 205. CrossRef - Tumor Volume Doubling Time in Active Surveillance of Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma: A Multicenter Cohort Study in Korea
Meihua Jin, Hye In Kim, Jeonghoon Ha, Min Ji Jeon, Won Gu Kim, Dong-Jun Lim, Tae Yong Kim, Jae Hoon Chung, Young Kee Shong, Tae Hyuk Kim, Won Bae Kim
Thyroid.2021; 31(10): 1494. CrossRef - Long-Term Efficacy of Ultrasound-Guided Laser Ablation for Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma: Results of a 10-Year Retrospective Study
Ho Jin Kim, Seung Min Chung, Hanbyul Kim, Ju Young Jang, Jae Hong Yang, Jun Sung Moon, Gitak Son, Jong-Ryool Oh, Jong Yup Bae, Hyundae Yoon
Thyroid.2021; 31(11): 1723. CrossRef - Cost-Effectiveness Analysis of Active Surveillance Compared to Early Surgery in Small Papillary Thyroid Cancer: A Systemic Review
Han-sang Baek, Chai-ho Jeong, Jeonghoon Ha, Ja-Seong Bae, Jeong-soo Kim, Dong-Jun Lim, Chul-Min Kim
Cancer Management and Research.2021; Volume 13: 6721. CrossRef - More Aggressive Cancer Behaviour in Thyroid Cancer Patients in the Post-COVID-19 Pandemic Era: A Retrospective Study
Hanqing Liu, Ling Zhan, Liantao Guo, Xizi Yu, Lingrui Li, Hongfang Feng, Dan Yang, Zhiliang Xu, Yi Tu, Chuang Chen, Shengrong Sun
International Journal of General Medicine.2021; Volume 14: 7197. CrossRef - Completion Thyroidectomy
Yongil Cheon, Sung-Chan Shin, Byung-Joo Lee
International Journal of Thyroidology.2021; 14(2): 87. CrossRef - Deep Learning based Classification of Thyroid Cancer using Different Medical Imaging Modalities : A Systematic Review
Maheen Ilyas, Hassaan Malik, Muhammad Adnan, Umair Bashir, Wajahat Anwaar Bukhari, Muhammad Imran Ali Khan, Adnan Ahmad
VFAST Transactions on Software Engineering.2021; 9(4): 1. CrossRef - Does the ATA Risk Stratification Apply to Patients with Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma?
Dessislava I. Stefanova, Arpita Bose, Timothy M. Ullmann, Jessica N. Limberg, Brendan M. Finnerty, Rasa Zarnegar, Thomas J. Fahey, Toni Beninato
World Journal of Surgery.2020; 44(2): 452. CrossRef - Clinical Outcomes after Early and Delayed Radioiodine Remnant Ablation in Patients with Low-Risk Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma: Propensity Score Matching Analysis
Jonghwa Ahn, Meihua Jin, Eyun Song, Min Ji Jeon, Tae Yong Kim, Jin-Sook Ryu, Won Bae Kim, Young Kee Shong, Ji Min Han, Won Gu Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2020; 35(4): 830. CrossRef - Impact of the new guidelines of the American Thyroid Association on the treatment of the differentiated thyroid tumor in an Italian center with medium-high volume thyroid surgery
Aldo Bove, Paolo Panaccio, Gino Palone, Ludovica Esposito, Lucia Marino, Giuseppe Bongarzoni
BMC Surgery.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Malignancy risk of initially benign thyroid nodules: validation with various Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data System guidelines
Su Min Ha, Jung Hwan Baek, Young Jun Choi, Sae Rom Chung, Tae Yon Sung, Tae Yong Kim, Jeong Hyun Lee
European Radiology.2019; 29(1): 133. CrossRef - Proteomic analysis of the papillary thyroid microcarcinoma
Shan Jin, Wuyuntu Bao, Yun-Tian Yang, Quan Fu, Yinbao Bai, Yousheng Liu
Annales d'Endocrinologie.2019; 80(5-6): 293. CrossRef - Quality of Life in Patients with Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma Managed by Active Surveillance or Lobectomy: A Cross-Sectional Study
Min Ji Jeon, Yu-Mi Lee, Tae-Yon Sung, Minkyu Han, Yong-Wook Shin, Won Gu Kim, Tae Yong Kim, Ki-Wook Chung, Young Kee Shong, Won Bae Kim
Thyroid.2019; 29(7): 956. CrossRef - Papillary Thyroid Micro Carcinoma: The Incidence of High-Risk Features and Its Prognostic Implications
Rui Gao, Xi Jia, Yiqian Liang, Kun Fan, Xiaoxiao Wang, Yuanbo Wang, Lulu Yang, Aimin Yang, Guangjian Zhang
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Tumor Volume Doubling Time in Active Surveillance of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
Hye-Seon Oh, Hyemi Kwon, Eyun Song, Min Ji Jeon, Tae Yong Kim, Jeong Hyun Lee, Won Bae Kim, Young Kee Shong, Ki-Wook Chung, Jung Hwan Baek, Won Gu Kim
Thyroid.2019; 29(5): 642. CrossRef - Deciphering novel biomarkers of lymph node metastasis of thyroid papillary microcarcinoma using proteomic analysis of ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration biopsy samples
Peng Lin, Zhina Yao, Yu Sun, Wenjuan Li, Yan Liu, Kai Liang, Yuan Liu, Jun Qin, Xinguo Hou, Li Chen
Journal of Proteomics.2019; 204: 103414. CrossRef - Diagnostic performance of CT in detection of metastatic cervical lymph nodes in patients with thyroid cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Se Jin Cho, Chong Hyun Suh, Jung Hwan Baek, Sae Rom Chung, Young Jun Choi, Jeong Hyun Lee
European Radiology.2019; 29(9): 4635. CrossRef - Diagnostic Performance of Practice Guidelines for Thyroid Nodules: Thyroid Nodule Size versus Biopsy Rates
Su Min Ha, Jung Hwan Baek, Dong Gyu Na, Chong Hyun Suh, Sae Rom Chung, Young Jun Choi, Jeong Hyun Lee
Radiology.2019; 291(1): 92. CrossRef - Update on thyroid ultrasound
Xiao-Wen Liang, Yong-Yi Cai, Jin-Sui Yu, Jian-Yi Liao, Zhi-Yi Chen
Chinese Medical Journal.2019; 132(16): 1974. CrossRef - Primary versus Tertiary Care Follow-Up of Low-Risk Differentiated Thyroid Cancer: Real-World Comparison of Outcomes and Costs for Patients and Health Care Systems
Syed Ali Imran, Karen Chu, Murali Rajaraman, Drew Rajaraman, Sunita Ghosh, Sarah De Brabandere, Stephanie M. Kaiser, Stan Van Uum
European Thyroid Journal.2019; 8(4): 208. CrossRef - Active Surveillance of Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma: A Mini-Review from Korea (Endocrinol Metab2017;32:399-406, Tae Yong Kim et al.)
Hui Sun, Gianlorenzo Dionigi
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2018; 33(1): 135. CrossRef - Active Surveillance of Low-Risk Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma: A Multi-Center Cohort Study in Korea
Hye-Seon Oh, Jeonghoon Ha, Hye In Kim, Tae Hyuk Kim, Won Gu Kim, Dong-Jun Lim, Tae Yong Kim, Sun Wook Kim, Won Bae Kim, Young Kee Shong, Jae Hoon Chung, Jung Hwan Baek
Thyroid.2018; 28(12): 1587. CrossRef - Ultrasound-guided percutaneous microwave ablation versus surgery for papillary thyroid microcarcinoma
Jianming Li, Yujiang Liu, Jibin Liu, Linxue Qian
International Journal of Hyperthermia.2018; 34(5): 653. CrossRef - Diagnosis and treatment of low-risk papillary thyroid microcarcinoma
Jae Hoon Moon, Young Joo Park
Journal of the Korean Medical Association.2018; 61(4): 232. CrossRef
- Clinical Study
- Disease-Specific Mortality of Differentiated Thyroid Cancer Patients in Korea: A Multicenter Cohort Study
-
Min Ji Jeon, Won Gu Kim, Tae Hyuk Kim, Hee Kyung Kim, Bo Hyun Kim, Hyon-Seung Yi, Eun Sook Kim, Hosu Kim, Young Nam Kim, Eun Heui Kim, Tae Yong Kim, Sun Wook Kim, Ho-Cheol Kang, Jae Hoon Chung, Young Kee Shong, Won Bae Kim
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2017;32(4):434-441. Published online November 22, 2017
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2017.32.4.434
-
-
5,831
View
-
53
Download
-
29
Web of Science
-
26
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF Supplementary Material Supplementary Material PubReader PubReader
- Background
Little is known regarding disease-specific mortality of differentiated thyroid cancer (DTC) patients and its risk factors in Korea. MethodsWe retrospectively reviewed a large multi-center cohort of thyroid cancer from six Korean hospitals and included 8,058 DTC patients who underwent initial surgery between 1996 and 2005. ResultsMean age of patients at diagnosis was 46.2±12.3 years; 87% were females. Most patients had papillary thyroid cancer (PTC; 97%) and underwent total thyroidectomy (85%). Mean size of the primary tumor was 1.6±1.0 cm. Approximately 40% of patients had cervical lymph node (LN) metastases and 1.3% had synchronous distant metastases. During 11.3 years of follow-up, 150 disease-specific mortalities (1.9%) occurred; the 10-year disease-specific survival (DSS) rate was 98%. According to the year of diagnosis, the number of disease-specific mortality was not different. However, the rate of disease-specific mortality decreased during the study period (from 7.7% to 0.7%). Older age (≥45 years) at diagnosis, male, follicular thyroid cancer (FTC) versus PTC, larger tumor size (>2 cm), presence of extrathyroidal extension (ETE), lateral cervical LN metastasis, distant metastasis and tumor node metastasis (TNM) stage were independent risk factors of disease-specific mortality of DTC patients. ConclusionThe rate of disease-specific mortality of Korean DTC patients was 1.9%; the 10-year DSS rate was 98% during 1996 to 2005. Older age at diagnosis, male, FTC, larger tumor size, presence of ETE, lateral cervical LN metastasis, distant metastasis, and TNM stages were significant risk factors of disease-specific mortality of Korean DTC patients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Log odds of negative lymph nodes/T stage ratio (LONT): A new prognostic tool for differentiated thyroid cancer without metastases in patients aged 55 and older
Xuezhen Wang, Yufan Wu, Xiaoxia Li, Jinsheng Hong, Mingwei Zhang
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The association between vitamin D supplementation and the long-term prognosis of differentiated thyroid cancer patients: a retrospective observational cohort study with propensity score matching
Jong-hyuk Ahn, Hoonsung Choi, Su-jin Kim, Sun Wook Cho, Kyu Eun Lee, Do Joon Park, Young Joo Park
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Linear association between radioactive iodine dose and second primary malignancy risk in thyroid cancer
Kyeong Jin Kim, Kyoung Jin Kim, Jimi Choi, Nam Hoon Kim, Sin Gon Kim
JNCI: Journal of the National Cancer Institute.2023; 115(6): 695. CrossRef - Outcomes of Advanced Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma in the Era of Targeted Therapy
Nicholas L. Kesby, Alexander J. Papachristos, Matti Gild, Ahmad Aniss, Mark S. Sywak, Roderick Clifton-Bligh, Stan B. Sidhu, Anthony R. Glover
Annals of Surgical Oncology.2022; 29(1): 64. CrossRef - Clinical Implication of Mutifocality for Risk of Recurrence in Patients With Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
Kwangsoon Kim, Ja Seong Bae, Jeong Soo Kim
Journal of Endocrine Surgery.2022; 22(1): 10. CrossRef - Clinical Factors Predictive of Lymph Node Metastasis in Thyroid Cancer Patients: A Multivariate Analysis
Hui Zheng, Victoria Lai, Jana Lu, Jin K Kang, Jiling Chou, Kenneth D Burman, Leonard Wartofsky, Jennifer E Rosen
Journal of the American College of Surgeons.2022; 234(4): 691. CrossRef - Minimal extrathyroidal extension is associated with lymph node metastasis in single papillary thyroid microcarcinoma: a retrospective analysis of 814 patients
Ra-Yeong Song, Hee Sung Kim, Kyung Ho Kang
World Journal of Surgical Oncology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Central Lymph Node Ratio Predicts Recurrence in Patients with N1b Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
Il Ku Kang, Kwangsoon Kim, Joonseon Park, Ja Seong Bae, Jeong Soo Kim
Cancers.2022; 14(15): 3677. CrossRef - Characterization of the CpG island methylator phenotype subclass in papillary thyroid carcinoma
Pengfei Gu, Yu Zeng, Weike Ma, Wei Zhang, Yu Liu, Fengli Guo, Xianhui Ruan, Jiadong Chi, Xiangqian Zheng, Ming Gao
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - MicroRNA Profile for Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarkers in Thyroid Cancer
Jong-Lyul Park, Seon-Kyu Kim, Sora Jeon, Chan-Kwon Jung, Yong-Sung Kim
Cancers.2021; 13(4): 632. CrossRef - Lactate Dehydrogenase A as a Potential New Biomarker for Thyroid Cancer
Eun Jeong Ban, Daham Kim, Jin Kyong Kim, Sang-Wook Kang, Jandee Lee, Jong Ju Jeong, Kee-Hyun Nam, Woong Youn Chung, Kunhong Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(1): 96. CrossRef - Male sex is not an independent risk factor for recurrence of differentiated thyroid cancer: a propensity score-matching study
Joonseon Park, Kwangsoon Kim, Dong-Jun Lim, Ja Seong Bae, Jeong Soo Kim
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - A Newly Developed Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma in a Patient with Advanced Thyroid Cancer under Long-Term Sorafenib Use
Min Ji Kim, Han-Sang Baek, Sung Hak Lee, Dong-Jun Lim
International Journal of Thyroidology.2021; 14(2): 175. CrossRef - Modified risk stratification based on cervical lymph node metastases following lobectomy for papillary thyroid carcinoma
Eyun Song, Jonghwa Ahn, Dong Eun Song, Won Woong Kim, Min Ji Jeon, Tae‐Yon Sung, Tae Yong Kim, Ki Wook Chung, Won Bae Kim, Young Kee Shong, Suck Joon Hong, Yu‐Mi Lee, Won Gu Kim
Clinical Endocrinology.2020; 92(4): 358. CrossRef - Long-term scintigraphic and clinical follow up in patients with differentiated thyroid cancer and iodine avid bone metastases
Omnia Mohamed Talaat, Ismail Mohamed Ali, Sherif Maher Abolyazid, Bader Abdelmaksoud, Ibrahim Mansour Nasr
Nuclear Medicine Communications.2020; 41(4): 327. CrossRef - Highly prevalent BRAF V600E and low-frequency TERT promoter mutations underlie papillary thyroid carcinoma in Koreans
Sue Youn Kim, Taeeun Kim, Kwangsoon Kim, Ja Seong Bae, Jeong Soo Kim, Chan Kwon Jung
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2020; 54(4): 310. CrossRef - Clinical Implication of World Health Organization Classification in Patients with Follicular Thyroid Carcinoma in South Korea: A Multicenter Cohort Study
Meihua Jin, Eun Sook Kim, Bo Hyun Kim, Hee Kyung Kim, Hyon-Seung Yi, Min Ji Jeon, Tae Yong Kim, Ho-Cheol Kang, Won Bae Kim, Young Kee Shong, Mijin Kim, Won Gu Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2020; 35(3): 618. CrossRef - The age threshold of the 8th edition AJCC classification is useful for indicating patients with aggressive papillary thyroid cancer in clinical practice
Krzysztof Kaliszewski, Dorota Diakowska, Łukasz Nowak, Beata Wojtczak, Jerzy Rudnicki
BMC Cancer.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Lobectomy Is Feasible for 1–4 cm Papillary Thyroid Carcinomas: A 10-Year Propensity Score Matched-Pair Analysis on Recurrence
Eyun Song, Minkyu Han, Hye-Seon Oh, Won Woong Kim, Min Ji Jeon, Yu-Mi Lee, Tae Yong Kim, Ki Wook Chung, Won Bae Kim, Young Kee Shong, Suck Joon Hong, Tae-Yon Sung, Won Gu Kim
Thyroid.2019; 29(1): 64. CrossRef - The binary presence or absence of lymph node metastasis or extrathyroidal extension is not associated with survival in papillary thyroid cancers: Implications for staging systems
Hyun-Soo Zhang, Eun-Kyung Lee, Yuh-Seog Jung, Byung-Ho Nam, Boyoung Park
Cancer Epidemiology.2019; 63: 101589. CrossRef - Risk of Adverse Obstetric Outcomes and the Abnormal Growth of Offspring in Women with a History of Thyroid Cancer
Geum Joon Cho, So-youn Kim, Hoi Chang Lee, Kyu-Min Lee, Sung Won Han, Min-Jeong Oh, Teresa K. Woodruff
Thyroid.2019; 29(6): 879. CrossRef - Changes in Serum Thyroglobulin Levels After Lobectomy in Patients with Low-Risk Papillary Thyroid Cancer
Suyeon Park, Min Ji Jeon, Hye-Seon Oh, Yu-Mi Lee, Tae-Yon Sung, Minkyu Han, Ji Min Han, Tae Yong Kim, Ki-Wook Chung, Won Bae Kim, Young Kee Shong, Won Gu Kim
Thyroid.2018; 28(8): 997. CrossRef - Clinical Outcomes of Differentiated Thyroid Cancer Patients with Local Recurrence or Distant Metastasis Detected in Old Age
Ji Min Han, Ji Cheol Bae, Hye In Kim, Sam Kwon, Min Ji Jeon, Won Gu Kim, Tae Yong Kim, Young Kee Shong, Won Bae Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2018; 33(4): 459. CrossRef - Prognosis of Differentiated Thyroid Carcinoma with Initial Distant Metastasis: A Multicenter Study in Korea
Hosu Kim, Hye In Kim, Sun Wook Kim, Jaehoon Jung, Min Ji Jeon, Won Gu Kim, Tae Yong Kim, Hee Kyung Kim, Ho-Cheol Kang, Ji Min Han, Yoon Young Cho, Tae Hyuk Kim, Jae Hoon Chung
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2018; 33(2): 287. CrossRef - Decreasing Disease-Specific Mortality of Differentiated Thyroid Cancer in Korea: A Multicenter Cohort Study
Min Ji Jeon, Hee Kyung Kim, Eun Heui Kim, Eun Sook Kim, Hyon-Seung Yi, Tae Yong Kim, Ho-Cheol Kang, Young Kee Shong, Won Bae Kim, Bo Hyun Kim, Won Gu Kim
Thyroid.2018; 28(9): 1121. CrossRef - Active Surveillance of Low-Risk Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma: A Multi-Center Cohort Study in Korea
Hye-Seon Oh, Jeonghoon Ha, Hye In Kim, Tae Hyuk Kim, Won Gu Kim, Dong-Jun Lim, Tae Yong Kim, Sun Wook Kim, Won Bae Kim, Young Kee Shong, Jae Hoon Chung, Jung Hwan Baek
Thyroid.2018; 28(12): 1587. CrossRef
- Clinical Guidelines for the Management of Adrenal Incidentaloma
-
Jung-Min Lee, Mee Kyoung Kim, Seung-Hyun Ko, Jung-Min Koh, Bo-Yeon Kim, Sang Wan Kim, Soo-Kyung Kim, Hae Jin Kim, Ohk-Hyun Ryu, Juri Park, Jung Soo Lim, Seong Yeon Kim, Young Kee Shong, Soon Jib Yoo
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2017;32(2):200-218. Published online June 23, 2017
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2017.32.2.200
-
-
16,288
View
-
694
Download
-
80
Web of Science
-
78
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader
An adrenal incidentaloma is an adrenal mass found in an imaging study performed for other reasons unrelated to adrenal disease and often accompanied by obesity, diabetes, or hypertension. The prevalence and incidence of adrenal incidentaloma increase with age and are also expected to rise due to the rapid development of imaging technology and frequent imaging studies. The Korean Endocrine Society is promoting an appropriate practice guideline to meet the rising incidence of adrenal incidentaloma, in cooperation with the Korean Adrenal Gland and Endocrine Hypertension Study Group. In this paper, we discuss important core issues in managing the patients with adrenal incidentaloma. After evaluating core proposition, we propose the most critical 20 recommendations from the initially organized 47 recommendations by Delphi technique. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - The improvement of postoperative blood pressure and associated factors in patients with hormone‐negative adrenal adenoma and hypertension
Jiaxing Sun, Yingchun Dong, Hanbo Wang, Xudong Guo, Ning Suo, Shangjian Li, Xiangbin Ren, Shaobo Jiang
Journal of Surgical Oncology.2024; 129(6): 1073. CrossRef - Clinical features and treatment options for pediatric adrenal incidentalomas: a retrospective single center study
Xiaojiang Zhu, Saisai Liu, Yimin Yuan, Nannan Gu, Jintong Sha, Yunfei Guo, Yongji Deng
BMC Pediatrics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Characterizing incidental mass lesions in abdominal dual-energy CT compared to conventional contrast-enhanced CT
Jack Junchi Xu, Peter Sommer Ulriksen, Camilla Wium Bjerrum, Michael Patrick Achiam, Timothy Andrew Resch, Lars Lönn, Kristoffer Lindskov Hansen
Acta Radiologica.2023; 64(3): 945. CrossRef - Metastatic Adrenal PEComa: Case Report and Short Review of the Literature
Enrico Battistella, Luca Pomba, Marica Mirabella, Michele Gregianin, Antonio Scapinello, Marco Volante, Antonio Toniato
Medicina.2023; 59(1): 149. CrossRef - Surgical management and outcomes of spinal metastasis of malignant adrenal tumor: A retrospective study of six cases and literature review
Xiangzhi Ni, Jing Wang, Jiashi Cao, Kun Zhang, Shuming Hou, Xing Huang, Yuanjin Song, Xin Gao, Jianru Xiao, Tielong Liu
Frontiers in Oncology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - An adrenal incidentaloma that had appeared to produce dehydroepiandrosterone-sulfate in excess before immunohistochemical study of the tumor
Toshihide Yamamoto, Takuma Kimura, Yuki Kubo, Shin-ichi Nakatsuka, Hiromasa Harada, Takashi Suzuki, Hironobu Sasano
Endocrine Journal.2023; 70(1): 43. CrossRef - Mortality Not Increased in Patients With Nonfunctional Adrenal Adenomas: A Matched Cohort Study
Albin Kjellbom, Ola Lindgren, Malin Danielsson, Henrik Olsen, Magnus Löndahl
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2023; 108(8): e536. CrossRef - Construction of a novel clinical nomogram to predict cancer-specific survival in patients with primary malignant adrenal tumors: a large population-based retrospective study
Mingzhen Li, Xiaoying Duan, Di You, Linlin Liu
Frontiers in Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Primary Aldosteronism Prevalence – An Unfolding
Story
Suranut Charoensri, Adina F. Turcu
Experimental and Clinical Endocrinology & Diabetes.2023; 131(07/08): 394. CrossRef - Management of Adrenal Cortical Adenomas: Assessment of Bone Status in Patients with (Non-Functioning) Adrenal Incidentalomas
Alexandra-Ioana Trandafir, Mihaela Stanciu, Simona Elena Albu, Vasile Razvan Stoian, Irina Ciofu, Cristian Persu, Claudiu Nistor, Mara Carsote
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(13): 4244. CrossRef - Clinical manifestations of functionally autonomous cortisol secretion in patients with adrenal masse
T. R. Chzhen, T. P. Kiseleva
Ural Medical Journal.2023; 22(3): 13. CrossRef - Tumor enlargement in adrenal incidentaloma is related to glaucoma: a new prognostic feature?
M. Caputo, T. Daffara, A. Ferrero, M. Romanisio, E. Monti, C. Mele, M. Zavattaro, S. Tricca, A. Siani, A. Clemente, C. Palumbo, S. De Cillà, A. Carriero, A. Volpe, P. Marzullo, G. Aimaretti, F. Prodam
Journal of Endocrinological Investigation.2023; 47(2): 377. CrossRef - Adrenal ganglioneuroma: Features and outcomes of cases series
Pei Li, Rongchang Zhang, Guang Wang, Jiongming Li
Asian Journal of Surgery.2023; 46(11): 5272. CrossRef - Recent Updates on the Management of Adrenal Incidentalomas
Seung Shin Park, Jung Hee Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(4): 373. CrossRef - Adrenal malakoplakia a rare lesion that mimics a neoplasm
Orión Erenhú Rodríguez González, Jesus Eduardo Osorio, Edgar Iván Bravo Castro
Urology Case Reports.2023; 51: 102568. CrossRef - LC-MS based simultaneous profiling of adrenal hormones of steroids, catecholamines, and metanephrines
Jongsung Noh, Chaelin Lee, Jung Hee Kim, Seung Woon Myung, Man Ho Choi
Journal of Lipid Research.2023; 64(11): 100453. CrossRef - Incidentaloma adrenal. Del hallazgo casual al diagnóstico definitivo
Mercedes Retamal Ortíz, Ana Belén Vicario Parada, Elena Vázquez Jarén
Actualización en Medicina de Familia.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Diagnosis and management of adrenal incidentaloma: use of clinical judgment and evidence in dialog with the patient
Yusaku Yoshida, Kiyomi Horiuchi, Michio Otsuki, Takahiro Okamoto
Surgery Today.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Can MDCT Enhancement Patterns Be Helpful in Differentiating Secretory from Non-Functional Adrenal Adenoma?
Svetlana Kocic, Vladimir Vukomanovic, Aleksandar Djukic, Jovica Saponjski, Dusan Saponjski, Vuk Aleksic, Vesna Ignjatovic, Katarina Vuleta Nedic, Vladan Markovic, Radisa Vojinovic
Medicina.2023; 60(1): 72. CrossRef - Computer-assisted Reporting and Decision Support Increases Compliance with Follow-up Imaging and Hormonal Screening of Adrenal Incidentalomas
Renata R. Almeida, Bernardo C. Bizzo, Ramandeep Singh, Katherine P. Andriole, Tarik K. Alkasab
Academic Radiology.2022; 29(2): 236. CrossRef - Incidental Adrenal Masses: Adherence to Guidelines and Methods to Improve Initial Follow-Up: A Systematic Review
Timothy Feeney, Andrea Madiedo, Philip E. Knapp, Avneesh Gupta, David McAneny, Frederick Thurston Drake
Journal of Surgical Research.2022; 269: 18. CrossRef - Incidental Adrenal Lesions May Not Always Require Further Imaging Work-up
Deborah A. Baumgarten
Radiology.2022; 302(1): 138. CrossRef - Adrenal Nodules Detected at Staging CT in Patients with Resectable Gastric Cancers Have a Low Incidence of Malignancy
Hae Young Kim, Won Chang, Yoon Jin Lee, Ji Hoon Park, Jungheum Cho, Hee Young Na, Hyungwoo Ahn, Sung Il Hwang, Hak Jong Lee, Young Hoon Kim, Kyoung Ho Lee
Radiology.2022; 302(1): 129. CrossRef - Management of incidental adrenal nodules: a survey of abdominal radiologists conducted by the Society of Abdominal Radiology Disease-Focused Panel on Adrenal Neoplasms
Michael T. Corwin, Nicola Schieda, Erick M. Remer, Elaine M. Caoili
Abdominal Radiology.2022; 47(4): 1360. CrossRef - Primary hyperaldosteronism: indications for screening
Novella M. Chikhladze
Terapevticheskii arkhiv.2022; 94(1): 107. CrossRef - Pathophysiological Link between Insulin Resistance and Adrenal Incidentalomas
Jordan A. Higgs, Alyssa P. Quinn, Kevin D. Seely, Zeke Richards, Shad P. Mortensen, Cody S. Crandall, Amanda E. Brooks
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(8): 4340. CrossRef - Can Radiomics Provide Additional Diagnostic Value for Identifying Adrenal Lipid-Poor Adenomas From Non-Adenomas on Unenhanced CT?
Binhao Zhang, Huangqi Zhang, Xin Li, Shengze Jin, Jiawen Yang, Wenting Pan, Xue Dong, Jin Chen, Wenbin Ji
Frontiers in Oncology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Adrenal Surgery in the Era of Multidisciplinary Endocrine Tumor
Boards
Costanza Chiapponi, Daniel Pinto Dos Santos, Milan Janis Michael Hartmann, Matthias Schmidt, Michael Faust, Roger Wahba, Christiane Josephine Bruns, Anne Maria Schultheis, Hakan Alakus
Hormone and Metabolic Research.2022; 54(05): 294. CrossRef - Optimal and novel imaging of the adrenal glands
Patrick J. Navin, Michael R. Moynagh
Current Opinion in Endocrinology, Diabetes & Obesity.2022; 29(3): 253. CrossRef - Adrenal Tumors in Young Adults: Case Reports and Literature Review
Małgorzata Zdrojewska, Emilia Mech-Siebieszuk, Renata Świątkowska-Stodulska, Bartosz Regent, Michał Kunc, Łukasz Zdrojewski, Krzysztof Sworczak
Medicina.2022; 58(6): 746. CrossRef - Incidence of malignancy in adrenal nodules detected on staging CTs of patients with potentially resectable colorectal cancer
Hae Young Kim, Yoon Jin Lee, Won Chang, Ji Hoon Park, Jungheum Cho, Hyeon Jeong Oh, Young Hoon Kim, Kyoung Ho Lee
European Radiology.2022; 32(12): 8560. CrossRef - Appendiceal Incidentalomas: Prevalence, Radiographic Characteristics, Management, and Outcomes
Adam Kelly, Stacy O’Connor, Diana Kane, Chiang-Ching Huang, Harveshp Mogal
Annals of Surgical Oncology.2022; 29(13): 8265. CrossRef - Laparoscopic large adrenal mass resection: why we should be more careful?
Mohsen Varyani, Mahmood Parvin, Hamidreza Akbari Gilani
African Journal of Urology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Serum Visfatin/NAMPT as a Potential Risk Predictor for Malignancy of Adrenal Tumors
Nadia Sawicka-Gutaj, Hanna Komarowska, Dawid Gruszczyński, Aleksandra Derwich, Anna Klimont, Marek Ruchała
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(19): 5563. CrossRef - Application of radiomics in adrenal incidentaloma: a literature review
Cheng Li, Yan Fu, Xiaoping Yi, Xiao Guan, Longfei Liu, Bihong T. Chen
Discover Oncology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Hormone-inactive adrenal tumors in clinician’s practice
T. R. Chzhen, T. P. Kiseleva
Perm Medical Journal.2022; 39(5): 48. CrossRef - The diagnostic value of salivary cortisol and salivary cortisone in patients with suspected hypercortisolism
Vendela Berndt, Per Dahlqvist, Jennie de Verdier, Henrik Ryberg, Oskar Ragnarsson
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Role of Intraoperative Indocyanine Green (ICG) and Preoperative 3-Dimensional (3D) Reconstruction in Laparoscopic Adrenalectomy: A Propensity Score-matched Analysis
Giuseppe Palomba, Vincenza Paola Dinuzzi, Francesca Pegoraro, Roberto Ivan Troisi, Roberto Montalti, Giovanni Domenico De Palma, Giovanni Aprea
Surgical Laparoscopy, Endoscopy & Percutaneous Techniques.2022; 32(6): 643. CrossRef - The Etiological Profile of Adrenal Incidentalomas
Fatima-Zahra Lahmamssi, Loubna Saadaoui, Hayat Aynaou, Houda Salhi, Hanan El Ouahabi
Cureus.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Forty Years Together, New Leap Forward! The 40th Anniversary of the Korean Endocrine Society
Jong Chul Won, Ki-Hyun Baek
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(6): 851. CrossRef - Conduite à tenir face à un fortuitome surrénalien chez le chien ou le chat
Diane Pichard, Ghita Benckekroun
Le Nouveau Praticien Vétérinaire canine & féline.2022; 19(82): 40. CrossRef - Laparoscopic transperitoneal adrenalectomy: a comparative study of different techniques for vessel sealing
Luca Cardinali, Edlira Skrami, Elisa Catani, Flavia Carle, Monica Ortenzi, Andrea Balla, Mario Guerrieri
Surgical Endoscopy.2021; 35(2): 673. CrossRef - Epidemiology and Comorbidity of Adrenal Cushing Syndrome: A Nationwide Cohort Study
Chang Ho Ahn, Jung Hee Kim, Man Young Park, Sang Wan Kim
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2021; 106(3): e1362. CrossRef - Urine steroid profile as a new promising tool for the evaluation of adrenal tumors. Literature review
Marta Araujo-Castro, Pablo Valderrábano, Héctor F. Escobar-Morreale, Felicia A. Hanzu, Gregori Casals
Endocrine.2021; 72(1): 40. CrossRef - A Rare Neoplasm: Primary Adrenal Leiomyosarcoma
Jack T. Barnett, Christine W. Liaw, Reza Mehrazin
Urology.2021; 148: e11. CrossRef - Adrenal Ganglioneuroma Presenting as an Incidentaloma in an Adolescent Patient
Sonia G. Sharma, Steven N. Levine, Xin Gu
AACE Clinical Case Reports.2021; 7(1): 61. CrossRef - Feasibility of Iodine-131 6β-Methyl-Iodo-19 Norcholesterol (NP-59) Scintigraphy to Complement Adrenal Venous Sampling in Management of Primary Aldosteronism: A Case Series
Jeongmin Lee, Jeonghoon Ha, Sang-Kuon Lee, Hye Lim Park, Sung-Hoon Kim, Dong-Jun Lim, Jung Min Lee, Sang-Ah Chang, Moo Il Kang, Min-Hee Kim
International Journal of General Medicine.2021; Volume 14: 673. CrossRef - Best Achievements in Pituitary and Adrenal Diseases in 2020
Chang Ho Ahn, Jung Hee Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(1): 51. CrossRef - Adrenal surgery: Review of 35 years experience in a single centre
Enrico Battistella, Stefania Ferrari, Luca Pomba, Antonio Toniato
Surgical Oncology.2021; 37: 101554. CrossRef - Adrenocortical Carcinoma: A Case of Missed Diagnosis
Yusef Hazimeh, Carlie Sigel, Carsello Carie, Mathew Leinung, Zaynab Khalaf
Cureus.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Imagerie fonctionnelle en endocrinologie : nouveaux paradigmes à l’horizon 2020
E. Marchal
Médecine Nucléaire.2021; 45(3): 158. CrossRef - Adrenal Incidentaloma
Caren G. Solomon, Electron Kebebew
New England Journal of Medicine.2021; 384(16): 1542. CrossRef - Can Hematological Parameters Play a Role in the Differential Diagnosis of Adrenal Tumors?
Mehmet Gürkan Arıkan, Göktan Altuğ Öz, Nur Gülce İşkan, Necdet Süt, İlkan Yüksel, Ersan Arda
Uro.2021; 1(2): 39. CrossRef - Incidental Adrenal Nodules
Daniel I. Glazer, Michael T. Corwin, William W. Mayo-Smith
Radiologic Clinics of North America.2021; 59(4): 591. CrossRef - Antioxidant Barrier and Oxidative Damage to Proteins, Lipids, and DNA/RNA in Adrenal Tumor Patients
Barbara Choromańska, Piotr Myśliwiec, Tomasz Kozłowski, Magdalena Łuba, Piotr Wojskowicz, Jacek Dadan, Hanna Myśliwiec, Katarzyna Choromańska, Anna Gibała, Anna Starzyńska, Małgorzata Żendzian-Piotrowska, Anna Zalewska, Mateusz Maciejczyk, Jos L. Quiles
Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Laparoscopic Retroperitoneoscopic Removal of an Adrenal Hemangioma: a Case Report
Kristin McCoy, Katherine Howe, Daniel Tershak
Journal of Endocrine Surgery.2021; 21(3): 70. CrossRef - Metabolic Subtyping of Adrenal Tumors: Prospective Multi-Center Cohort Study in Korea
Eu Jeong Ku, Chaelin Lee, Jaeyoon Shim, Sihoon Lee, Kyoung-Ah Kim, Sang Wan Kim, Yumie Rhee, Hyo-Jeong Kim, Jung Soo Lim, Choon Hee Chung, Sung Wan Chun, Soon-Jib Yoo, Ohk-Hyun Ryu, Ho Chan Cho, A Ram Hong, Chang Ho Ahn, Jung Hee Kim, Man Ho Choi
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(5): 1131. CrossRef - Cross-Talk Between Nitrosative Stress, Inflammation and Hypoxia-Inducible Factor in Patients with Adrenal Masses
Barbara Choromańska, Piotr Myśliwiec, Tomasz Kozłowski, Magdalena Łuba, Piotr Wojskowicz, Jacek Dadan, Hanna Myśliwiec, Katarzyna Choromańska, Katarzyna Makarewicz, Anna Zalewska, Mateusz Maciejczyk
Journal of Inflammation Research.2021; Volume 14: 6317. CrossRef - Cirugía laparoscópica en incidentaloma suprarrenal para el cirujano general: serie de casos
Martín Adrián Bolívar-Rodríguez, Marcel Antonio Cázarez-Aguilar, Pedro Alejandro Magaña-Zavala, Francisco Magaña-Olivas, José Martín Niebla-Moreno
Revista Mexicana de Cirugía Endoscópica.2021; 22(1): 8. CrossRef - Adrenal adenomas: what to do with them? Review 2
S. Rybakov
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENDOCRINOLOGY (Ukraine).2021; 17(3): 241. CrossRef - Is Follow-up of Adrenal Incidentalomas Always Mandatory?
Giuseppe Reimondo, Alessandra Muller, Elisa Ingargiola, Soraya Puglisi, Massimo Terzolo
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2020; 35(1): 26. CrossRef - Imaging Findings of Primary Adrenal Leiomyosarcoma: A Case Report
Hye Ran Yoon, Dong Hee Park
Journal of the Korean Society of Radiology.2020; 81(2): 459. CrossRef - WFUMB position paper on the management incidental findings: adrenal incidentaloma
Christoph F. Dietrich, Jean Michel Correas, Yi Dong, Christian Nolsoe, Susan Campbell Westerway, Christian Jenssen
Ultrasonography.2020; 39(1): 11. CrossRef - A nationwide survey of adrenal incidentalomas in Japan: the first report of clinical and epidemiological features
Takamasa Ichijo, Hajime Ueshiba, Hajime Nawata, Toshihiko Yanase
Endocrine Journal.2020; 67(2): 141. CrossRef - Mimics, pitfalls, and misdiagnoses of adrenal masses on CT and MRI
Khaled M. Elsayes, Mohab M. Elmohr, Sanaz Javadi, Christine O. Menias, Erick M. Remer, Ajaykumar C. Morani, Akram M. Shaaban
Abdominal Radiology.2020; 45(4): 982. CrossRef - Adrenal Incidentaloma
Mark Sherlock, Andrew Scarsbrook, Afroze Abbas, Sheila Fraser, Padiporn Limumpornpetch, Rosemary Dineen, Paul M Stewart
Endocrine Reviews.2020; 41(6): 775. CrossRef - A Web Application for Adrenal Incidentaloma Identification, Tracking, and Management Using Machine Learning
Wasif Bala, Jackson Steinkamp, Timothy Feeney, Avneesh Gupta, Abhinav Sharma, Jake Kantrowitz, Nicholas Cordella, James Moses, Frederick Thurston Drake
Applied Clinical Informatics.2020; 11(04): 606. CrossRef - Presentation and outcome of patients with an adrenal mass: A retrospective observational study
Nadeema Rafiq, Tauseef Nabi, SajadAhmad Dar, Shahnawaz Rasool
Clinical Cancer Investigation Journal.2020; 9(5): 198. CrossRef - Evaluation of Functionality and Growth Rates in Adrenal Incidentalomas: Single Center Experience
Suna AVCI, Yüksel Aslı OZTURKMEN, Sayid ZUHUR, Gulkan OZKAN, Elif GUVEN, Nazan DEMİR, Yuksel ALTUNTAS
Phoenix Medical Journal.2020; 2(3): 125. CrossRef - Percutaneous Adrenal Radiofrequency Ablation: A Short Review for Endocrinologists
Byung Kwan Park
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2020; 35(4): 750. CrossRef - Autonomous cortisol secretion in adrenal incidentalomas
Marta Araujo-Castro, Miguel Antonio Sampedro Núñez, Mónica Marazuela
Endocrine.2019; 64(1): 1. CrossRef - Primary adrenal schwannoma: a series of 31 cases emphasizing their clinicopathologic features and favorable prognosis
Jun Zhou, Dandan Zhang, Wencai Li, Luting Zhou, Haimin Xu, Saifang Zheng, Chaofu Wang
Endocrine.2019; 65(3): 662. CrossRef - Challenging risk factors for right and left laparoscopic adrenalectomy: A single centre experience with 272 cases
Kadir Omur Gunseren, Mehmet Cagatay Cicek, Hakan Vuruskan, Yakup Kordan, Ismet Yavascaoglu
International braz j urol.2019; 45(4): 747. CrossRef - A case report on 111In chloride bone marrow scintigraphy in management of adrenal myelolipoma
Tatsuya Yamamoto, Mitsuru Koizumi, Atsushi Kohno, Noboru Numao, Kentaro Inamura
Medicine.2019; 98(8): e14625. CrossRef - PRACTICAL ASPECTS OF LAPAROSCOPIC ADRENALECTOMY IN CHILDREN WITH BENIGN ADRENAL TUMORS
I. V. Poddubny, R. S. Oganesyan, K. N. Tolstov, M. A. Kareva
Russian Journal of Pediatric Surgery.2019; 23(5): 248. CrossRef - Incidental neuroblastoma with bilateral retinoblastoma: what are the chances?
Kelsey Roelofs, Furqan Shaikh, William Astle, Brenda L. Gallie, Sameh E. Soliman
Ophthalmic Genetics.2018; 39(3): 410. CrossRef - Surgical Considerations in Subclinical Cushing’s Syndrome. When is it Time to Operate?
Alexander M. Nixon, C Aggeli, C Tserkezis, GN Zografos
Hellenic Journal of Surgery.2018; 90(1): 27. CrossRef - Adrenal incidentaloma – diagnostic and treating problem – own experience
Ryszard Pogorzelski, Krzysztof Celejewski, Sadegh Toutounchi, Ewa Krajewska, Tomasz Wołoszko, Małgorzata Szostek, Wawrzyniec Jakuczun, Patryk Fiszer, Małgorzata Legocka, Zbigniew Gałązka
Open Medicine.2018; 13(1): 281. CrossRef
- Clinical Study
- Molecular Diagnosis Using Residual Liquid-Based Cytology Materials for Patients with Nondiagnostic or Indeterminate Thyroid Nodules
-
Hyemi Kwon, Won Gu Kim, Markus Eszlinger, Ralf Paschke, Dong Eun Song, Mijin Kim, Suyeon Park, Min Ji Jeon, Tae Yong Kim, Young Kee Shong, Won Bae Kim
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2016;31(4):586-591. Published online November 4, 2016
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2016.31.4.586
-
-
4,215
View
-
42
Download
-
11
Web of Science
-
12
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader
- Background
Molecular analysis for common somatic mutations in thyroid cancer can improve diagnostic accuracy of fine-needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) in the nondiagnostic or indeterminate category of thyroid nodules. In this study, we evaluated the feasibility of molecular diagnosis from residual liquid-based cytology (LBC) material after cytological diagnosis. MethodsThis prospective study enrolled 53 patients with thyroid nodules diagnosed as nondiagnostic, atypia of undetermined significance (AUS), or follicular lesion of undetermined significance (FLUS) after FNAC. DNAs and RNAs were isolated from residual LBC materials. BRAFV600E and RAS point mutations, PAX8/peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ), RET/PTC1, and RET/PTC3 rearrangements were evaluated by real-time polymerase chain reaction and pyrosequencing. ResultsAll DNAs from 53 residual LBC samples could be analysed and point mutations were detected in 10 samples (19%). In 17 AUS nodules, seven samples (41%) had point mutations including BRAF (n=4), NRAS (n=2), and KRAS (n=1). In 20 FLUS nodules, three samples (15%) had NRAS point mutations. RNA from only one FLUS nodule could be analysed for rearrangements and there was no abnormality. ConclusionMolecular analysis for BRAF and RAS mutations was feasible in residual LBC materials and might be useful for diagnosis of indeterminate thyroid nodules.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Kras Gene Analysis Using Liquid-Based Cytology Specimens Predicts Therapeutic Responses and Prognosis in Patients with Pancreatic Cancer
Masahiro Itonaga, Reiko Ashida, Shin-Ichi Murata, Yasunobu Yamashita, Keiichi Hatamaru, Takashi Tamura, Yuki Kawaji, Yuudai Kayama, Tomoya Emori, Manabu Kawai, Hiroki Yamaue, Ibu Matsuzaki, Hirokazu Nagai, Yuichi Kinoshita, Ke Wan, Toshio Shimokawa, Masay
Cancers.2022; 14(3): 551. CrossRef - From Traditional Histology to Next-Generation Pathology: A Review of The Workflow for the Characterisation and Molecular Profiling of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Samples
EMJ Oncology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Preanalytic variables in quality and quantity of nucleic acids extracted from FNA specimens of thyroid gland nodules collected in CytoLyt: Cellularity and storage time
Jonas J. Heymann, Lorene M. Yoxtheimer, Hyeon Jin Park, Evan M. Fernandez, Kirk E. Facey, Susan A. Alperstein, Hung V. Tran, Inji Baek, Theresa Scognamiglio, Hanna Rennert, Momin T. Siddiqui, Wei Song
Cancer Cytopathology.2020; 128(9): 656. CrossRef - Diagnostic accuracy of molecular testing with three molecular markers on thyroid fine‐needle aspiration cytology with abnormal category
Hatice Seneldir, Gozde Kir, Tuce Soylemez, Rabia B. Girgin, Nurver Ozbay, Filiz Ozen, Handan Ankarali, Gurhan Bas, Orhan Alimoglu
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2020; 48(6): 507. CrossRef - Small but powerful: the promising role of small specimens for biomarker testing
Qiong Gan, Sinchita Roy-Chowdhuri
Journal of the American Society of Cytopathology.2020; 9(5): 450. CrossRef - Centrifuged supernatants from FNA provide a liquid biopsy option for clinical next‐generation sequencing of thyroid nodules
Wenrui Ye, Brette Hannigan, Stephanie Zalles, Meenakshi Mehrotra, Bedia A. Barkoh, Michelle D. Williams, Maria E. Cabanillas, Beth Edeiken‐Monroe, Peter Hu, Dzifa Duose, Ignacio I. Wistuba, L. Jeffrey Medeiros, John Stewart, Rajyalakshmi Luthra, Sinchita
Cancer Cytopathology.2019; 127(3): 146. CrossRef - Molecular testing of residual cytology samples: Rethink, reclaim, repurpose
Sinchita Roy‐Chowdhuri
Cancer Cytopathology.2019; 127(1): 15. CrossRef - K-ras mutation analysis of residual liquid-based cytology specimens from endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration improves cell block diagnosis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
Yoko Sekita-Hatakeyama, Takeshi Nishikawa, Mao Takeuchi, Kouhei Morita, Maiko Takeda, Kinta Hatakeyama, Tokiko Nakai, Tomoko Uchiyama, Hiroe Itami, Tomomi Fujii, Akira Mitoro, Masayuki Sho, Chiho Ohbayashi, Giancarlo Troncone
PLOS ONE.2018; 13(3): e0193692. CrossRef - Comparison of Immunohistochemistry and Direct Sanger Sequencing for Detection of theBRAFV600EMutation in Thyroid Neoplasm
Hye-Seon Oh, Hyemi Kwon, Suyeon Park, Mijin Kim, Min Ji Jeon, Tae Yong Kim, Young Kee Shong, Won Bae Kim, Jene Choi, Won Gu Kim, Dong Eun Song
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2018; 33(1): 62. CrossRef - Next-Generation Sequencing Identifies Gene Mutations That Are Predictive of Malignancy in Residual Needle Rinses Collected From Fine-Needle Aspirations of Thyroid Nodules
Maren Y. Fuller, Dina Mody, April Hull, Kristi Pepper, Heather Hendrickson, Randall Olsen
Archives of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine.2018; 142(2): 178. CrossRef - Articles inEndocrinology and Metabolismin 2016
Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2017; 32(1): 62. CrossRef - Loss of c-KIT expression in thyroid cancer cells
Sara Franceschi, Francesca Lessi, Federica Panebianco, Elena Tantillo, Marco La Ferla, Michele Menicagli, Paolo Aretini, Alessandro Apollo, Antonio Giuseppe Naccarato, Ivo Marchetti, Chiara Maria Mazzanti, Aamir Ahmad
PLOS ONE.2017; 12(3): e0173913. CrossRef
- Endocrine Research
- Comparison of Thyroglobulin Measurements Using Three Different Immunoassay Kits: A BRAMHS Tg-Plus RIA Kit, a BRAMHS hTg Sensitive Kryptor Kit, and a Beckman Coulter ACCESS Immunoassay Kit
-
Mijin Kim, Min Ji Jeon, Won Gu Kim, Jong Jin Lee, Jin-Sook Ryu, Eun-Jung Cho, Dae-Hyun Ko, Woochang Lee, Sail Chun, Won-Ki Min, Tae Yong Kim, Young Kee Shong, Won Bae Kim
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2016;31(3):462-468. Published online August 2, 2016
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2016.31.3.462
-
-
5,093
View
-
49
Download
-
8
Web of Science
-
7
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader
- Background
Second-generation thyroglobulin immunometric assays (Tg-IMAs) have been developed with improved sensitivity. Our aim was to compare the diagnostic value of Tg-IMA measurements using a Kryptor (BRAHMS AG) kit (Tg-K) and an ACCESS (Beckman Coulter) kit (Tg-A) with that of the first-generation Tg measurement using a Tg-plus (BRAHMS AG) kit (Tg+). MethodsWe enrolled 82 differentiated thyroid cancer patients who underwent total thyroidectomy with radioactive iodine remnant ablation and who underwent diagnostic whole body scan using recombinant human thyroid stimulating hormone (rhTSH). The Tg+, Tg-K, and Tg-A were measured before rhTSH administration during levothyroxine treatment (suppressed Tg) from the same sample. Serum Tg+ was measured after rhTSH stimulation (stimulated Tg). ResultsSuppressed Tg+ was more significantly correlated with suppressed Tg-K (R2=0.919, P<0.001) than with suppressed Tg-A (R2=0.536, P<0.001). The optimal cut-off values of suppressed Tg+, Tg-K, and Tg-A for predicting stimulated Tg+ of 1 ng/mL were 0.3, 0.2, and 0.2 ng/mL, respectively. The sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy of suppressed Tg+ were 67%, 100%, and 90%, respectively; those of suppressed Tg-K were 83%, 90%, and 88%; those of suppressed Tg-A were 96%, 82%, and 87%, respectively. The positive predictive and negative predictive values of Tg+ were 100% and 87%, respectively; those of Tg-K were 79% and 92%; and those of Tg-A were 73% and 98%. ConclusionWe could not clearly demonstrate which kit had better diagnostic performance after comparison of first-generation Tg measurements with Tg-IMA measurements. Also, there were kit-to-kit variations between Tg-IMA kits. Suppressed Tg measured by Tg-IMA was insufficient to completely substitute for a stimulated Tg measurement.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Comparison of the diagnostic performances of US-guided fine needle aspiration cytology and thyroglobulin measurement for lymph node metastases in patients with differentiated thyroid carcinoma: a meta-analysis
Rong-Bin Liu, Da-Lei Zhou, Bo-Heng Xu, Xin-Hua Yang, Qing Liu, Xiao Zhang, Tao Tang, Zu-Lu Ye, Yue Li
European Radiology.2021; 31(5): 2903. CrossRef - Preoperative Serum Thyroglobulin and Its Correlation with the Burden and Extent of Differentiated Thyroid Cancer
Hosu Kim, So Young Park, Jun-Ho Choe, Jee Soo Kim, Soo Yeon Hahn, Sun Wook Kim, Jae Hoon Chung, Jaehoon Jung, Tae Hyuk Kim
Cancers.2020; 12(3): 625. CrossRef - Estimating the Growth Rate of Lung Metastases in Differentiated Thyroid Carcinoma: Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors or Doubling Time?
Eyun Song, Jonghwa Ahn, Min Ji Jeon, Sang Min Lee, Jeong Hyun Lee, Tae Yong Kim, Jung Hwan Baek, Won Bae Kim, Young Kee Shong, Won Gu Kim
Thyroid.2020; 30(3): 418. CrossRef - Impact of delayed radioiodine therapy in intermediate‐/high‐risk papillary thyroid carcinoma
Mijin Kim, Minkyu Han, Min Ji Jeon, Won Gu Kim, In Joo Kim, Jin‐Sook Ryu, Won Bae Kim, Young Kee Shong, Tae Yong Kim, Bo Hyun Kim
Clinical Endocrinology.2019; 91(3): 449. CrossRef - Tertiary Care Experience of Sorafenib in the Treatment of Progressive Radioiodine-Refractory Differentiated Thyroid Carcinoma: A Korean Multicenter Study
Mijin Kim, Tae Hyuk Kim, Dong Yeob Shin, Dong Jun Lim, Eui Young Kim, Won Bae Kim, Jae Hoon Chung, Young Kee Shong, Bo Hyun Kim, Won Gu Kim
Thyroid.2018; 28(3): 340. CrossRef - A Follow-Up Strategy for Patients with an Excellent Response to Initial Therapy for Differentiated Thyroid Carcinoma: Less Is Better
Min Ji Jeon, Mijin Kim, Suyeon Park, Hye-Seon Oh, Tae Yong Kim, Won Bae Kim, Young Kee Shong, Won Gu Kim
Thyroid.2018; 28(2): 187. CrossRef - Preoperative serum thyroglobulin predicts initial distant metastasis in patients with differentiated thyroid cancer
Hosu Kim, Young Nam Kim, Hye In Kim, So Young Park, Jun-Ho Choe, Jung-Han Kim, Jee Soo Kim, Jae Hoon Chung, Tae Hyuk Kim, Sun Wook Kim
Scientific Reports.2017;[Epub] CrossRef
- Clinical Study
- Usefulness of Measuring Thyroid Stimulating Antibody at the Time of Antithyroid Drug Withdrawal for Predicting Relapse of Graves Disease
-
Hyemi Kwon, Won Gu Kim, Eun Kyung Jang, Mijin Kim, Suyeon Park, Min Ji Jeon, Tae Yong Kim, Jin-Sook Ryu, Young Kee Shong, Won Bae Kim
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2016;31(2):300-310. Published online April 25, 2016
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2016.31.2.300
-
-
5,013
View
-
87
Download
-
20
Web of Science
-
20
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader
- Background
Hyperthyroidism relapse in Graves disease after antithyroid drug (ATD) withdrawal is common; however, measuring the thyrotropin receptor antibody (TRAb) at ATD withdrawal in order to predict outcomes is controversial. This study compared measurement of thyroid stimulatory antibody (TSAb) and thyrotropin-binding inhibitory immunoglobulin (TBII) at ATD withdrawal to predict relapse. MethodsThis retrospective study enrolled patients with Graves disease who were treated with ATDs and whose serum thyroid-stimulating hormone levels were normal after receiving low-dose ATDs. ATD therapy was stopped irrespective of TRAb positivity after an additional 6 months of receiving the minimum dose of ATD therapy. Patients were followed using thyroid function tests and TSAb (TSAb group; n=35) or TBII (TBII group; n=39) every 3 to 6 months for 2 years after ATD withdrawal. ResultsTwenty-eight patients (38%) relapsed for a median follow-up of 21 months, and there were no differences in baseline clinical characteristics between groups. In the TSAb group, relapse was more common in patients with positive TSAb at ATD withdrawal (67%) than patients with negative TSAb (17%; P=0.007). Relapse-free survival was shorter in TSAb-positive patients. In the TBII group, there were no differences in the relapse rate and relapse-free survivals according to TBII positivity. For predicting Graves disease relapse, the sensitivity and specificity of TSAb were 63% and 83%, respectively, whereas those of TBII were 28% and 65%. ConclusionTSAb at ATD withdrawal can predict the relapse of Graves hyperthyroidism, but TBII cannot. Measuring TSAb at ATD withdrawal can assist with clinical decisions making for patients with Graves disease.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Thyroid stimulating receptor autoantibodies
Yumeng Gao, Ling Qiu, Songlin Yu, Xinqi Cheng
Clinica Chimica Acta.2024; : 119700. CrossRef - Analysis of Related Factors in Refractory Graves’ Disease
鑫 王
Advances in Clinical Medicine.2023; 13(08): 13439. CrossRef - Interpretation of Thyroid Autoantibodies in Hyperthyroidism
Han-Sang Baek, Dong-Jun Lim
The Korean Journal of Medicine.2023; 98(3): 132. CrossRef - The Early Changes in Thyroid-Stimulating Immunoglobulin Bioassay over Anti-Thyroid Drug Treatment Could Predict Prognosis of Graves’ Disease
Jin Yu, Han-Sang Baek, Chaiho Jeong, Kwanhoon Jo, Jeongmin Lee, Jeonghoon Ha, Min Hee Kim, Jungmin Lee, Dong-Jun Lim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(3): 338. CrossRef - Thyroid-Stimulatory Antibody as a Predictive Factor for Graves’ Disease Relapse
Tiago Da Silva Santos, José Carlos Oliveira, Cláudia Freitas, André Couto de Carvalho
Cureus.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Prediction Model Using Thyroid-stimulating Immunoglobulin Bioassay For Relapse of Graves’ Disease
Han-Sang Baek, Jaejun Lee, Chai-Ho Jeong, Jeongmin Lee, Jeonghoon Ha, Kwanhoon Jo, Min-Hee Kim, Jae Hyoung Cho, Moo Il Kang, Dong-Jun Lim
Journal of the Endocrine Society.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Identification of patients with Graves’ disease who benefit from high-dose radioactive iodine therapy
Shiro Watanabe, Shozo Okamoto, Kazumasa Akikawa, Noriyuki Miyamoto, Miyuki Okamura-Kawasaki, Yuko Uchiyama, Junki Takenaka, Takuya Toyonaga, Kenji Hirata, Kohsuke Kudo
Annals of Nuclear Medicine.2022; 36(11): 923. CrossRef - The relationship between atherosclerotic disease and relapse during ATD treatment
Xinxin Zhu, Yaguang Zhang, Xiaoyu Zhao, Xiaona Zhang, Zixuan Ru, Yanmeizhi Wu, Xu Yang, Boyu Hou, Hong Qiao
Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Antithyroid Drug Treatment in Graves’ Disease
Jae Hoon Chung
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(3): 491. CrossRef - The prognostic value of thyroid-stimulating immunoglobulin in the management of Graves’ disease
Yulin Zhou, Mengxi Zhou, Yicheng Qi, Weiqing Wang, Xinxin Chen, Shu Wang
Therapeutic Advances in Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 12: 204201882110449. CrossRef - Changes in Thyroid Peroxidase and Thyroglobulin Antibodies Might Be Associated with Graves' Disease Relapse after Antithyroid Drug Therapy
Yun Mi Choi, Mi Kyung Kwak, Sang Mo Hong, Eun-Gyoung Hong
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2019; 34(3): 268. CrossRef - Graves' Disease: Can It Be Cured?
Wilmar M. Wiersinga
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2019; 34(1): 29. CrossRef - Medical Treatment of Graves' Disease
Hyun-Kyung Chung
International Journal of Thyroidology.2019; 12(2): 79. CrossRef - When should antithyroid drug therapy to reduce the relapse rate of hyperthyroidism in Graves’ disease be discontinued?
Suyeon Park, Eyun Song, Hye-Seon Oh, Mijin Kim, Min Ji Jeon, Won Gu Kim, Tae Yong Kim, Young Kee Shong, Doo Man Kim, Won Bae Kim
Endocrine.2019; 65(2): 348. CrossRef - Elevated Serum IL-17 Expression at Cessation Associated with Graves’ Disease Relapse
Jianhui Li, Xiaohua Sun, Danzhen Yao, Jinying Xia
International Journal of Endocrinology.2018; 2018: 1. CrossRef - Active Surveillance for Patients With Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma: A Single Center’s Experience in Korea
Hyemi Kwon, Hye-Seon Oh, Mijin Kim, Suyeon Park, Min Ji Jeon, Won Gu Kim, Won Bae Kim, Young Kee Shong, Dong Eun Song, Jung Hwan Baek, Ki-Wook Chung, Tae Yong Kim
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2017; 102(6): 1917. CrossRef - Free Thyroxine, Anti-Thyroid Stimulating Hormone Receptor Antibody Titers, and Absence of Goiter Were Associated with Responsiveness to Methimazole in Patients with New Onset Graves' Disease
Hoon Sung Choi, Won Sang Yoo
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2017; 32(2): 281. CrossRef - The Second Antithyroid Drug Treatment Is Effective in Relapsed Graves' Disease Patients: A Median 11-Year Follow-Up Study
Ye An Kim, Sun Wook Cho, Hoon Sung Choi, Shinje Moon, Jae Hoon Moon, Kyung Won Kim, Do Joon Park, Ka Hee Yi, Young Joo Park, Bo Youn Cho
Thyroid.2017; 27(4): 491. CrossRef - The Recurrence Rate of Graves' Disease among Patients with Subclinical Thyrotoxicosis after Initial Remission with Antithyroid Agents
Myoung Sook Shim, Soo Min Nam, Jin Sae Yoo, Hae Kyung Kim, Sang Jun Lee, Mi Young Lee
International Journal of Thyroidology.2017; 10(2): 77. CrossRef - Articles inEndocrinology and Metabolismin 2016
Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2017; 32(1): 62. CrossRef
- Clinical Study
- Low Prevalence of Somatic TERT Promoter Mutations in Classic Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
-
Min Ji Jeon, Won Gu Kim, Soyoung Sim, Seonhee Lim, Hyemi Kwon, Tae Yong Kim, Young Kee Shong, Won Bae Kim
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2016;31(1):100-104. Published online March 16, 2016
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2016.31.1.100
-
-
4,367
View
-
32
Download
-
16
Web of Science
-
15
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader
- Background
Transcriptional activating mutations of telomerase reverse transcriptase (TERT) are associated with more aggressive thyroid cancer. We evaluated the significance of TERT promoter mutations in Korean patients with classic papillary thyroid cancer (PTC). MethodsGenomic DNA was isolated from four thyroid cancer cell lines and 35 fresh-frozen PTC tissues. TERT promoter mutations (C228T and C250T) and the BRAF V600E mutation were evaluated by polymerase chain reaction amplification and direct sequencing. ResultsThe CC228229TT mutation in the TERT promoter was detected in BCPAP cells and the C250T mutation was found in 8505C cells. No TERT promoter mutation was observed in Cal-62 or ML-1 cells. The C228T mutation was found in only 1 of 35 (2.8%) PTCs and no C250T mutations were detected in any of the study subjects. The BRAF V600E mutation was found in 20 of 35 (57.1%) PTCs. One patient with the C228T TERT mutation also harbored the BRAF V600E mutation and developed a recurrence. ConclusionThe prevalence of somatic TERT promoter mutations was low in Korean patients with classic PTC. Therefore, the prognostic role of TERT promoter mutations might be limited in this patient cohort.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Risk Factors for TERT Promoter Mutations with Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Patients: A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review
Jingxin Mao, Xingliang Huang, Mohammad K. Okla, Mostafa A. Abdel-Maksoud, Ayman Mubarak, Zahid Hameed, Razia Noreen, Aqsa Chaudhary, Shakira Ghazanfar, Yixuan Liao, Yasir Hameed, Chen Li, Min Tang
Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Telomerase reverse transcriptase promoter mutations in cancers derived from multiple organ sites among middle eastern population
Abdul K. Siraj, Rong Bu, Kaleem Iqbal, Sandeep Kumar Parvathareddy, Nabil Siraj, Sarah Siraj, Mark Ranier F. Diaz, Dionne Rae Rala, Allianah D. Benito, Maria Angelita Sabido, Maha Al-Rasheed, Khadija A.S. Al-Obaisi, Wael Al-Haqawi, Ingrid G. Victoria, Waf
Genomics.2020; 112(2): 1746. CrossRef - Association between TERT promoter mutations and clinical behaviors in differentiated thyroid carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Jing Yang, Yanping Gong, Shuping Yan, Hui Chen, Siqin Qin, Rixiang Gong
Endocrine.2020; 67(1): 44. CrossRef - The Combination of RET, BRAF and Demographic Data Identifies Subsets of Patients with Aggressive Papillary Thyroid Cancer
Jose R. W. Martínez, Sergio Vargas-Salas, Soledad Urra Gamboa, Estefanía Muñoz, José Miguel Domínguez, Augusto León, Nicolás Droppelmann, Antonieta Solar, Mark Zafereo, F. Christopher Holsinger, Hernán E. González
Hormones and Cancer.2019; 10(2-3): 97. CrossRef - Correlation between TERT C228T and clinic-pathological features in pediatric papillary thyroid carcinoma
Jiangqiao Geng, Yuanhu Liu, Yongli Guo, Huanmin Wang, Jun Tai, Yaqiong Jin, Jie Zhang, Yongbo Yu, Shengcai Wang, Yingluan Song, Xin Ni
Science China Life Sciences.2019; 62(12): 1563. CrossRef - Human telomerase reverse transcriptase in papillary thyroid cancer: gene expression, effects of silencing and regulation by BET inhibitors in thyroid cancer cells
Valentina Maggisano, Marilena Celano, Saverio Massimo Lepore, Marialuisa Sponziello, Francesca Rosignolo, Valeria Pecce, Antonella Verrienti, Federica Baldan, Catia Mio, Lorenzo Allegri, Marianna Maranghi, Rosa Falcone, Giuseppe Damante, Diego Russo, Stef
Endocrine.2019; 63(3): 545. CrossRef - BRAF and RAS Mutational Status in Noninvasive Follicular Thyroid Neoplasm with Papillary-Like Nuclear Features and Invasive Subtype of Encapsulated Follicular Variant of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma in Korea
Mijin Kim, Min Ji Jeon, Hye-Seon Oh, Suyeon Park, Tae Yong Kim, Young Kee Shong, Won Bae Kim, Kyunggon Kim, Won Gu Kim, Dong Eun Song
Thyroid.2018; 28(4): 504. CrossRef - The role of TERT promoter mutations in postoperative and preoperative diagnosis and prognosis in thyroid cancer
Anqi Jin, Jianhao Xu, Yan Wang
Medicine.2018; 97(29): e11548. CrossRef - Telomere Maintenance Mechanisms in Cancer
Tiago Bordeira Gaspar, Ana Sá, José Manuel Lopes, Manuel Sobrinho-Simões, Paula Soares, João Vinagre
Genes.2018; 9(5): 241. CrossRef - Anti-hTERT siRNA-Loaded Nanoparticles Block the Growth of Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer Xenograft
Giovanni E. Lombardo, Valentina Maggisano, Marilena Celano, Donato Cosco, Chiara Mignogna, Federica Baldan, Saverio M. Lepore, Lorenzo Allegri, Sonia Moretti, Cosimo Durante, Giuseppe Damante, Massimo Fresta, Diego Russo, Stefania Bulotta, Efisio Puxeddu
Molecular Cancer Therapeutics.2018; 17(6): 1187. CrossRef - Silencing of hTERT blocks growth and migration of anaplastic thyroid cancer cells
Valentina Maggisano, Marilena Celano, Giovanni Enrico Lombardo, Saverio Massimo Lepore, Marialuisa Sponziello, Francesca Rosignolo, Antonella Verrienti, Federica Baldan, Efisio Puxeddu, Cosimo Durante, Sebastiano Filetti, Giuseppe Damante, Diego Russo, St
Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology.2017; 448: 34. CrossRef - Articles inEndocrinology and Metabolismin 2016
Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2017; 32(1): 62. CrossRef - Telomerase: The Devil Inside
Mukesh Kumar, Andre Lechel, Çagatay Güneş
Genes.2016; 7(8): 43. CrossRef - Cancer-Specific Telomerase Reverse Transcriptase (TERT) Promoter Mutations: Biological and Clinical Implications
Tiantian Liu, Xiaotian Yuan, Dawei Xu
Genes.2016; 7(7): 38. CrossRef - Transcription Regulation of the Human Telomerase Reverse Transcriptase (hTERT) Gene
Muhammad Ramlee, Jing Wang, Wei Toh, Shang Li
Genes.2016; 7(8): 50. CrossRef
- Clinical Study
- Thyrotoxic Periodic Paralysis and Polymorphisms of the ADRB2, AR, and GABRA3 Genes in Men with Graves Disease
-
Suyeon Park, Tae Yong Kim, Soyoung Sim, Seonhee Lim, Mijin Kim, Hyemi Kwon, Min Ji Jeon, Won Gu Kim, Young Kee Shong, Won Bae Kim
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2016;31(1):142-146. Published online March 16, 2016
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2016.31.1.142
-
-
3,760
View
-
39
Download
-
4
Web of Science
-
4
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader
- Background
Thyrotoxic periodic paralysis (TPP) is a rare complication of thyrotoxicosis characterized by acute attacks of muscle weakness and hypokalemia. Recently, variation in several genes was suggested to be associated with TPP. This study evaluated the genetic predisposition to TPP in terms of the β2-adrenergic receptor (ADRB2), androgen receptor (AR), and γ-aminobutyric acid receptor α3 subunit (GABRA3) genes. MethodsThis study enrolled 48 men with Graves disease (GD) and TPP, and 48 GD patients without TPP. We compared the frequencies of candidate polymorphisms between the two groups. ResultsThe frequency of the Gly16/Gly16 genotype in ADRB2 was not significantly associated with TPP (P=0.32). More CAG repeats (≥26) in the AR gene were not correlated with TPP (odds ratio [OR], 2.46; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.81 to 8.09; P=0.08). The allele frequency of the TT genotype in the GABRA3 gene was not associated with TPP (OR, 1.83; 95% CI, 0.54 to 6.74; P=0.41). ConclusionThe polymorphisms in the ADRB2, AR, and GABRA3 genes could not explain the genetic susceptibility to TPP in Korean men with GD.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - RNASET2,GPR174, and PTPN22 gene polymorphisms are related to the risk of liver damage associated with the hyperthyroidism in patients with Graves’ disease
Qing Zhang, Shaozheng Liu, Yanxing Guan, Qingjie Chen, Qing Zhang, Xiang Min
Journal of Clinical Laboratory Analysis.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Articles inEndocrinology and Metabolismin 2016
Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2017; 32(1): 62. CrossRef - Periodic Paralysis and Encephalopathy as Initial Manifestations of Graves’ Disease
Theocharis Tsironis, Athanasios Tychalas, Dimitrios Kiourtidis, Jannis Kountouras, Georgia Xiromerisiou, Jobst Rudolf, Georgia Deretzi
The Neurologist.2017; 22(4): 134. CrossRef - Thyrotoxic periodic paralysis
Zdeněk Doležel, Dana Novotná, Helena Schneiderová, Jan Papež, Martin Jouza
Pediatrie pro praxi.2016; 17(6): 379. CrossRef
- Clinical Study
- Characteristics of Korean Patients with Antithyroid Drug-Induced Agranulocytosis: A Multicenter Study in Korea
-
Hee Kyung Kim, Jee Hee Yoon, Min Ji Jeon, Tae Yong Kim, Young Kee Shong, Min Jin Lee, Bo Hyun Kim, In Joo Kim, Ji Young Joung, Sun Wook Kim, Jae Hoon Chung, Ho-Cheol Kang
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2015;30(4):475-480. Published online December 31, 2015
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2015.30.4.475
-
-
4,251
View
-
59
Download
-
16
Web of Science
-
16
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader
- Background
Antithyroid drugs (ATDs) can lead to the development of agranulocytosis, which is the most serious adverse effect. Characteristics of ATD-induced agranulocytosis (AIA) have seldom been reported due to the rarity. In this study, we characterized the clinical features for AIA in Korean patients. MethodsWe retrospectively reviewed data from patients with AIA diagnosed between 1997 and 2014 at four tertiary hospitals. Agranulocytosis was defined as an absolute neutrophil count (ANC) below 500/mm3. ResultsThe mean age of the patients (11 males, 43 females) was 38.2±14.9 years. Forty-eight patients (88.9%) with AIA had fever and sore throat on initial presentation, 20.4% of patients developed AIA during the second course of treatment, and 75.9% of patients suffered AIA within 3 months after initiation of ATD. The patients taking methimazole (n=39) showed lower levels of ANC and more frequent use of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor than propylthiouracil (n=15) users. The median duration of agranulocytosis was 5.5 days (range, 1 to 20). No differences were observed between the long (≥6 days) and short recovery time (≤5 days) groups in terms of age, gender, ATDs, duration of ATDs, or initial ANC levels. Four patients (7.4%) who were taking ATDs for less than 2 months died of sepsis on the first or second day of hospitalization. ConclusionThe majority of AIA incidents occur in the early treatment period. Considering the high fatality rate of AIA, an early aggressive therapeutic approach is critical and patients should be well informed regarding the warning symptoms of the disease.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Novel Association of KLRC4-KLRK1 Gene Polymorphisms with
Susceptibility and Progression of Antithyroid Drug-Induced
Agranulocytosis
Yayi He, Pan Ma, Yuanlin Luo, Xiaojuan Gong, Jiayang Gao, Yuxin Sun, Pu Chen, Suliang Zhang, Yuxin Tian, Bingyin Shi, Bao Zhang
Experimental and Clinical Endocrinology & Diabetes.2024; 132(01): 17. CrossRef - A Disproportionality Analysis of the Adverse Effect Profiles of Methimazole and Propylthiouracil in Patients with Hyperthyroidism Using the Japanese Adverse Drug Event Report Database
Masanori Arai, Takahiro Tsuno, Hiromi Konishi, Kuniyuki Nishiyama, Yasuo Terauchi, Ryota Inoue, Jun Shirakawa
Thyroid®.2023; 33(7): 804. CrossRef - The Current Status of Hyperthyroidism in Korea
Hyemi Kwon
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(4): 392. CrossRef - Clinical characteristics of neutropenic patients under antithyroid drug: Twelve-year experience in a medical center
Chih-Hsueh Tseng, Chi-Lung Tseng, Harn-Shen Chen, Pei-Lung Chen, Chun-Jui Huang
Journal of the Chinese Medical Association.2023; 86(9): 826. CrossRef - Association of MICA gene polymorphisms with thionamide-induced agranulocytosis
P. Ma, P. Chen, J. Gao, H. Guo, S. Li, J. Yang, J. Lai, X. Yang, B. Zhang, Y. He
Journal of Endocrinological Investigation.2021; 44(2): 363. CrossRef - Efficacy and adverse events related to the initial dose of methimazole in children and adolescents with Graves’ disease
Hyun Gyung Lee, Eun Mi Yang, Chan Jong Kim
Annals of Pediatric Endocrinology & Metabolism.2021; 26(3): 199. CrossRef - MICA polymorphisms associated with antithyroid drug‐induced agranulocytosis in the Chinese Han population
Xiaojuan Gong, Pu Chen, Pan Ma, Jiayang Gao, Jingsi Yang, Hui Guo, Chunxia Yan, Bao Zhang, Yayi He
Immunity, Inflammation and Disease.2020; 8(4): 695. CrossRef - The Management of Thyroid Disease in COVID-19 Pandemic
Won Sang Yoo, Hyun-Kyung Chung
International Journal of Thyroidology.2020; 13(2): 65. CrossRef - Increased Risk of Antithyroid Drug Agranulocytosis Associated with Amiodarone-Induced Thyrotoxicosis: A Population-Based Cohort Study
Michal Gershinsky, Walid Saliba, Idit Lavi, Chen Shapira, Naomi Gronich
Thyroid.2019; 29(2): 193. CrossRef - A Case of Acute Supraglottitis Following Anti-Thyroid Drug-Induced Agranulocytosis
Jung Jun Lee, Dong Young Kim, Jeon Yeob Jang
Journal of The Korean Society of Laryngology, Phoniatrics and Logopedics.2019; 30(2): 128. CrossRef - Association of HLA-B∗38:02 with Antithyroid Drug-Induced Agranulocytosis in Kinh Vietnamese Patients
Mai Phuong Thao, Pham Vo Anh Tuan, Le Gia Hoang Linh, Lam Van Hoang, Phan Huu Hen, Le Tuyet Hoa, Hoang Anh Vu, Do Duc Minh
International Journal of Endocrinology.2018; 2018: 1. CrossRef - Severe Gingival Ulceration and Necrosis Caused by an Antithyroid Drug: One Case Report and Proposed Clinical Approach
Ying‐Ying Chang, Chih‐Wen Tseng, Kuo Yuan
Clinical Advances in Periodontics.2018; 8(1): 11. CrossRef - Emphasis on the early diagnosis of antithyroid drug-induced agranulocytosis: retrospective analysis over 16 years at one Chinese center
Y. He, J. Li, J. Zheng, Z. Khan, W. Qiang, F. Gao, Y. Zhao, B. Shi
Journal of Endocrinological Investigation.2017; 40(7): 733. CrossRef - Association of HLA-B and HLA-DRB1 polymorphisms with antithyroid drug-induced agranulocytosis in a Han population from northern China
Yayi He, Jie Zheng, Qian Zhang, Peng Hou, Feng Zhu, Jian Yang, Wenhao Li, Pu Chen, Shu Liu, Bao Zhang, Bingyin Shi
Scientific Reports.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Use of granulocyte colony‐stimulating factor in the treatment of methimazole‐induced agranulocytosis: a case report
Asha Birmingham, Carissa Mancuso, Craig Williams
Clinical Case Reports.2017; 5(10): 1701. CrossRef - 2016 American Thyroid Association Guidelines for Diagnosis and Management of Hyperthyroidism and Other Causes of Thyrotoxicosis
Douglas S. Ross, Henry B. Burch, David S. Cooper, M. Carol Greenlee, Peter Laurberg, Ana Luiza Maia, Scott A. Rivkees, Mary Samuels, Julie Ann Sosa, Marius N. Stan, Martin A. Walter
Thyroid.2016; 26(10): 1343. CrossRef
- Thyroid
- Lack of Associations between Body Mass Index and Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
-
Hyemi Kwon, Mijin Kim, Yun Mi Choi, Eun Kyung Jang, Min Ji Jeon, Won Gu Kim, Tae Yong Kim, Young Kee Shong, Dong Eun Song, Jung Hwan Baek, Suck Joon Hong, Won Bae Kim
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2015;30(3):305-311. Published online November 26, 2014
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2015.30.3.305
-
-
4,215
View
-
39
Download
-
13
Web of Science
-
14
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader
- Background
Obesity is associated with aggressive pathological features and poor clinical outcomes in breast and prostate cancers. In papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC), these relationships remain still controversial. This study aimed to evaluate the associations between body mass index (BMI) and the clinical outcomes of patients with PTC. MethodsThis retrospective study included 1,189 patients who underwent total thyroidectomy for PTCs equal to or larger than 1 cm in size. Clinical outcomes were evaluated and compared based on the BMI quartiles. ResultsThere were no significant associations between BMI quartiles and primary tumor size, extrathyroidal invasion, cervical lymph node metastasis, or distant metastasis. However, an increase in mean age was associated with an increased BMI (P for trend <0.001). Multifocality and advanced tumor-node-metastasis (TNM) stage (stage III or IV) were significantly associated with increases of BMI (P for trend 0.02 and <0.001, respectively). However, these associations of multifocality and advanced TNM stage with BMI were not significant in multivariate analyses adjusted for age and gender. Moreover, there were no differences in recurrence-free survivals according to BMI quartiles (P=0.26). ConclusionIn the present study, BMI was not associated with the aggressive clinicopathological features or recurrence-free survivals in patients with PTC.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - A Data-Driven Approach to Refine Predictions of Differentiated Thyroid Cancer Outcomes: A Prospective Multicenter Study
Giorgio Grani, Michele Gentili, Federico Siciliano, Domenico Albano, Valentina Zilioli, Silvia Morelli, Efisio Puxeddu, Maria Chiara Zatelli, Irene Gagliardi, Alessandro Piovesan, Alice Nervo, Umberto Crocetti, Michela Massa, Maria Teresa Samà, Chiara Mel
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2023; 108(8): 1921. CrossRef - Potential impact of obesity on the aggressiveness of low- to intermediate-risk papillary thyroid carcinoma: results from a MASTER cohort study
Mijin Kim, Yae Eun Kang, Young Joo Park, Bon Seok Koo, Eu Jeong Ku, June Young Choi, Eun Kyung Lee, Bo Hyun Kim
Endocrine.2023; 82(1): 134. CrossRef - Potential Impact of Body Mass Index on the Clinical Outcome of Papillary Thyroid Cancer After High-Dose Radioactive Iodine Therapy
Jingjia Cao, Xiaolu Zhu, Yaru Sun, Xiao Li, Canhua Yun, Wei Zhang
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Nutritional status and follicular-derived thyroid cancer: An update
Luigi Barrea, Marco Gallo, Rosaria Maddalena Ruggeri, Paola Di Giacinto, Franz Sesti, Natalie Prinzi, Valerio Adinolfi, Viola Barucca, Valerio Renzelli, Giovanna Muscogiuri, Annamaria Colao, Roberto Baldelli
Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition.2021; 61(1): 25. CrossRef - Effects of concomitant obesity and diabetes on the aggressiveness and outcomes of differentiated thyroid cancer patients
Onur Elbasan, Dilek Gogas Yavuz
Archives of Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of BMI with Clinicopathological Features of Papillary Thyroid Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta‐Analysis
R. J. O'Neill, S. Abd Elwahab, M. J. Kerin, A. J. Lowery
World Journal of Surgery.2021; 45(9): 2805. CrossRef - Association Between Aggressive Clinicopathologic Features of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma and Body Mass Index: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Aliki Economides, Konstantinos Giannakou, Ioannis Mamais, Panayiotis A. Economides, Panagiotis Papageorgis
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Potential Impact of BMI on the Aggressiveness of Presentation and Clinical Outcome of Differentiated Thyroid Cancer
Antonio Matrone, Giovanni Ceccarini, Marianna Beghini, Federica Ferrari, Carla Gambale, Mariaida D’Aqui, Paolo Piaggi, Liborio Torregrossa, Eleonora Molinaro, Fulvio Basolo, Paolo Vitti, Ferruccio Santini, Rossella Elisei
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2020; 105(4): e1124. CrossRef - Correlation between obesity and clinicopathological characteristics in patients with papillary thyroid cancer: a study of 1579 cases: a retrospective study
Huijuan Wang, Pingping Wang, Yu Wu, Xiukun Hou, Zechun Peng, Weiwei Yang, Lizhao Guan, Linfei Hu, Jingtai Zhi, Ming Gao, Xiangqian Zheng
PeerJ.2020; 8: e9675. CrossRef - Lack of association between obesity and aggressiveness of differentiated thyroid cancer
G. Grani, L. Lamartina, T. Montesano, G. Ronga, V. Maggisano, R. Falcone, V. Ramundo, L. Giacomelli, C. Durante, D. Russo, M. Maranghi
Journal of Endocrinological Investigation.2019; 42(1): 85. CrossRef - Mitochondrial DNA haplogroup K as a contributor to protection against thyroid cancer in a population from southeast Europe
Relu Cocoş, Sorina Schipor, Corin Badiu, Florina Raicu
Mitochondrion.2018; 39: 43. CrossRef - The impact of BMI on clinical progress, response to treatment, and disease course in patients with differentiated thyroid cancer
Danuta Gąsior-Perczak, Iwona Pałyga, Monika Szymonek, Artur Kowalik, Agnieszka Walczyk, Janusz Kopczyński, Katarzyna Lizis-Kolus, Tomasz Trybek, Estera Mikina, Dorota Szyska-Skrobot, Klaudia Gadawska-Juszczyk, Stefan Hurej, Artur Szczodry, Anna Słuszniak,
PLOS ONE.2018; 13(10): e0204668. CrossRef - Pretreatment BMI Is Associated with Aggressive Clinicopathological Features of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma: A Multicenter Study
Shi-tong Yu, Wanzhi Chen, Qian Cai, Faya Liang, Debin Xu, Ping Han, Jichun Yu, Xiaoming Huang
International Journal of Endocrinology.2017; 2017: 1. CrossRef - Associations between body mass index and lymph node metastases of patients with papillary thyroid cancer
Changhua Wu, Liang Wang, Wanjun Chen, Shujuan Zou, Aiju Yang
Medicine.2017; 96(9): e6202. CrossRef
- Thyroid
- Erratum: Figure Correction: Standardized Thyroid Cancer Mortality in Korea between 1985 and 2010
-
Yun Mi Choi, Tae Yong Kim, Eun Kyung Jang, Hyemi Kwon, Min Ji Jeon, Won Gu Kim, Young Kee Shong, Won Bae Kim
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2015;30(1):116. Published online March 27, 2015
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2015.30.1.116
-
-
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader
- Thyroid
- Standardized Thyroid Cancer Mortality in Korea between 1985 and 2010
-
Yun Mi Choi, Tae Yong Kim, Eun Kyung Jang, Hyemi Kwon, Min Ji Jeon, Won Gu Kim, Young Kee Shong, Won Bae Kim
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2014;29(4):530-535. Published online December 29, 2014
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2014.29.4.530
-
-
4,245
View
-
39
Download
-
23
Web of Science
-
36
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader
- Background
The prevalence of thyroid cancer has increased very rapidly in Korea. However, there is no published report focusing on thyroid cancer mortality in Korea. In this study, we aimed to evaluate standardized thyroid cancer mortality using data from Statistics Korea (the Statistical Office of Korea). MethodsPopulation and mortality data from 1985 to 2010 were obtained from Statistics Korea. Age-standardized rates of thyroid cancer mortality were calculated according to the standard population of Korea, as well as World Health Organization (WHO) standard population and International Cancer Survival Standard (ICSS) population weights. ResultsThe crude thyroid cancer mortality rate increased from 0.1 to 0.7 per 100,000 between 1985 and 2010. The pattern was the same for both sexes. The age-standardized mortality rate (ASMR) for thyroid cancer for Korean resident registration population increased from 0.19 to 0.67 between 1985 and 2000. However, it decreased slightly, from 0.67 to 0.55, between 2000 and 2010. When mortality was adjusted using the WHO standard population and ICSS population weights, the ASMR similarly increased until 2000, and then decreased between 2000 and 2010. ConclusionThyroid cancer mortality increased until 2000 in Korea. It started to decrease from 2000.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Trends in incidence and overdiagnosis of thyroid cancer in China, Japan, and South Korea
Yongtian Lin, Yu Wu
Cancer Science.2023; 114(10): 4052. CrossRef - Risk of Adverse Pregnancy Outcomes in Young Women with Thyroid Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Shinje Moon, Ka Hee Yi, Young Joo Park
Cancers.2022; 14(10): 2382. CrossRef - Asymptomatic Patients and Rising Incidence of Thyroid Cancer—Reply
Mirabelle Sajisevi, Louise Davies
JAMA Otolaryngology–Head & Neck Surgery.2022; 148(12): 1186. CrossRef - Asymptomatic Patients and Rising Incidence of Thyroid Cancer
Shijie Yang, Xiequn Xu
JAMA Otolaryngology–Head & Neck Surgery.2022; 148(12): 1185. CrossRef - Does the radioactive iodine dose affect smell, taste sensation and nose function?
B Tutar, T Özülker, G Berkiten, S Karaketir, M E Ekincioğlu, Z Saltürk, Ö Onaran, B Gürpınar, Ş Karaketir, T L Kumral, Y Uyar
The Journal of Laryngology & Otology.2021; 135(1): 50. CrossRef - Disparities in Cancer-Related Avoidable Mortality by the Level of Area Deprivation in South Korea
Woorim Kim, Seongkyeong Jang, Gangeun Lee, Yoon Jung Chang
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(15): 7856. CrossRef - Thyroid cancer: incidence and mortality trends in China, 2005–2015
Junyi Wang, Fangfang Yu, Yanna Shang, Zhiguang Ping, Li Liu
Endocrine.2020; 68(1): 163. CrossRef - A miRNA-clinicopathological nomogram for the prediction of central lymph node metastasis in papillary thyroid carcinoma-analysis from TCGA database
Mingjun Wang, Rongjing Li, Xiuhe Zou, Tao Wei, Rixiang Gong, Jingqiang Zhu, Zhihui Li
Medicine.2020; 99(35): e21996. CrossRef - Trends in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Patients with Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma in Korea
Hwa Young Ahn, Jae Eun Chae, Hyemi Moon, Junghyun Noh, Young Joo Park, Sin Gon Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2020; 35(4): 811. CrossRef - Optimal Thyrotropin Suppression Therapy in Low-Risk Thyroid Cancer Patients after Lobectomy
Lee, Jeon, Kim, Sung, Chung, Shong, Hong
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2019; 8(9): 1279. CrossRef - Improved survival after early detection of asymptomatic distant metastasis in patients with thyroid cancer
Hosu Kim, So Young Park, Jaehoon Jung, Jung-Han Kim, Soo Yeon Hahn, Jung Hee Shin, Young Lyun Oh, Man Ki Chung, Hye In Kim, Sun Wook Kim, Jae Hoon Chung, Tae Hyuk Kim
Scientific Reports.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Do aggressive variants of papillary thyroid carcinoma have worse clinical outcome than classic papillary thyroid carcinoma?
Eyun Song, Min Ji Jeon, Hye-Seon Oh, Minkyu Han, Yu-Mi Lee, Tae Yong Kim, Ki-Wook Chung, Won Bae Kim, Young Kee Shong, Dong Eun Song, Won Gu Kim
European Journal of Endocrinology.2018; 179(3): 135. CrossRef - Study Protocol of Multicenter Prospective Cohort Study of Active Surveillance on Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma (MAeSTro)
Jae Hoon Moon, Ji-hoon Kim, Eun Kyung Lee, Kyu Eun Lee, Sung Hye Kong, Yeo Koon Kim, Woo-jin Jung, Chang Yoon Lee, Roh-Eul Yoo, Yul Hwangbo, Young Shin Song, Min Joo Kim, Sun Wook Cho, Su-jin Kim, Eun Jae Jung, June Young Choi, Chang Hwan Ryu, You Jin Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2018; 33(2): 278. CrossRef - Surgeon volume and prognosis of patients with advanced papillary thyroid cancer and lateral nodal metastasis
H I Kim, T H Kim, J-H Choe, J-H Kim, J S Kim, Y N Kim, H Kim, S W Kim, J H Chung
British Journal of Surgery.2018; 105(3): 270. CrossRef - Ultrasound requested by general practitioners or for symptoms unrelated to the thyroid gland may explain higher prevalence of thyroid nodules in females
Ana Germano, Willian Schmitt, Pedro Almeida, Rui Mateus-Marques, Valeriano Leite
Clinical Imaging.2018; 50: 289. CrossRef - Associations between Hashimoto Thyroiditis and Clinical Outcomes of Papillary Thyroid Cancer: A Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies
Shinje Moon, Hye Soo Chung, Jae Myung Yu, Hyung Joon Yoo, Jung Hwan Park, Dong Sun Kim, Young Joo Park
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2018; 33(4): 473. CrossRef - Refining the eighth edition AJCC TNM classification and prognostic groups for papillary thyroid cancer with lateral nodal metastasis
Hye In Kim, Kyunga Kim, So Young Park, Jun-Ho Choe, Jung-Han Kim, Jee Soo Kim, Young Lyun Oh, Soo Yeon Hahn, Jung Hee Shin, Hyeon Seon Ahn, Sun Wook Kim, Tae Hyuk Kim, Jae Hoon Chung
Oral Oncology.2018; 78: 80. CrossRef - Decreasing Disease-Specific Mortality of Differentiated Thyroid Cancer in Korea: A Multicenter Cohort Study
Min Ji Jeon, Hee Kyung Kim, Eun Heui Kim, Eun Sook Kim, Hyon-Seung Yi, Tae Yong Kim, Ho-Cheol Kang, Young Kee Shong, Won Bae Kim, Bo Hyun Kim, Won Gu Kim
Thyroid.2018; 28(9): 1121. CrossRef - Are pregnancy, parity, menstruation and breastfeeding risk factors for thyroid cancer? Results from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2010‐2015
Hosu Kim, Kyong Young Kim, Jong Ha Baek, Jaehoon Jung
Clinical Endocrinology.2018; 89(2): 233. CrossRef - Case–Control Study of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma on Urinary and Dietary Iodine Status in South Korea
Joon‐Hyop Lee, Ra‐Yeong Song, Jin Wook Yi, Hyeong Won Yu, Hyungju Kwon, Su‐jin Kim, Young Jun Chai, June Young Choi, Jae Hoon Moon, Kyu Eun Lee, Young Joo Park, Sue K. Park
World Journal of Surgery.2018; 42(5): 1424. CrossRef - Patterns of Initial Recurrence in Completely Resected Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
Hosu Kim, Tae Hyuk Kim, Jun-Ho Choe, Jung-Han Kim, Jee Soo Kim, Young Lyun Oh, Soo Yeon Hahn, Jung Hee Shin, Sang ah Chi, Sin-Ho Jung, Young Nam Kim, Hye In Kim, Sun Wook Kim, Jae Hoon Chung
Thyroid.2017; 27(7): 908. CrossRef - Changes in standardized mortality rates from thyroid cancer in Korea between 1985 and 2015: Analysis of Korean national data
Yun Mi Choi, Won Gu Kim, Hyemi Kwon, Min Ji Jeon, Minkyu Han, Tae Yong Kim, Young Kee Shong, Sang Mo Hong, Eun‐Gyoung Hong, Won Bae Kim
Cancer.2017; 123(24): 4808. CrossRef - Thyrotropin Suppressive Therapy for Low-Risk Small Thyroid Cancer: A Propensity Score–Matched Cohort Study
Suyeon Park, Won Gu Kim, Minkyu Han, Min Ji Jeon, Hyemi Kwon, Mijin Kim, Tae-Yon Sung, Tae Yong Kim, Won Bae Kim, Suck Joon Hong, Young Kee Shong
Thyroid.2017; 27(9): 1164. CrossRef - Preoperative serum thyroglobulin predicts initial distant metastasis in patients with differentiated thyroid cancer
Hosu Kim, Young Nam Kim, Hye In Kim, So Young Park, Jun-Ho Choe, Jung-Han Kim, Jee Soo Kim, Jae Hoon Chung, Tae Hyuk Kim, Sun Wook Kim
Scientific Reports.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Young Age and Male Sex Are Predictors of Large-Volume Central Neck Lymph Node Metastasis in Clinical N0 Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinomas
Hye-Seon Oh, Suyeon Park, Mijin Kim, Hyemi Kwon, Eyun Song, Tae-Yon Sung, Yu-Mi Lee, Won Gu Kim, Tae Yong Kim, Young Kee Shong, Won Bae Kim, Min Ji Jeon
Thyroid.2017; 27(10): 1285. CrossRef - Restratification of survival prognosis of N1b papillary thyroid cancer by lateral lymph node ratio and largest lymph node size
Hye In Kim, Tae Hyuk Kim, Jun‐Ho Choe, Jung‐Han Kim, Jee Soo Kim, Young Lyun Oh, Soo Yeon Hahn, Jung Hee Shin, Hye Won Jang, Young Nam Kim, Hosu Kim, Hyeon Seon Ahn, Kyunga Kim, Sun Wook Kim, Jae Hoon Chung
Cancer Medicine.2017; 6(10): 2244. CrossRef - Risk factors associated with high thyroglobulin level following radioactive iodine ablation, measured 12 months after treatment for papillary thyroid carcinoma
Eun Young Kim, Kee Hoon Hyun, Yong Lai Park, Chan Heun Park, Ji-Sup Yun
Annals of Surgical Treatment and Research.2017; 92(1): 1. CrossRef - Disease-Specific Mortality of Differentiated Thyroid Cancer Patients in Korea: A Multicenter Cohort Study
Min Ji Jeon, Won Gu Kim, Tae Hyuk Kim, Hee Kyung Kim, Bo Hyun Kim, Hyon-Seung Yi, Eun Sook Kim, Hosu Kim, Young Nam Kim, Eun Heui Kim, Tae Yong Kim, Sun Wook Kim, Ho-Cheol Kang, Jae Hoon Chung, Young Kee Shong, Won Bae Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2017; 32(4): 434. CrossRef - Features of papillary thyroid microcarcinoma associated with lateral cervical lymph node metastasis
Min Ji Jeon, Mi Sun Chung, Hyemi Kwon, Mijin Kim, Suyeon Park, Jung Hwan Baek, Dong Eun Song, Tae‐Yon Sung, Suck Joon Hong, Tae Yong Kim, Won Bae Kim, Young Kee Shong, Jeong Hyun Lee, Won Gu Kim
Clinical Endocrinology.2017; 86(6): 845. CrossRef - Dynamic Risk Stratification for Predicting Recurrence in Patients with Differentiated Thyroid Cancer Treated Without Radioactive Iodine Remnant Ablation Therapy
Suyeon Park, Won Gu Kim, Eyun Song, Hye-Seon Oh, Mijin Kim, Hyemi Kwon, Min Ji Jeon, Tae Yong Kim, Young Kee Shong, Won Bae Kim
Thyroid.2017; 27(4): 524. CrossRef - Clinical outcomes of low-dose and high-dose postoperative radioiodine therapy in patients with intermediate-risk differentiated thyroid cancer
Ju Hye Jeong, Eun Jung Kong, Shin Young Jeong, Sang-Woo Lee, Ihn Ho Cho, Kyung Ah Chun, Jaetae Lee, Byeong-Cheol Ahn
Nuclear Medicine Communications.2017; 38(3): 228. CrossRef - Single-Incision, Gasless, Endoscopic Trans-Axillary Total Thyroidectomy: A Feasible and Oncologic Safe Surgery in Patients with Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
Eun Young Kim, Kwan Ho Lee, Yong Lai Park, Chan Heun Park, Cho Rok Lee, Jong Ju Jeong, Kee-Hyun Nam, Woong Youn Chung, Ji-Sup Yun
Journal of Laparoendoscopic & Advanced Surgical Techniques.2017; 27(11): 1158. CrossRef - Prognostic value of the eighth edition AJCC TNM classification for differentiated thyroid carcinoma
Tae Hyuk Kim, Young Nam Kim, Hye In Kim, So Young Park, Jun-Ho Choe, Jung-Han Kim, Jee Soo Kim, Young Lyun Oh, Soo Yeon Hahn, Jung Hee Shin, Kyunga Kim, Jong Gill Jeong, Sun Wook Kim, Jae Hoon Chung
Oral Oncology.2017; 71: 81. CrossRef - Changing trends in the clinicopathological features and clinical outcomes of medullary thyroid carcinoma
Hyemi Kwon, Won Gu Kim, Tae‐Yon Sung, Min Ji Jeon, Dong Eun Song, Yu‐Mi Lee, Jong Ho Yoon, Ki‐Wook Chung, Suck Joon Hong, Jung Hwan Baek, Jeong Hyun Lee, Tae Yong Kim, Young Kee Shong, Won Bae Kim
Journal of Surgical Oncology.2016; 113(2): 152. CrossRef - Thyroid lobectomy with minimal incision approach
Tsuyoshi Kojima, Kazuhiko Shoji, Ryusuke Hori, Yusuke Okanoue, Shintaro Fujimura, Hideaki Okuyama, Masayuki Kitano
JOURNAL OF JAPAN SOCIETY FOR HEAD AND NECK SURGERY.2016; 26(2): 283. CrossRef - Articles in 'Endocrinology and Metabolism' in 2014
Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2015; 30(1): 47. CrossRef
- Thyroid
- Solitary Skin Metastasis of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
-
Hyemi Kwon, Hyojung Kim, Sojung Park, Dong Eun Song, Won Gu Kim, Tae Yong Kim, Young Kee Shong, Won Bae Kim
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2014;29(4):579-583. Published online December 29, 2014
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2014.29.4.579
-
-
4,017
View
-
41
Download
-
7
Web of Science
-
8
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader
A solitary skin metastasis is a rare manifestation of papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC). A 55-year-old woman presented with a movable subcutaneous nodule in her anterior neck for several months. Three years ago, she underwent total thyroidectomy and remnant ablation for classical PTC (pT3N0M0) and was under thyroxine suppression therapy without any evidence of recurrent disease. The subcutaneous nodule was 0.4 cm in size, firm, and movable without any change in the overlying skin. Recurrent PTC was confirmed after excision biopsy. Eight months after, she got a new nodule along the previous excision site. After punch biopsy, metastatic PTC was confirmed in the deep dermis and was re-excised with a clear resection margin. This is the first report of a case of solitary skin metastasis of PTC in Korea. Although solitary skin metastasis of PTC is rare, it should be considered in patients with a skin nodule. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Skin Metastasis Occurring 30 Years After Thyroidectomy for Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
Mohammed S Alwhaid, Olaa Mhish, Mutahir A Tunio, Salman AlMalki, Mushabbab Al Asiri, Khalid Al-Qahtani
Cureus.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Solitary Nasopharyngeal Metastasis From Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Shown on FDG PET/CT
Anqi Xu, Xiao Jie, Yan Xiu, Hongcheng Shi
Clinical Nuclear Medicine.2022; 47(5): e425. CrossRef - PD-L1-positive Anaplastic Transformation in a BRAF V600E Expressing Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma with Cutaneous Metastasis: An Unusual Case Report
Pooja Ramakant, Anand Mishra, Chanchal Rana, Kulranjan Singh
Indian Journal of Endocrine Surgery and Research.2022; 17(1): 21. CrossRef - Unusual Thyroid Carcinoma Metastases: a Case Series and Literature Review
Eleonora Farina, Fabio Monari, Giovanni Tallini, Andrea Repaci, Renzo Mazzarotto, Francesca Giunchi, Riccardo Panzacchi, Silvia Cammelli, Gilbert D. A. Padula, Francesco Deodato, Renato Pasquali, Stefano Fanti, Michelangelo Fiorentino, Alessio G. Morganti
Endocrine Pathology.2016; 27(1): 55. CrossRef - Skin manifestations of endocrine and neuroendocrine tumors
Jonathan S. Leventhal, Irwin M. Braverman
Seminars in Oncology.2016; 43(3): 335. CrossRef - Isolated Metastasis in Male Breast from Differentiated Thyroid Carcinoma – Oncological Curiosity. A Case Report and Review of Literature
Lakshminarasimman Parasuraman, Shubhada V. Kane, Prathamesh S. Pai, Kintan Shanghvi
Indian Journal of Surgical Oncology.2016; 7(1): 91. CrossRef - A Closer Look at Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
Won Bae Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2015; 30(1): 1. CrossRef - Articles in 'Endocrinology and Metabolism' in 2014
Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2015; 30(1): 47. CrossRef
- Thyroid
- Current Status and Future Perspectives in Differentiated Thyroid Cancer
-
Tae Yong Kim, Won Gu Kim, Won Bae Kim, Young Kee Shong
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2014;29(3):217-225. Published online September 25, 2014
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2014.29.3.217
-
-
4,424
View
-
35
Download
-
76
Web of Science
-
61
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader
Thyroid cancer is increasing all over the world. The exact cause of this increase is still debated and there are conflicting reports. Sophisticated molecular studies suggest that environmental chemicals may have effects of thyroid carcinogenesis. The development of powerful molecular biology techniques has enabled targeted next-generation sequencing for detection of mutations in thyroid cancer, and this technique can make a specific diagnosis of thyroid cancer in cytologically indeterminate cases. The initial treatment of well-differentiated thyroid cancer (DTC) is surgery followed by radioiodine remnant ablation. However, further studies are needed to determine the optimal dosage of radioactive iodine for DTC patients with lateral neck metastasis. DTC is an indolent tumor and may cause death even decades later. Thus, long-term follow-up is mandatory. Recently, dynamic risk stratification (DRS) has begun to use stimulated thyroglobulin level at 1 year after the initial treatment and restratified the risk in accordance with the response to the initial treatment. This DRS strategy accurately predicts disease free survival and can be widely used in daily clinical settings. For the iodine refractory metastatic disease, redifferentiation therapy and targeted therapy are two promising alternative treatments. Sorafenib is the first approved agent for the treatment of progressive iodine refractory advanced thyroid cancer in Korea and may be very helpful for radioactive-refractory locally advanced or metastatic DTC. Selumetinib may be an effective redifferentiating agent and could be used within several years. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and the Risk of Thyroid Cancer Among Young Adults in South Korea
Hyemi Kwon, Kyung-Do Han, Sun Joon Moon, Se Eun Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2024; 109(3): e1095. CrossRef - Dual targeting of MAPK and PI3K pathways unlocks redifferentiation of Braf-mutated thyroid cancer organoids
Hélène Lasolle, Andrea Schiavo, Adrien Tourneur, Pierre Gillotay, Bárbara de Faria da Fonseca, Lucieli Ceolin, Olivier Monestier, Benilda Aganahi, Laura Chomette, Marina Malta Letro Kizys, Lieven Haenebalcke, Tim Pieters, Steven Goossens, Jody Haigh, Vinc
Oncogene.2024; 43(3): 155. CrossRef - Clinical significance and diagnostic value of QPCT, SCEL and TNFRSF12A in papillary thyroid cancer
Tairong Liang, Xiuqian Wu, Lan Wang, Zhengzhong Ni, Ying Fan, Peishan Wu, Hongzhi Wang, Yongdong Niu, Haihua Huang
Pathology - Research and Practice.2023; 245: 154431. CrossRef - Thyroidkeeper: a healthcare management system for patients with thyroid diseases
Jing Zhang, Jianhua Li, Yi Zhu, Yu Fu, Lixia Chen
Health Information Science and Systems.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Repeated Low High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol and the Risk of Thyroid Cancer: A Nationwide Population- Based Study in Korea
Jinyoung Kim, Mee Kyoung Kim, Ki-Hyun Baek, Ki-Ho Song, Kyungdo Han, Hyuk-Sang Kwon
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(2): 303. CrossRef - Comparison of the prognostic value of AJCC cancer staging system 7th and 8th editions for differentiated thyroid cancer
Y. J. Morosán Allo, L. Bosio, A. Morejón, C. Parisi, M. C. Faingold, V. Ilera, A. Gauna, G. Brenta
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Immune Profiling of Advanced Thyroid Cancers Using Fluorescent Multiplex Immunohistochemistry
Jonghwa Ahn, Meihua Jin, Eyun Song, Yeon-mi Ryu, Dong Eun Song, Sang-Yeob Kim, Tae Yong Kim, Won Bae Kim, Young Kee Shong, Min Ji Jeon, Won Gu Kim
Thyroid.2021; 31(1): 61. CrossRef - A double mutation of BRAF L597Q and V600E in situ and solitary brain metastasis of occult papillary thyroid carcinoma
Ling Chen, Yue Wu, Huili Bai, Huandong Liu, Xiaosong Li
Medicine.2021; 100(6): e24458. CrossRef - Mutation in Genes Encoding Key Functional Groups Additively Increase Mortality in Patients with BRAFV600E-Mutant Advanced Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
Eyun Song, Meihua Jin, Ahreum Jang, Min Ji Jeon, Dong Eun Song, Hye Jin Yoo, Won Bae Kim, Young Kee Shong, Won Gu Kim
Cancers.2021; 13(22): 5846. CrossRef - Current Status and Future Perspective of the Treatment for Radioiodine Refractory Differentiated Thyroid Cancer
Young Kee Shong
International Journal of Thyroidology.2021; 14(2): 98. CrossRef - Comprehensive evaluation of risk factors for lymph node metastasis in patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma
Yan Dong, Dan Wang, Yisheng Luo, Ling Chen, Huili Bai, Yifan Shen, Yangli Zhang, Xueping Chen, Xinliang Su, Jinqiu Zhao, Huandong Liu, Jungao Lu, Zuoyi Yao, Yajing Zhao, Changlong He, Xiaosong Li
Oncology Letters.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Lenvatinib for Radioactive Iodine-Refractory Differentiated Thyroid Carcinoma and Candidate Biomarkers Associated with Survival: A Multicenter Study in Korea
Eyun Song, Mijin Kim, Eui Young Kim, Bo Hyun Kim, Dong Yeob Shin, Ho-Cheol Kang, Byeong-Cheol Ahn, Won Bae Kim, Young Kee Shong, Min Ji Jeon, Dong Jun Lim
Thyroid.2020; 30(5): 732. CrossRef - Radioiodine ablation in thyroid cancer patients: renal function and external radiation dose rate at discharge according to patient preparation
Yeon-Hee Han, Hwan-Jeong Jeong, Myung-Hee Sohn, Sun Y. Lee, Seok T. Lim
The Quarterly Journal of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Metabolic Syndrome and the Risk of Thyroid Cancer: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study
Joo-Hyun Park, Moonyoung Choi, Jung-Hun Kim, Jaemin Kim, Kyungdo Han, Bongsung Kim, Do-Hoon Kim, Yong-Gyu Park
Thyroid.2020; 30(10): 1496. CrossRef - Serum Adiponectin and Progranulin Level in Patients with Benign Thyroid Nodule or Papillary Thyroid Cancer
Hyemi Kwon, Se Eun Park, Ji-Sup Yun, Cheol-Young Park
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2020; 35(2): 396. CrossRef - The role of Slit2 as a tumor suppressor in thyroid cancer
Min Ji Jeon, Seonhee Lim, Mi-hyeon You, Yangsoon Park, Dong Eun Song, Soyoung Sim, Tae Yong Kim, Young Kee Shong, Won Bae Kim, Won Gu Kim
Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology.2019; 483: 87. CrossRef - Metabolic Obesity Phenotypes and Thyroid Cancer Risk: A Cohort Study
Hyemi Kwon, Yoosoo Chang, Ara Cho, Jiin Ahn, Se Eun Park, Cheol-Young Park, Won-Young Lee, Ki-Won Oh, Sung-Woo Park, Hocheol Shin, Seungho Ryu, Eun-Jung Rhee
Thyroid.2019; 29(3): 349. CrossRef - Impact of delayed radioiodine therapy in intermediate‐/high‐risk papillary thyroid carcinoma
Mijin Kim, Minkyu Han, Min Ji Jeon, Won Gu Kim, In Joo Kim, Jin‐Sook Ryu, Won Bae Kim, Young Kee Shong, Tae Yong Kim, Bo Hyun Kim
Clinical Endocrinology.2019; 91(3): 449. CrossRef - Myxedema coma precipitated by diabetic ketoacidosis after total thyroidectomy: a case report
Jin Joo Kim, Eun Young Kim
Journal of Medical Case Reports.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Comprehensive analysis for diagnosis of preoperative non-invasive follicular thyroid neoplasm with papillary-like nuclear features
Hye Seung Lee, Jae-Wook Lee, Ji Hyun Park, Wan-Seop Kim, Hye Seung Han, Seung Eun Lee, Paula Soares
PLOS ONE.2019; 14(7): e0218046. CrossRef - Rutin Scavenges Reactive Oxygen Species, Inactivates 5′-Adenosine Monophosphate-Activated Protein Kinase, and Increases Sodium–Iodide Symporter Expression in Thyroid PCCL3 Cells
Carlos Frederico Lima Gonçalves, Mariana Lopes de Freitas, Rodrigo Soares Fortunato, Leandro Miranda-Alves, Denise P. Carvalho, Andrea Claudia Freitas Ferreira
Thyroid.2018; 28(2): 265. CrossRef - Prevalence of BRAFV600E Mutation in Follicular Variant of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma and Non-Invasive Follicular Tumor with Papillary-Like Nuclear Features (NIFTP) in a BRAFV600E Prevalent Area
Hyereen Kim, Bo Hyun Kim, Young Keum Kim, Jeong Mi Kim, Seo Young Oh, Eun Heui Kim, Min Jin Lee, Jong Ho Kim, Yun Kyung Jeon, Sang Soo Kim, Byung Joo Lee, Yong Ki Kim, In Joo Kim
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Whole-Exome Sequencing Identifies Two Discrete Druggable Signaling Pathways in Follicular Thyroid Cancer
Neeta J. Erinjeri, Norman G. Nicolson, Christine Deyholos, Reju Korah, Tobias Carling
Journal of the American College of Surgeons.2018; 226(6): 950. CrossRef - Efficacy and Affecting Factors of 131I Thyroid Remnant Ablation After Surgical Treatment of Differentiated Thyroid Carcinoma
Chen Wang, Hongcui Diao, Ping Ren, Xufu Wang, Yangang Wang, Wenjuan Zhao
Frontiers in Oncology.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Do aggressive variants of papillary thyroid carcinoma have worse clinical outcome than classic papillary thyroid carcinoma?
Eyun Song, Min Ji Jeon, Hye-Seon Oh, Minkyu Han, Yu-Mi Lee, Tae Yong Kim, Ki-Wook Chung, Won Bae Kim, Young Kee Shong, Dong Eun Song, Won Gu Kim
European Journal of Endocrinology.2018; 179(3): 135. CrossRef - SPC24 is critical for anaplastic thyroid cancer progression
Huabin Yin, Tong Meng, Lei Zhou, Haiyan Chen, Dianwen Song
Oncotarget.2017; 8(13): 21884. CrossRef - Analysis of radioiodine therapy and prognostic factors of differentiated thyroid cancer patients with pulmonary metastasis
Renfei Wang, Yueqian Zhang, Jian Tan, Guizhi Zhang, Ruiguo Zhang, Wei Zheng, Yajing He
Medicine.2017; 96(19): e6809. CrossRef - Effect of Rifampin on Thyroid Function Test in Patients on Levothyroxine Medication
Hye In Kim, Tae Hyuk Kim, Hosu Kim, Young Nam Kim, Hye Won Jang, Jae Hoon Chung, Seong Mi Moon, Byung Woo Jhun, Hyun Lee, Won-Jung Koh, Sun Wook Kim, Dongmei Li
PLOS ONE.2017; 12(1): e0169775. CrossRef - Delayed TSH recovery after dose adjustment during TSH‐suppressive levothyroxine therapy of thyroid cancer
Hye In Kim, Tae Hyuk Kim, Hosu Kim, Young Nam Kim, Hye Won Jang, Jung‐Han Kim, Kyu Yeon Hur, Jae Hoon Chung, Sun Wook Kim
Clinical Endocrinology.2017; 87(3): 286. CrossRef - Serum vitamin D3 levels are not associated with thyroid cancer prevalence in euthyroid subjects without autoimmune thyroid disease
Yun Mi Choi, Won Gu Kim, Tae Yong Kim, Sung Jin Bae, Hong-Kyu Kim, Eun Kyung Jang, Min Ji Jeon, Ji Min Han, Young Kee Shong, Won Bae Kim
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2017; 32(1): 102. CrossRef - Optimal cut-off age in the TNM Staging system of differentiated thyroid cancer: is 55 years better than 45 years?
Mijin Kim, Young Nam Kim, Won Gu Kim, Suyeon Park, Hyemi Kwon, Min Ji Jeon, Hyeon Seon Ahn, Sin-Ho Jung, Sun Wook Kim, Won Bae Kim, Jae Hoon Chung, Young Kee Shong, Tae Hyuk Kim, Tae Yong Kim
Clinical Endocrinology.2017; 86(3): 438. CrossRef - Initial Size of Metastatic Lesions Is Best Prognostic Factor in Patients with Metastatic Differentiated Thyroid Carcinoma Confined to the Lung
Mijin Kim, Won Gu Kim, Suyeon Park, Hyemi Kwon, Min Ji Jeon, Jong Jin Lee, Jin-Sook Ryu, Tae Yong Kim, Young Kee Shong, Won Bae Kim
Thyroid.2017; 27(1): 49. CrossRef - Refining Dynamic Risk Stratification and Prognostic Groups for Differentiated Thyroid Cancer With TERT Promoter Mutations
Tae Hyuk Kim, Chang-Seok Ki, Hye Seung Kim, Kyunga Kim, Jun-Ho Choe, Jung-Han Kim, Jee Soo Kim, Young Lyun Oh, Soo Yeon Hahn, Jung Hee Shin, Hye Won Jang, Sun Wook Kim, Jae Hoon Chung
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2017; 102(5): 1757. CrossRef - Comparison of the Seventh and Eighth Editions of the American Joint Committee on Cancer/Union for International Cancer Control Tumor-Node-Metastasis Staging System for Differentiated Thyroid Cancer
Mijin Kim, Won Gu Kim, Hye-Seon Oh, Suyeon Park, Hyemi Kwon, Dong Eun Song, Tae Yong Kim, Young Kee Shong, Won Bae Kim, Tae-Yon Sung, Min Ji Jeon
Thyroid.2017; 27(9): 1149. CrossRef - Growth Kinetics of Macronodular Lung Metastases and Survival in Differentiated Thyroid Carcinoma
Mijin Kim, Won Gu Kim, Suyeon Park, Hyemi Kwon, Min Ji Jeon, Sang Min Lee, Jeong Hyun Lee, Tae Yong Kim, Young Kee Shong, Won Bae Kim
Thyroid.2017; 27(7): 915. CrossRef - Preoperative clinicopathological characteristics of patients with solitary encapsulated follicular variants of papillary thyroid carcinomas
Hyemi Kwon, Min Ji Jeon, Jong Ho Yoon, Suck Joon Hong, Jeong Hyun Lee, Tae Yong Kim, Young Kee Shong, Won Bae Kim, Won Gu Kim, Dong Eun Song
Journal of Surgical Oncology.2017; 116(6): 746. CrossRef - Prescribed Activity of 131I Therapy in Differentiated Thyroid Cancer
Douglas Van Nostrand
Journal of Nuclear Medicine.2017; 58(5): 697. CrossRef - Metabolomics of papillary thyroid carcinoma tissues: potential biomarkers for diagnosis and promising targets for therapy
Xingchen Shang, Xia Zhong, Xingsong Tian
Tumor Biology.2016; 37(8): 11163. CrossRef - Recent Updates on the Management of Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma
Bo Hyun Kim, In Joo Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2016; 31(3): 392. CrossRef - Intraoperative Near‐infrared Imaging for Parathyroid Gland Identification by Auto‐fluorescence: A Feasibility Study
Frederic De Leeuw, Ingrid Breuskin, Muriel Abbaci, Odile Casiraghi, Haïtham Mirghani, Aïcha Ben Lakhdar, Corinne Laplace‐Builhé, Dana Hartl
World Journal of Surgery.2016; 40(9): 2131. CrossRef - Papillary thyroid carcinoma: different clinical behavior among pT3 tumors
Maria Joana Santos, Maria João Bugalho
Endocrine.2016; 53(3): 754. CrossRef - Changing trends in the clinicopathological features and clinical outcomes of medullary thyroid carcinoma
Hyemi Kwon, Won Gu Kim, Tae‐Yon Sung, Min Ji Jeon, Dong Eun Song, Yu‐Mi Lee, Jong Ho Yoon, Ki‐Wook Chung, Suck Joon Hong, Jung Hwan Baek, Jeong Hyun Lee, Tae Yong Kim, Young Kee Shong, Won Bae Kim
Journal of Surgical Oncology.2016; 113(2): 152. CrossRef - Assessment of radioiodine therapy efficacy for treatment of differentiated thyroid cancer patients with pulmonary metastasis undetected by chest computed tomography
BIN LONG, MENGDI YANG, ZHIWEN YANG, HEQING YI, LINFA LI
Oncology Letters.2016; 11(2): 965. CrossRef - Usefulness of PET/CT in the diagnosis of recurrent or metastasized differentiated thyroid carcinoma
CUN-ZHI LU, SU-SHENG CAO, WEI WANG, JUN LIU, NING FU, FENG LU
Oncology Letters.2016; 11(4): 2420. CrossRef - Coexistence of papillary thyroid microcarcinoma and mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma in a context of Hashimoto's thyroiditis
Saul Levy-Blitchtein, Stefany Plasencia-Rebata, Domingo Morales Luna, Juana del Valle Mendoza
Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Medicine.2016; 9(8): 812. CrossRef - Iodine-131 Therapy and Nasolacrimal Duct Obstructions: What We Know and What We Need to Know
Mohammad Javed Ali
Ophthalmic Plastic & Reconstructive Surgery.2016; 32(4): 243. CrossRef - Low Prevalence of Somatic TERT Promoter Mutations in Classic Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
Min Ji Jeon, Won Gu Kim, Soyoung Sim, Seonhee Lim, Hyemi Kwon, Tae Yong Kim, Young Kee Shong, Won Bae Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2016; 31(1): 100. CrossRef - Dietary evaluation of a low-iodine diet in Korean thyroid cancer patients preparing for radioactive iodine therapy in an iodine-rich region
Dal Lae Ju, Young Joo Park, Hee-Young Paik, Min-Ji Kim, Seonyeong Park, Kyong Yeun Jung, Tae Hyuk Kim, Hun Sung Choi, Yoon Ju Song
Nutrition Research and Practice.2016; 10(2): 167. CrossRef - Features Predictive of Distant Metastasis in Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinomas
Min Ji Jeon, Won Gu Kim, Yun Mi Choi, Hyemi Kwon, Yu-Mi Lee, Tae-Yon Sung, Jong Ho Yoon, Ki-Wook Chung, Suck Joon Hong, Tae Yong Kim, Young Kee Shong, Dong Eun Song, Won Bae Kim
Thyroid.2016; 26(1): 161. CrossRef - Alpha lipoic acid inhibits proliferation and epithelial mesenchymal transition of thyroid cancer cells
Min Ji Jeon, Won Gu Kim, Seonhee Lim, Hyun-Jeung Choi, Soyoung Sim, Tae Yong Kim, Young Kee Shong, Won Bae Kim
Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology.2016; 419: 113. CrossRef - Differentiated Thyroid Cancer in Asians
Bo Hyun Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2016; 31(1): 62. CrossRef - Sub-Classification of Lateral Cervical Lymph Node Metastasis in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma by Pathologic Criteria
Min Ji Jeon, Won Gu Kim, Eun Kyung Jang, Yun Mi Choi, Dong Eun Song, Tae-Yon Sung, Jong Ho Yoon, Ki-Wook Chung, Suck Joon Hong, Jin-Sook Ryu, Ji Min Han, Tae Yong Kim, Young Kee Shong, Won Bae Kim, Konradin Metze
PLOS ONE.2015; 10(7): e0133625. CrossRef - The Impact of Low Adherence to the Low-iodine Diet on the Efficacy of the Radioactive Iodine Ablation Therapy
Dal Lae Ju, Young Joo Park, Hee-Young Paik, YoonJu Song
Clinical Nutrition Research.2015; 4(4): 267. CrossRef - High metabolic tumor volume and total lesion glycolysis are associated with lateral lymph node metastasis in patients with incidentally detected thyroid carcinoma
Bo Hyun Kim, Seong-Jang Kim, Keunyoung Kim, Heeyoung Kim, So Jung Kim, Won Jin Kim, Yun Kyung Jeon, Sang Soo Kim, Yong Ki Kim, In Joo Kim
Annals of Nuclear Medicine.2015; 29(8): 721. CrossRef - Articles in 'Endocrinology and Metabolism' in 2014
Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2015; 30(1): 47. CrossRef - Changes in the Pulmonary Function Test after Radioactive Iodine Treatment in Patients with Pulmonary Metastases of Differentiated Thyroid Cancer
Eun Kyung Jang, Won Gu Kim, Ho-Cheol Kim, Jin-Won Huh, Hyemi Kwon, Yun Mi Choi, Min Ji Jeon, Tae Yong Kim, Young Kee Shong, Jin-Sook Ryu, Won Bae Kim, Karen M. Tordjman
PLOS ONE.2015; 10(4): e0125114. CrossRef - Negative Expression of CPSF2 Predicts a Poorer Clinical Outcome in Patients with Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
Tae Yon Sung, Mijin Kim, Tae Yong Kim, Won Gu Kim, Yangsoon Park, Dong Eun Song, Su-Yeon Park, Hyemi Kwon, Yun Mi Choi, Eun Kyung Jang, Min Ji Jeon, Young Kee Shong, Suck Joon Hong, Won Bae Kim
Thyroid.2015; 25(9): 1020. CrossRef - Thyroglobulin Level in Fine-Needle Aspirates for Preoperative Diagnosis of Cervical Lymph Node Metastasis in Patients with Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma: Two Different Cutoff Values According to Serum Thyroglobulin Level
Min Ji Jeon, Won Gu Kim, Eun Kyung Jang, Yun Mi Choi, Yu-Mi Lee, Tae-Yon Sung, Jong Ho Yoon, Ki-Wook Chung, Suck Joon Hong, Jung Hwan Baek, Jeong Hyun Lee, Tae Yong Kim, Young Kee Shong, Won Bae Kim
Thyroid.2015; 25(4): 410. CrossRef - A Closer Look at Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
Won Bae Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2015; 30(1): 1. CrossRef - Protecting the normal in order to better kill the cancer
Bingya Liu, Lewis Ezeogu, Lucas Zellmer, Baofa Yu, Ningzhi Xu, Dezhong Joshua Liao
Cancer Medicine.2015; 4(9): 1394. CrossRef - Recent Changes in the Clinical Outcome of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma With Cervical Lymph Node Metastasis
Min Ji Jeon, Won Gu Kim, Yun Mi Choi, Hyemi Kwon, Dong Eun Song, Yu-Mi Lee, Tae-Yon Sung, Jong Ho Yoon, Suck Joon Hong, Jung Hwan Baek, Jeong Hyun Lee, Jin-Sook Ryu, Tae Yong Kim, Young Kee Shong, Ki-Wook Chung, Won Bae Kim
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2015; 100(9): 3470. CrossRef
- Long-Term Survival of a Patient with Pulmonary Artery Intimal Sarcoma after Sequential Metastasectomies of the Thyroid and Adrenal Glands
-
Yun Mi Choi, Eun Kyung Jang, Seong Hee Ahn, Min Ji Jeon, Ji Min Han, Seong Chul Kim, Duck Jong Han, Gyungyup Gong, Tae Yong Kim, Young Kee Shong, Won Bae Kim
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2013;28(1):46-49. Published online March 25, 2013
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2013.28.1.46
-
-
3,654
View
-
28
Download
-
9
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader
Cancer metastases to the thyroid or adrenal gland are uncommon. Furthermore, cases showing long-term survival after surgical resection of those metastatic tumors are rare. We report a case of pulmonary artery intimal sarcoma with metastases to the thyroid and adrenal glands sequentially that was successfully treated with sequential metastasectomies. A 62-year-old woman presented with a 4-week history of dyspnea on exertion and facial edema in November 1999. Echocardiography and chest computed tomography (CT) revealed an embolism-like mass in the pulmonary trunk. Pulmonary artery endarterectomy with pulmonary valve replacement was performed, and histopathology revealed pulmonary artery intimal sarcoma. A thyroid nodule was found by chest CT in November 2001 (2 years after initial surgery). During follow-up, this lesion showed no change, but we decided to obtain fine needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) in August 2004 (4.7 years after initial surgery). FNAC revealed atypical spindle cells suggestive of metastatic intimal sarcoma. She underwent total thyroidectomy. During follow-up, a right adrenal gland mass was detected by chest CT in March 2006 (6.3 years after initial surgery), and adrenalectomy was done, which also revealed metastatic sarcoma. She has been followed up without any evidence of recurrent disease until May 2012 (12.5 years after initial surgery). -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Reoperation of Pulmonary Artery Intimal Sarcoma for Recurrence After Pulmonary Artery Replacement
Kentaro Miyazaki, Isao Matsumoto, Satoshi Nishikawa, Takashi Wada, Tetsuya Takayama, Daisuke Saito, Shuhei Yoshida, Kenji Iino, Hirofumi Takemura
Annals of Thoracic Surgery Short Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Pulmonary artery sarcoma: An important mimic of pulmonary embolism—Case reports and literature review
Colin Tuft, Krishan Maheepala, Ajantha Raguparan, Anas Naeem, Suhrid Lodh, Steven Lindstrom
Respirology Case Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Rare case of metastatic liposarcoma to the thyroid gland and a review of the literature of metastatic sarcomas to the thyroid
Monica H. Xing, Neil Mundi, Aparna Govindan, Azita Khorsandi, Margaret Brandwein‐Weber, Ammar Matloob, Bobby Liaw, Mark L. Urken
Head & Neck.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Left pneumonectomy with pulmonary arterioplasty under cardiopulmonary bypass for pulmonary artery intimal sarcoma
Akihiko Kitahara, Yuki Shimizu, Tatsuya Goto, Seijiro Sato, Terumoto Koike, Masanori Tsuchida
The Journal of the Japanese Association for Chest Surgery.2018; 32(4): 492. CrossRef - Intimal sarcoma of the pulmonary artery with multiple lung metastases: Long-term survival case
Sonia García-Cabezas, Macarena Centeno-Haro, Simona Espejo-Pérez, Elvira Carmona-Asenjo, Alberto L Moreno-Vega, Rosa Ortega-Salas, Amalia Palacios-Eito
World Journal of Clinical Oncology.2017; 8(4): 366. CrossRef - Clinical Characteristics and Treatment Outcomes of Primary Pulmonary Artery Sarcoma in Korea
Yunkyoung Lee, Hyun Jung Kim, Heeyoung Yoon, Chang-Min Choi, Yeon-Mok Oh, Sang-Do Lee, Chae-Man Lim, Woo-Sung Kim, Younsuck Koh, Jae Seung Lee
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2016; 31(11): 1755. CrossRef - An Extraordinary Case of Mesenchymal Chondrosarcoma Metastasis in the Thyroid
Santiago Ortiz, Francisco Tortosa, Manuel Sobrinho Simões
Endocrine Pathology.2015; 26(1): 33. CrossRef - Presentation and management of pulmonary artery sarcoma
Han Hsi Wong, Ioannis Gounaris, Ann McCormack, Marius Berman, Dochka Davidson, Gail Horan, Joanna Pepke-Zaba, David Jenkins, Helena M Earl, Helen M Hatcher
Clinical Sarcoma Research.2015;[Epub] CrossRef - Brief Review of Articles in 'Endocrinology and Metabolism' in 2013
Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2014; 29(3): 251. CrossRef
- Four Cases of Malignant Pleural Effusion in Patients with Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma.
-
Min Ji Jeon, Ji Hye Yim, Eui Young Kim, Won Gu Kim, Tae Yong Kim, Won Bae Kim, Young Kee Shong
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2011;26(4):330-334. Published online December 1, 2011
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2011.26.4.330
-
-
40,501
View
-
30
Download
-
3
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Papillary thyroid carcinoma could be a rare cause of malignant pleural effusion. The development of malignant pleural effusion in patients with papillary thyroid cancer is an extremely adverse prognostic indicator. Here, we report four cases that showed development of malignant pleural effusion during the clinical course of the papillary thyroid carcinoma and consider the prognosis. In four patients, the median survival time after the development of malignant pleural effusion was only 17 months.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Pleural fluid due to papillary thyroid cancer
Tomohiro Tamura, Toshihiro Shiozawa, Hiroaki Satoh, Koichi Kurishima, Katsunori Kagohashi, Norio Takayashiki, Nobuyuki Hizawa
Oncology Letters.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Outcome and characteristics of patients with malignant pleural effusion from differentiated thyroid carcinoma
Chisato Tomoda, Yuna Ogimi, Fumi Saito, Chie Masaki, Junko Akaishi, Kenichi Matsuzu, Akifumi Suzuki, Takashi Uruno, Keiko Ohkuwa, Hiroshi Shibuya, Wataru Kitagawa, Mitsuji Nagahama, Kiminori Sugino, Koichi Ito
Endocrine Journal.2016; 63(3): 257. CrossRef - A distinctive colour associated with high iodine content in malignant pleural effusion from metastatic papillary thyroid cancer: a case report
Andrew Rosenstengel, Ee Mun Lim, Michael Millward, YC Gary Lee
Journal of Medical Case Reports.2013;[Epub] CrossRef
- Comparison of Different Staging Systems for Predicting Recurrence of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma.
-
Won Gu Kim, Eui Young Kim, Ji Hye Yim, Ji Min Han, Min Ji Jeon, Tae Yong Kim, Jin Sook Ryu, Gyungyub Gong, Suck Joon Hong, Won Bae Kim, Young Kee Shong
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2011;26(1):53-61. Published online March 1, 2011
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2011.26.1.53
-
-
2,304
View
-
24
Download
-
10
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- BACKGROUND
Various staging systems for thyroid cancer that focus on cancer specific death have been suggested, but this approach had a limitation due to the relatively long clinical course and very low rate of cancer death. This study was performed to evaluate the staging systems and to determine the most predictive staging system for predicting recurrence. METHODS: The patients who underwent first total or near total thyroidectomy due to papillary thyroid cancer (PTC) at Asan Medical Center between January 1995 and December 2001 were the subjects of this study. The commonly used 8 staging systems were applied to these subjects. Disease free survival (DFS) and the relative importance of each staging system were determined by the Kaplan-Meier method, the Cox-proportional hazards model and the proportion of variation in the survival time explained (PVE). RESULTS: A total of 952 patients (M = 117, F = 835) were enrolled and their mean age was 45 years. During a median of 10 years of follow-up, 146 (15.3%) of 952 patients had recurred tumor. The independent prognostic factors were male gender, tumor size, extrathyroidal invasion and cervical lymph node metastasis. Risk stratification according to the American thyroid association (ATA) guideline was the most predictive staging system for recurrence of PTC (PVE 88.6%). The staging systems from EORTC (PVE 79.5%), and MACIS (PVE 68.4%) had significant values for predicting recurrence of PTC. The stage of NTCTCS could not predict recurrence (PVE 4.5%, P = 0.11). CONCLUSION: Risk stratification according to the ATA was most predictive staging system for predicting recurrence of PTC. The MACIS and EORTC staging systems have good value for predicting recurrence of PTC.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Unmet Clinical Needs in the Treatment of Patients with Thyroid Cancer
Won Bae Kim, Min Ji Jeon, Won Gu Kim, Tae Yong Kim, Young Kee Shong
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2020; 35(1): 14. CrossRef - Impact of delayed radioiodine therapy in intermediate‐/high‐risk papillary thyroid carcinoma
Mijin Kim, Minkyu Han, Min Ji Jeon, Won Gu Kim, In Joo Kim, Jin‐Sook Ryu, Won Bae Kim, Young Kee Shong, Tae Yong Kim, Bo Hyun Kim
Clinical Endocrinology.2019; 91(3): 449. CrossRef - Clinical Value of Lymph Node Ratio Integration with the 8th Edition of the UICC TNM Classification and 2015 ATA Risk Stratification Systems for Recurrence Prediction in Papillary Thyroid Cancer
Jandee Lee, Seul Gi Lee, Kwangsoon Kim, Seung Hyuk Yim, Haengrang Ryu, Cho Rok Lee, Sang Wook Kang, Jong Ju Jeong, Kee-Hyun Nam, Woong Youn Chung, Young Suk Jo
Scientific Reports.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical prognostic significance of cancer stem cell markers in patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma
Yoon‑Jong Ryu, Ji‑Young Choe, Kyoungyul Lee, Soon‑Hyun Ahn
Oncology Letters.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Dynamic Risk Stratification for Predicting Recurrence in Patients with Differentiated Thyroid Cancer Treated Without Radioactive Iodine Remnant Ablation Therapy
Suyeon Park, Won Gu Kim, Eyun Song, Hye-Seon Oh, Mijin Kim, Hyemi Kwon, Min Ji Jeon, Tae Yong Kim, Young Kee Shong, Won Bae Kim
Thyroid.2017; 27(4): 524. CrossRef - Optimal cut-off age in the TNM Staging system of differentiated thyroid cancer: is 55 years better than 45 years?
Mijin Kim, Young Nam Kim, Won Gu Kim, Suyeon Park, Hyemi Kwon, Min Ji Jeon, Hyeon Seon Ahn, Sin-Ho Jung, Sun Wook Kim, Won Bae Kim, Jae Hoon Chung, Young Kee Shong, Tae Hyuk Kim, Tae Yong Kim
Clinical Endocrinology.2017; 86(3): 438. CrossRef - Sub-Classification of Lateral Cervical Lymph Node Metastasis in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma by Pathologic Criteria
Min Ji Jeon, Won Gu Kim, Eun Kyung Jang, Yun Mi Choi, Dong Eun Song, Tae-Yon Sung, Jong Ho Yoon, Ki-Wook Chung, Suck Joon Hong, Jin-Sook Ryu, Ji Min Han, Tae Yong Kim, Young Kee Shong, Won Bae Kim, Konradin Metze
PLOS ONE.2015; 10(7): e0133625. CrossRef - Recent Changes in the Clinical Outcome of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma With Cervical Lymph Node Metastasis
Min Ji Jeon, Won Gu Kim, Yun Mi Choi, Hyemi Kwon, Dong Eun Song, Yu-Mi Lee, Tae-Yon Sung, Jong Ho Yoon, Suck Joon Hong, Jung Hwan Baek, Jeong Hyun Lee, Jin-Sook Ryu, Tae Yong Kim, Young Kee Shong, Ki-Wook Chung, Won Bae Kim
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2015; 100(9): 3470. CrossRef - Differentiating the location of cervical lymph node metastasis is very useful for estimating the risk of distant metastases in papillary thyroid carcinoma
Min Ji Jeon, Tae Yong Kim, Won Gu Kim, Ji Min Han, Eun Kyung Jang, Yun Mi Choi, Dong Eun Song, Jong Ho Yoon, Ki‐Wook Chung, Suck Joon Hong, Young Kee Shong, Won Bae Kim
Clinical Endocrinology.2014; 81(4): 593. CrossRef - Influences of Hashimoto's Thyroiditis as Prognostic Factor of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
Hyun Ju Park, Dong Kun Lee, Ji Won Seo, Myung Koo Kang, Heon Soo Park, Rock Bum Kim, Sung Hwan Suh, Mi Kyoung Park, Duk Kyu Kim, Jong Chul Hong
Korean Journal of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery.2014; 57(5): 320. CrossRef
- Postoperative Findings of the Cytological Diagnosis of Follicular Neoplasm or Hurthle Cell Neoplasm and the Risk of Malignancy.
-
Ji Hye Yim, Eui Young Kim, Won Gu Kim, Tae Yong Kim, Gyungyup Gong, Suck Joon Hong, Won Bae Kim, Young Kee Shong
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2010;25(4):316-320. Published online December 1, 2010
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2010.25.4.316
-
-
2,092
View
-
31
Download
-
4
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- BACKGROUND
Follicular neoplasm (FN) or Hurthle cell neoplasm (HN) is a less well understood pitfall when evaluating thyroid nodule with fine-needle aspiration (FNA). This study aimed to determine the rates of malignancy and the predictive factors for malignancy in thyroid nodules with a cytological diagnosis of FN or HN. METHODS: The patients who were cytologically diagnosed as having FN or HN after FNA between 1995 and 2004 at Asan Medical Center were included in this study. We collected the pathology data until 2009 and we analyzed the clinical characteristics associated with malignancy. RESULTS: A total 478 patients were cytologically diagnosed as having FN or HN during the study period and 327 (68%) among them underwent thyroid surgery. Thyroid malignancy was confirmed in 157 (48%) of 327 patients. Malignancy was confirmed in 124 patients with FN (124/253, 49%). They were 48 papillary, 65 follicular, 7 Hurthle cell and 3 medullary carcinomas and 1 anaplastic carcinoma. The malignancy in the cases of HN (33/71, 44.6%) was 9 papillary, 4 follicular and 20 Hurthle cell carcinomas. The risk of malignancy was not associated with male gender, a larger tumor size (> 4 cm) or the diagnosis of HN. However, an age below 20 years (RR 3.6, P = 0.03) and above 60 years (RR 2.3, P = 0.04) was associated with an increased risk of malignancy. CONCLUSION: About half of the patients with FN or HN on FNA cytology were diagnosed as having thyroid cancer after surgery. The malignancy rate for the cytologic diagnosis of HN was similar to that for FN. Thyroid surgery should be recommended for this situation, and especially for patients younger than 20 years or older than 60 years.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Diagnostic Value of Preoperative Serum Thyroglobulin Measurement for the Diagnosis of Malignancy in Follicular or Hürthle Cell Neoplasms of the Thyroid Gland
Nam Kyu Kim, Seong Joo Kang, Weon Hyoung Lee, Go Eun Yeo, You Jin Han, Bu Kyung Kim, Su Kyoung Kwon, Yo-Han Park, Young Sik Choi
Kosin Medical Journal.2014; 29(1): 17. CrossRef - Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology of Thyroid Follicular Neoplasm: Cytohistologic Correlation and Accuracy
Changyoung Yoo, Hyun Joo Choi, Soyoung Im, Ji Han Jung, Kiouk Min, Chang Suk Kang, Young-Jin Suh
Korean Journal of Pathology.2013; 47(1): 61. CrossRef - Predictive Factors of Malignancy in Thyroid Nodules with a Cytological Diagnosis of Follicular Neoplasm
Seong Hyeon Lee, Jeong Su Baek, Joo Young Lee, Jung Ah Lim, Soo Youn Cho, Tae Hyun Lee, Yun Hyi Ku, Hong Il Kim, Min Joo Kim
Endocrine Pathology.2013; 24(4): 177. CrossRef - Postoperative Findings of the Cytological Diagnosis of Follicular Neoplasm or Hürthle Cell Neoplasm and Risk of Malignancy
Jung Uee Lee, Minho Shong
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2010; 25(4): 298. CrossRef
- Revised Korean Thyroid Association Management Guidelines for Patients with Thyroid Nodules and Thyroid Cancer.
-
Ka Hee Yi, Young Joo Park, Sung Soo Koong, Jung Han Kim, Dong Gyu Na, Jin Sook Ryu, So Yeon Park, In Ae Park, Chung Hwan Baek, Young Kee Shong, Young Don Lee, Jaetae Lee, Jeong Hyun Lee, Jae Hoon Chung, Chan Kwon Jung, Seung Ho Choi, Bo Youn Cho
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2010;25(4):270-297. Published online December 1, 2010
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2010.25.4.270
-
-
3,217
View
-
44
Download
-
35
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- No abstract available.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Imaging Recommendations for Diagnosis, Staging, and Management of Cancer of the Thyroid, Parathyroid, and Salivary Glands
Abhishek Mahajan, Shreya Shukla, Suman Kumar Ankathi, Anuradha Shukla, Richa Vaish, Shubham Suryavanshi, Ujjwal Agarwal, Vasundhara Patil, Arpita Sahu, Shubham Padashetty, Sarbani Ghosh Laskar, Vijay Patil, Vanita Noronha, Nandini Menon, Kumar Prabhash, A
Indian Journal of Medical and Paediatric Oncology.2023; 44(02): 159. CrossRef - Authors’ Reply: A Time Trend Analysis of 5000 Robotic Thyroidectomies via Bilateral Axillo‐Breast Approach
JungHak Kwak, Hyeong Won Yu, Jong‐hyuk Ahn, Su‐jin Kim, Young Jun Chai, June Young Choi, Kyu Eun Lee
World Journal of Surgery.2023; 47(8): 2086. CrossRef - 2023 Korean Thyroid Association Management Guidelines for Patients with Thyroid Nodules
Young Joo Park, Eun Kyung Lee, Young Shin Song, Soo Hwan Kang, Bon Seok Koo, Sun Wook Kim, Dong Gyu Na, Seung-Kuk Baek, So Won Oh, Min Kyoung Lee, Sang-Woo Lee, Young Ah Lee, Yong Sang Lee, Ji Ye Lee, Dong-Jun Lim, Leehi Joo, Yuh-Seog Jung, Chan Kwon Jung
International Journal of Thyroidology.2023; 16(1): 1. CrossRef - Optimization of the design parameters for a thyroid care nuclide monitoring diverging collimator using Monte Carlo simulation
Dong-Hee Han, Seung-Jae Lee, Jang-Oh Kim, Da-Eun Kwon, Kyung-Hwan Jung, Cheol-Ha Baek
Journal of the Korean Physical Society.2022; 81(7): 675. CrossRef - Active Surveillance for Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma in a Population with Restrictive Diagnostic Workup Strategies
Ivona Lončar, Sam P.J. van Dijk, Madelon J.H. Metman, Jia Feng Lin, Schelto Kruijff, Robin P. Peeters, Anton F. Engelsman, Tessa M. van Ginhoven
Thyroid.2021; 31(8): 1219. CrossRef - Decreasing trends in thyroid cancer incidence in South Korea: What happened in South Korea?
Chang‐Mo Oh, Jiwon Lim, Yuh Seog Jung, Yeol Kim, Kyu‐Won Jung, Seri Hong, Young‐Joo Won
Cancer Medicine.2021; 10(12): 4087. CrossRef - Efficacy of Differential Diagnosis of Thyroid Nodules by Shear Wave Elastography—the Stiffness Map
Myung Hi Yoo, Hye Jeong Kim, In Ho Choi, Suyeon Park, Sumi Yun, Hyeong Kyu Park, Dong Won Byun, Kyoil Suh
Journal of the Endocrine Society.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Spatial distribution and determinants of thyroid cancer incidence from 1999 to 2013 in Korea
Jieun Jang, Dae-Sung Yoo, Byung Chul Chun
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Income differences in screening, incidence, postoperative complications, and mortality of thyroid cancer in South Korea: a national population-based time trend study
Hee-Yeon Kang, Ikhan Kim, Yeon-Yong Kim, Jinwook Bahk, Young-Ho Khang
BMC Cancer.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Differential Diagnosis of Thyroid Follicular Neoplasm from Nodular Hyperplasia by Shear Wave Elastography
Myung Hi Yoo, Hye Jeong Kim, In Ho Choi, Ji-Oh Mok, Hyeong Kyu Park, Dong Won Byun, Kyoil Suh
Soonchunhyang Medical Science.2019; 25(1): 10. CrossRef - Diagnostic Performance of Shear Wave Elastography as Add-on Test in Thyroid Nodules: a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Sun-young Park, Ji Yang Song, Min Jin Lee, Kyung Min Lee, Mi Hye Jeon, Ryeo Jin Ko, Seok-Hyun Kim, Bong Joo Kang
International Journal of Thyroidology.2018; 11(1): 31. CrossRef - Structural Equation Modeling on Health-related Quality of Life among Patients with Thyroid Cancer
Seon Young Lee, Hyun Kyung Kim
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2018; 30(2): 171. CrossRef - Prevalence and Annual Incidence of Thyroid Disease in Korea from 2006 to 2015: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study
Hyemi Kwon, Jin-hyung Jung, Kyung-Do Han, Yong-Gyu Park, Jung-Hwan Cho, Da Young Lee, Ji Min Han, Se Eun Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2018; 33(2): 260. CrossRef - Ten Years of the Korean Thyroid Association: Achievement and Future
Young Joo Park, Young Shin Song, Ka Hee Yi
International Journal of Thyroidology.2018; 11(1): 1. CrossRef - Prediction of Contralateral Occult Malignant Nodule in Patients with Unilaterally Confined Papillary Thyroid Carcinomas
Sang Wook Jo, Ha Kyoung Park, Tae Kwun Ha
Journal of Endocrine Surgery.2018; 18(3): 191. CrossRef - Surgical Treatment Guidelines for Patients with Differentiated Thyroid Cancer: The Korean Association of Thyroid and Endocrine Surgeons (KATES) Guidelines Taskforce
Jin-Woo Park, Ki-Wook Chung, Ji-Sup Yun, Hyungju Kwon, Hoon Yub Kim, Kee Hyun Nam, Kyoung Sik Park, Min Ho Park, Ja Sung Bae, Hyun Jo Youn, Kyu Eun Lee, Chi Young Lim, Jin Hyang Jung, Jun-Ho Choe, Lee Su Kim, Su Jung Lee, Jung Han Yoon
Korean Journal of Endocrine Surgery.2017; 17(1): 1. CrossRef - Thyroid fine-needle aspiration biopsy positively correlates with increased diagnosis of thyroid cancer in South Korean patients
Yoon Jae Cho, Do Young Kim, Eun-Cheol Park, Kyu-Tae Han
BMC Cancer.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Current trends of practical issues concerning micropapillary thyroid carcinoma
Yoon Se Lee, Byung-Joo Lee, Hyun Joon Hong, Kang-Dae Lee
Medicine.2017; 96(45): e8596. CrossRef - The Use of the Bethesda System for Reporting Thyroid Cytopathology in Korea: A Nationwide Multicenter Survey by the Korean Society of Endocrine Pathologists
Mimi Kim, Hyo Jin Park, Hye Sook Min, Hyeong Ju Kwon, Chan Kwon Jung, Seoung Wan Chae, Hyun Ju Yoo, Yoo Duk Choi, Mi Ja Lee, Jeong Ja Kwak, Dong Eun Song, Dong Hoon Kim, Hye Kyung Lee, Ji Yeon Kim, Sook Hee Hong, Jang Sihn Sohn, Hyun Seung Lee, So Yeon Pa
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2017; 51(4): 410. CrossRef - Does the Risk of Metabolic Syndrome Increase in Thyroid Cancer Survivors?
Min-Hee Kim, Jin-young Huh, Dong-jun Lim, Moo-Il Kang
Thyroid.2017; 27(7): 936. CrossRef - Surgical Treatment Guidelines for Patients with Differentiated Thyroid Cancer: The Korean Association of Thyroid and Endocrine Surgeons (KATES) Guidelines Taskforce
Jin-Woo Park, Ki-Wook Chung, Ji-Sup Yun, Hyungju Kwon, Hoon Yub Kim, Kee Hyun Nam, Kyoung Sik Park, Min Ho Park, Ja Sung Bae, Hyun Jo Youn, Kyu Eun Lee, Chi Young Lim, Jin Hyang Jung, Jun-Ho Choe, Lee Su Kim, Su Jung Lee, Jung Han Yoon
Korean Journal of Endocrine Surgery.2017; 17(1): 1. CrossRef - Incidental Detection of Struma Ovarii on the Whole Body Scan in a Differentiated Thyroid Cancer Patient
Hye-Seon Oh, Eyun Song, Dong Eun Song, Won Bae Kim
International Journal of Thyroidology.2016; 9(2): 180. CrossRef - The Experience of Receiving Radioactive Iodine Therapy among Thyroid Cancer Patients
Kyung Ok Kang, Hyun Kyung Kim, Ji Young Kim, Seok Tae Lim
Journal of East-West Nursing Research.2016; 22(2): 148. CrossRef - Comparison of two- and three-dimensional sonography for the prediction of the extrathyroidal extension of papillary thyroid carcinomas
Yang Seon Yi, Sang Soo Kim, Won Jin Kim, Min Jung Bae, Ji Hyun Kang, Bo Gwang Choi, Yun Kyung Jeon, Bo Hyun Kim, Byung Joo Lee, Soo Geun Wang, In Joo Kim, Yong Ki Kim
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2016; 31(2): 313. CrossRef - Changing trends in the management of well-differentiated thyroid carcinoma in Korea
Yong Sang Lee, Hang-Seok Chang, Cheong Soo Park
Endocrine Journal.2016; 63(6): 515. CrossRef - Low Dose versus High Dose Radioiodine Therapy
Kyoung Sook Won
Journal of Korean Thyroid Association.2015; 8(1): 14. CrossRef - History of Korean Thyroid Association and Recent Debates on Diagnosis and Treatment of Thyroid Cancer in Korea
Kwang Woo Lee
Journal of Korean Thyroid Association.2015; 8(1): 36. CrossRef - Lowered cutoff of lymph node fine-needle aspiration thyroglobulin in thyroid cancer patients with serum anti-thyroglobulin antibody
Kwanhoon Jo, Min-Hee Kim, Yejee Lim, So-Lyung Jung, Ja-Seong Bae, Chan-Kwon Jung, Moo-Il Kang, Bong-Yun Cha, Dong-Jun Lim
European Journal of Endocrinology.2015; 173(4): 489. CrossRef - Time Trends Analysis of Characteristics of Patients with Thyroid Cancer in a Single Medical Center
Hyung Seo Jung, Min Ji Jeon, Dong Eun Song, Suck Joon Hong, Won Gu Kim, Tae Yong Kim, Young Kee Shong, Won Bae Kim
Journal of Korean Thyroid Association.2014; 7(2): 159. CrossRef - Unfounded Reports on Thyroid Cancer
Jae Hoon Chung
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2014; 29(8): 1033. CrossRef - Regional Lymph Node Metastasis in Papillary Thyroid Cancer
Jae Hyun Park, Kang San Lee, Keum-Seok Bae, Seong Joon Kang
Journal of Korean Thyroid Association.2014; 7(2): 129. CrossRef - Methods and Clinical Efficacy of Dosimetry-Based Treatment in Radioiodine Therapy of Thyroid Cancer
Jin Chul Paeng, June-Key Chung
Journal of Korean Thyroid Association.2013; 6(1): 43. CrossRef - Two Cases of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Masquerading as Metastatic Papillary Thyroid Cancer
Ju Hee Lee, Se-Hoon Lee, Hye Sook Min, Ji-hoon Kim, Do Joon Park, Young Joo Park
Journal of Korean Thyroid Association.2012; 5(2): 157. CrossRef - Diagnostic Dilemma of a Follicular Lesions/Neoplasm in Thyroid Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology
Chan Kwon Jung
Journal of Korean Thyroid Association.2012; 5(2): 104. CrossRef - Updated guidelines for the diagnosis and management of thyroid nodules
Ka Hee Yi
Journal of the Korean Medical Association.2011; 54(6): 629. CrossRef
- Factors Influencing Peripheral Conversion of Thyroxine to Tri-Iodothyronine in Athyreotic Individuals during Levothyroxine Replacement.
-
Eui Young Kim, Won Gu Kim, Tae Yong Kim, Jong Ho Yoon, Suck Joon Hong, Young Kee Shong, Won Bae Kim
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2010;25(2):119-124. Published online June 1, 2010
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2010.25.2.119
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- BACKGROUND
Tri-iodothyronine (T3) is the main active hormone, and 20% of this is derived from the thyroid gland and 80% is from the peripheral tissue according to 5'-monodeiodination of thyroxine (T4). In the previous studies, normal T3 levels were achieved with traditional levothyroxine (LT4) therapy alone in athyreotic patients, but there has been no data about the factors influencing peripheral conversion of LT4. The aim of this study was to determine the factor(s) influencing peripheral conversion of LT4 to T3 in athyreotic patients during LT4 replacement. METHODS: The patients who underwent total-thyroidectomy for any cause, and mostly for thyroid cancers, at Asan Medical Center between 2000 and 2008 were enrolled. The free T4, T3 and thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) levels and age, gender, weight, height, body mass index (BMI) and the T4 dose were measured. Only patients with normal ranges of free T4 and TSH were included in the analysis. RESULTS: A total of 143 patients were enrolled. The mean T3, free T4 and TSH levels were 143.7 ng/dL, 1.4 ng/dL and 1.6 microU/mL, respectively. The mean weight and BMI were 62.9 kg and 24.6 kg/m2, respectively. We divided them into two groups according to the serum T3 level and we compared the characteristics of the groups. There were no differences in age, the gender distribution, the T4 dose/weight and the BMI between the low T3 group (T3 < or = 122 ng/dL, n = 14) and the normal T3 group (T3 > 122 ng/dL, n = 129). In the low T3 group, the mean body weight was significantly lower than that of the normal T3 group (59.0 +/- 6.0 vs. 63.4 +/- 9.9, respectively, P = 0.025). CONCLUSION: Lean body mass seems to be an important factor for determining the peripheral conversion of T4 to T3 in human. This suggest that a combination of T3/T4 is better than T4 only when we treat the patients with hypothyroidism and who have a negligible amount of functioning thyroid tissue, if they have a low lean body mass.
- Effects of alpha-lipoic Acid on Differentiation of Thyroid Cancer Cells.
-
Won Gu Kim, Doo Hee Han, Hyun Jeung Choi, Eui Young Kim, Tae Yong Kim, Young Kee Shong, Won Bae Kim
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 2010;25(1):28-36. Published online March 1, 2010
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2010.25.1.28
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- BACKGROUND
Induction of re-differentiation is necessary for the proper treatment of patients with recurrent or metastatic differentiated thyroid cancer (DTC) because cancer cells show de-differentiation in about 30% of these patients. In this study, we evaluated the expression of thyroid specific genes after treatment with various agents to induce re-differentiation in the follicular thyroid cancer cell line FTC-133. METHODS: FTC-133 cells were treated with U0126, LY294002, trichostatin A, retinoic acid (RA), 5'-azacytidine and alpha-lipoic acid (ALA). We evaluated mRNA expression of thyroid specific genes, thyroglobulin (Tg), sodium iodine symporter (NIS), PAX-8 and TTF-1 by reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Quantified expression of Tg mRNA was also evaluated by real-time PCR. RESULTS: The expression of Tg mRNA increased after 48 h of treatment with 0.1 uM RA and the expression of Tg mRNA and TTF-1 mRNA increased after 48-72 h of treatment with ALA (10~100 uM). There was no change in thyroid specific gene expression by the other agents. Increased expression of Tg mRNA was confirmed by real-time PCR (1.3 times by 10 uM ALA and 3.6 times by 100 uM ALA). There was no basal NIS mRNA expression in FTC-133 cells and none of the tested agents induced expression of NIS mRNA. There was no change in phosphorylation of AMPK1-alpha after ALA treatment of FTC-133 cells. CONCLUSION: ALA increases mRNA expression of Tg and TTF-1 of FTC-133 thyroid cancer cells and these effects are not mediated by activation of AMP kinase. The finding that ALA could be a potential re-differentiation inducing agent in thyroid cancer cells is novel. Further studies are needed to elucidate the mechanism of induction of re-differentiation. Furthermore, the effect of ALA on NIS expression and on iodine uptake should be evaluated using diverse thyroid cancer cell lines.
- Effects of Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor (PPAR) Delta on the Growth and Invasion of a Thyroid Cancer Cell Line.
-
Won Gu Kim, Hyun Jeung Choi, Eui Young Kim, Tae Yong Kim, Won Bae Kim, Seong Chul Kim, Young Kee Shong
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 2009;24(1):25-32. Published online March 1, 2009
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2009.24.1.25
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- BACKGROUND
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor delta (PPAR-delta) is a ligand-activated nuclear transcription factor that is associated with many diseases, such as diabetes, obesity, metabolic syndrome, and cancer. However, the function of PPAR-delta is controversial in carcinogenesis since its ligands may inhibit or promote the growth of cancer cells. The purpose of this study was to determine the effect of GW501516, the specific agonist of PPAR-delta, in the growth and invasiveness of thyroid cancer cell lines by modulation of the target genes, ANGPTL-4 and MCP-1. METHODS: Three kinds of human cancer cell lines, FRO (thyroid anaplastic carcinoma), NPA (melanoma), and ARO (colon cancer) were treated with GW501516 in serum-free media. Cell viability was assayed using a colorimetric cell counting kit-8 assay. The changes in the level of expression of PPAR-delta and its target genes, angiopoietin-like protein-4 (ANGPTL-4) and monocyte chemotactic protein-1 (MCP-1), were determined by RT-PCR analysis and invasiveness was assessed by a cell invasion assay kit. RESULTS: GW501516 inhibited the cell growth of cancer cell lines in a dose-dependent manner and modulated the stimulation of ANGPTL-4, as well as inhibition of MCP-1. These effects were more prominent in NPA and ARO, but less effective in the thyroid cancer cell line, which had higher PPAR-delta and lower ANGPTL-4 mRNA levels. The inhibitory effects of GW501516 on cancer invasiveness had a similar pattern. CONCLUSION: The activation of PPAR-delta by GW501516 reduced the cell growth and invasiveness of the thyroid cancer cell line. This effect of GW501516 was associated with a stimulatory effect of ANGPTL4 and an inhibitory effect of MCP-1 in cancer cell lines. GW501516 was less effective in the thyroid cancer cell line, which had a low basal ANGPTL-4 mRNA level. The findings of our study serve as an impetus for further studies to elucidate the precise role of ANGPTL-4 and PPAR-delta in carcinogenesis.
- A Case of Painful Graves' Disease.
-
Ji Yun Jeong, Tae Yong Kim, Eun Hee Kim, Eui Young Kim, Sang Ah Lee, Ji Hye Yim, Kyung Min Kim, Won Bae Kim, Young Kee Shong
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 2008;23(5):337-341. Published online October 1, 2008
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2008.23.5.337
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Graves' disease rarely presents as pain and tenderness of goiter, with only a few cases reported in the literature. We describe a case of painful Graves' disease presenting as 2 episodes of painful goiter.
- A Case of Carcinoma Showing Thymus-Like Differentiation (CASTLE) in the Thyroid.
-
Eun Hee Kim, Ji Yun Jeong, Eui Young Kim, Sang Ah Lee, Kyung Min Kim, Ji Hye Yim, Won Gu Kim, Tae Yong Kim, Sun A Kim, Gyungyup Gong, Young Kee Shong, Won Bae Kim
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 2008;23(4):272-276. Published online August 1, 2008
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2008.23.4.272
-
-
1,700
View
-
24
Download
-
2
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Carcinoma Showing Thymus-Like Differentiation (CASTLE) is a very rare malignant neoplasm of the thyroid, and this resembles lymphoepithelioma or squamous cell carcinoma of the thymus. It originates from ectopic thymic tissue or remnants of the branchial pouches. We recently experienced a case of CASTLE in the thyroid gland of a 61-year-old woman. She presented with an asymptomatic mass in the right thyroid gland and she was diagnosed with 'poorly differentiated carcinoma' of the thyroid by fine needle aspiration cytology (FNAC). Total thyroidectomy was performed for both diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. Histologic examination of the resected tumor showed that the tumor was lobulated with expanding fibrous bands, and it was infiltrated by lymphocytes and plasma cells. The tumor cells had oval, large vesicular nuclei and prominent nucleoli, and the immunohistochemical staining was positive for CD5 and bcl-2, so the patient was diagnosed with thyroid CASTLE. We report here on a case of CASTLE in the thyroid gland treated by surgery and external neck radiation therapy.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Intrathyroidal thymic carcinoma exhibiting neuroendocrine differentiation: Case report with cytomorphology, immunocytochemistry, and review of the literature focusing on cytology
Wen‐hao Ren, Kun Dong, Xiao‐zheng Huang, Yan‐li Zhu
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2019; 47(11): 1197. CrossRef - Cytologic Findings of Thyroid Carcinoma Showing Thymus-like Differentiation: A Case Report
Sunhee Chang, Mee Joo, Hanseong Kim
Korean Journal of Pathology.2012; 46(3): 302. CrossRef
- Effects of Simvastatin on the Growth and Invasion of Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer Cells Lines.
-
Hyun Jeung Choi, Tae Yong Kim, Eui Young Kim, Won Gu Kim, Won Bae Kim, Young Kee Shong
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 2008;23(4):238-244. Published online August 1, 2008
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2008.23.4.238
-
-
1,893
View
-
21
Download
-
1
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- BACKGROUND
Anaplastic thyroid carcinoma has grave prognosis with most patient dying within 6 months of diagnosis. 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase inhibitors have been reported to have an anticancer effect in experimental and clinical studies. In this study, we investigated the effect of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors on cell growth, invasiveness, adherence and signal transduction to evaluate the possibility of simvastatin as an agent for treatment of thyroid cancer. METHODS: The viability of simvastatin treated 3 thyroid cancer cell lines (FRO, WRO, and ARO) were determined. We evaluated the cell migration, anchorage-independent growth and invasion ability in anaplastic thyroid cell line. The expression and phosphorylation of focal adhesion kinase (FAK) and extracellular signal-regurated kinase (ERK) were determined by immunoblot analysis. RESULTS: Three thyroid cancer cell lines showed concentration dependent decrease of viability after treatment with 100~200 mM of simvastatin. Anaplastic ARO cell line showed the most predominant decrease in viability. In ARO cell lines, cell migration was decreased by concentration dependent manner after treatment with simvastatin (concentration > or = 5 mM). Anchorage independent colony formation also decreased after simvastatin (> or = 10 mM). Finally, immunoblot analysis revealed that the phosphorylation status of FAK and ERK decreased in time dependent manner following treatment with 10 mM of simvastatin. CONCLUSION: The results of this study suggest that simvstatin exerts a favorable effect on the progression and metastasis of thyroid cancer. However, further studies are needed to elucidate the related mechanisms and signal transductions prior to its therapeutic application.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - The Effect of Atorvastatin and Simvastatin on NIS Expression of the TPC-1 Cell under the Therapeutic Blood Concentrations
Tae Kyoon Kim, Hye Sook Jung, Chang Shin Yoon, Jung Hae Ko, Hae Jung Jun, Min Jung Kwon, Sun Hee Lee, Mi Kyung Kim, Jeong Hyun Park
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2010; 25(3): 192. CrossRef
- A Case of Diffuse Hemorrhage into the Thyroid Gland after Fine Needle Aspiration, and This was Treated by Arterial Embolization.
-
Eui Young Kim, Jung Min Kim, Eun Hee Kim, Ji Yun Jeong, Sang Ah Lee, Ji Young Choi, Ji Hye Yim, Pil Hyung Lee, Tae Yong Kim, Young Kee Shong, Won Bae Kim
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 2008;23(3):199-203. Published online June 1, 2008
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2008.23.3.199
-
-
1,999
View
-
27
Download
-
2
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Although hematoma formation after fine needle aspiration cytology fine needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) is a most common complication and most of these hematomas are self-limiting with minimal pain, a massive intra-thyroidal hemorrhage that produces acute airway obstruction had rarely been reported on.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Characteristics Evaluation of Hobun Pigments according to Shell Types and Calcination
Ju Hyun Park, Sun Myung Lee, Myoung Nam Kim, Jin Young Hong
Economic and Environmental Geology.2023; 56(6): 899. CrossRef - Endovascular treatment of massive hemorrhage arising from inferior thyroid artery after fine needle aspiration of thyroid: a case report
Ho Sig Jang, Yook Kim
BMC Surgery.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- Association between Cigarette Smoking and Thyroid Function in Adults without Previous History of Thyroid Disease.
-
Bo Hyun Kim, Won Bae Kim, Tae Yong Kim, Hong Kyu Kim, Seong Hoon Jeon, Chang Won Lee, Young Kee Shong
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 2008;23(2):123-128. Published online April 1, 2008
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2008.23.2.123
-
-
2,179
View
-
31
Download
-
3
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- BACKGROUND
Cigarette smoking has a significant impact on thyroid function. However, the association between smoking and thyroid function is incompletely understood. METHODS: We conducted a cross-sectional study that included 90,970 adults (age range: 20 to 79) who had visited the health promotion center at Asan Medical Center between January 1, 2001, and December 31, 2003. Those subjects with previous known thyroid disease, a history of thyroid operation, a history of thyroid function altering medication (herb, estrogen or digestive) or a family history of thyroid disease were excluded. Finally, 47,577 subjects (males: 30,726, females: 16,851) were included in this study. We calculated the age-adjusted geometric mean of the serum TSH and the age-adjusted mean of the serum free T4 among the current, former and never smokers. We also analyzed the age-adjusted prevalence of hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism among each group. RESULTS: Among men, the geometric mean TSH level was significantly low in the current (1.40 mIU/L, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.38-1.41) and former smokers (1.59 mIU/L, 95% CI: 1.57-1.61) compared with the never smokers (1.65 mIU/L, 95% CI: 1.63-1.68). The mean free T4 level was high in the current smokers (1.236 ng/dL, 95% CI: 1.234-1.239) compared with the never smokers (1.234 ng/dL, 95% CI: 1.230-1.238). Similarly, among women, the geometric mean TSH level was low in the current smokers (1.75 mIU/L, 95% CI: 1.67-1.87) compared with the never smokers (1.85 mIU/L, 95% CI: 1.83-1.87). The mean free T4 level was high in the current smokers (1.149 ng/dL, 95% CI: 1.139-1.159) compared with the never smokers (1.138 ng/dL, 95% CI: 1.135-1.140). Among the current male smokers, heavy daily smoking (over 2 packs per day) was more associated with low TSH levels than moderate smoking (less than 1 pack per day). In men, the prevalence of subclinical hypothyroidism was low in the current smokers compared with the never smokers (odds ratio: 0.53, 95% CI: 0.43-0.66). CONCLUSION: We found that current smokers had lower TSH levels and higher free T4 levels than never smokers in both men and women and smoking was associated with a low prevalence of subclinical hypothyroidism in men, which may be of importance when evaluating subjects with subclinical hypothyroidism in Korea.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Reference interval for thyrotropin in a ultrasonography screened Korean population
Mijin Kim, Tae Yong Kim, Soo Han Kim, Yunkyoung Lee, Su-yeon Park, Hyung-don Kim, Hyemi Kwon, Yun Mi Choi, Eun Kyung Jang, Min Ji Jeon, Won Gu Kim, Young Kee Shong, Won Bae Kim
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2015; 30(3): 335. CrossRef - Clinical Review of Thyroid Dysfunction in the Subjects for Health Check-up
Ji Eun Park, Ho Chan Cho
Journal of Korean Thyroid Association.2012; 5(1): 52. CrossRef - Thyroid Dysfunction of North Korean Women Living in South Korea, Focusing on Subclinical Hypothyroidism
Joo Hyung Kim, Sol Ah Park, Nam Hoon Kim, Jae Hee Ahn, Yoon Jung Kim, Myongjin Cho, Yoon Jung Lee, Hye Jin Yoo, Hee Young Kim, Ji A Seo, Nan Hee Kim, Kyung Mook Choi, Sei Hyun Baik, Dong Seop Choi, Sin Gon Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2012; 27(3): 200. CrossRef
- CAG Repeats in the Androgen Receptor Polymorphism do not Correlate with Thyrotoxic Periodic Paralysis.
-
Won Gu Kim, Tae Yong Kim, Jung Min Kim, Yoon Soo Rhee, Hyun Jeung Choi, Won Bae Kim, Young Kee Shong
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 2008;23(2):117-122. Published online April 1, 2008
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2008.23.2.117
-
-
1,771
View
-
21
Download
-
3
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- BACKGROUND
Thyrotoxic periodic paralysis (TPP) occurs mostly in males, but no studies have addressed the role of androgen in the disease. Hyperinsulinemia can precipitate acute paralysis in TPP patients. CAG repeats in the androgen receptor (AR), an X-linked gene, correlate with serum insulin levels. AIM: To evaluate whether CAG repeats in the AR gene might predict the susceptibility to TPP in Korean male Graves' patients. METHODS: We evaluated CAG repeat length in a series of 33 male TPP patients and 48 control patients by direct sequencing of the PCR product of the AR promoter site. Control patients were male Graves' patients without a history of paralysis. RESULTS: The CAG repeat length varied from 15 to 34 (median of 23). The upper quartile of CAG length was equal to or above 26 repeats (long AR). The distribution of long AR was 0.30 in TPP and 0.15 in control patients, respectively (odds ratio, 2.51; 95% confidence interval, 0.92~6.85; P = 0.09). CONCLUSION: AR gene polymorphisms may not confer genetic susceptibility to TPP in Korean male patients with Graves' disease.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Contributions of CAG repeat length in the androgen receptor gene and androgen profiles to premature pubarche in Korean girls
Min Jae Kang, Jeong Seon Lee, Hwa Young Kim, Hae Woon Jung, Young Ah Lee, Sun Hee Lee, Ji-Young Seo, Jae Hyun Kim, Hye Rim Chung, Se Young Kim, Choong Ho Shin, Sei Won Yang
Endocrine Journal.2017; 64(1): 91. CrossRef - Thyrotoxic Periodic Paralysis and Polymorphisms of the ADRB2, AR, and GABRA3 Genes in Men with Graves Disease
Suyeon Park, Tae Yong Kim, Soyoung Sim, Seonhee Lim, Mijin Kim, Hyemi Kwon, Min Ji Jeon, Won Gu Kim, Young Kee Shong, Won Bae Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2016; 31(1): 142. CrossRef - Androgen Receptor Gene CAG Repeat Polymorphism and Effect of Testosterone Therapy in Hypogonadal Men in Korea
Min Joo Kim, Jin Taek Kim, Sun Wook Cho, Sang Wan Kim, Chan Soo Shin, Kyong Soo Park, Seong Yeon Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2011; 26(3): 225. CrossRef
- Trends Analysis of Characteristics of Thyroid Cancer Patients in One Medical Center.
-
Seung Hun Lee, Tae Yong Kim, Jin Sook Ryu, Gyungyub Gong, Won Bae Kim, Seong Chul Kim, Suck Joon Hong, Young Kee Shong
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 2008;23(1):35-43. Published online February 1, 2008
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2008.23.1.35
-
-
2,222
View
-
25
Download
-
15
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- BACKGROUND
The incidence of thyroid cancer is rapidly increasing. The aim of this study is to examine time trends in the characteristics of thyroid cancer and to determine the cause of the increase of thyroid cancer. METHODS: We evaluated 4,646 patients that underwent surgery at the Asan Medical Center for thyroid cancer between 1995 and 2006. Patients were evaluated concerning the histology, size of the primary tumor, sex, and age at the time of surgery. RESULTS: Surgically treated case of thyroid cancer increased from 91 in 1995 to 960 in 2006-a 10.5-fold increase during the 12-year period. Based on the histological categories, the proportion of papillary thyroid carcinomas (PTCs) increased from 79.1% to 94.5% during the 12-year period. According to the primary tumor size in the PTCs, the proportion of PTCs measuring 1 cm or smaller increased from 14% to 56% during the 12-year period. Whereas the proportion of PTCs measuring from 1 cm to 2 cm were similar (between 31% and 41% during the 12-year period), the proportion of PTC measuring from 2 cm to 4 cm decreased from 51% to 11% during the 12-year period. Thyroid cancer affected women more often than men by a ratio of 3.7. PTC was most common in patients in their forties, especially among women. CONCLUSIONS: The increasing number of surgically treated cases of thyroid cancer is predominantly due to an increase of papillary thyroid cancer measuring 1 cm or less. These trends suggest that the increase in surgically treated cases of thyroid cancer reflects increased detection of occult thyroid cancer due to advances in medical surveillance of impalpable nodules rather than a true increase in the number of thyroid cancers.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - A Case Report on Papillary Thyroid Cancer Patients after Thyroidectomy Treated with Korean Medicine and Immunotherapy
Eun-Bi Ko, Kwon-Jun Jang, Jung-min Yang, Jae-sung Oh
The Journal of Internal Korean Medicine.2021; 42(5): 746. CrossRef - Public perceptions of changing the terminology for low-risk thyroid cancer: a qualitative focus group study
Brooke Nickel, Caitlin Semsarian, Ray Moynihan, Alexandra Barratt, Susan Jordan, Donald McLeod, Juan P Brito, Kirsten McCaffery
BMJ Open.2019; 9(2): e025820. CrossRef - Study Protocol of Multicenter Prospective Cohort Study of Active Surveillance on Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma (MAeSTro)
Jae Hoon Moon, Ji-hoon Kim, Eun Kyung Lee, Kyu Eun Lee, Sung Hye Kong, Yeo Koon Kim, Woo-jin Jung, Chang Yoon Lee, Roh-Eul Yoo, Yul Hwangbo, Young Shin Song, Min Joo Kim, Sun Wook Cho, Su-jin Kim, Eun Jae Jung, June Young Choi, Chang Hwan Ryu, You Jin Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2018; 33(2): 278. CrossRef - Temporal Trends in the Presentation, Treatment, and Outcome of Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma: An Israeli Multicenter Study
Dania Hirsch, Orit Twito, Sigal Levy, Gideon Bachar, Eyal Robenshtok, David J. Gross, Haggi Mazeh, Carlos Benbassat, Simona Grozinsky-Glasberg
Thyroid.2018; 28(3): 369. CrossRef - Strong association of relatively low and extremely excessive iodine intakes with thyroid cancer in an iodine-replete area
Hye Jeong Kim, Na Kyung Kim, Hyeong Kyu Park, Dong Won Byun, Kyoil Suh, Myung Hi Yoo, Yong-Ki Min, Sun Wook Kim, Jae Hoon Chung
European Journal of Nutrition.2017; 56(3): 965. CrossRef - Clinical Analysis of Elderly Thyroid Cancer Patients Following Thyroidect
Keun Hee Lee, Hak Hoon Jun, Jong Woo Kim, Seung Ki Kim, Jin Hyung Heo
Korean Journal of Endocrine Surgery.2016; 16(4): 89. CrossRef - Use of CD56 and cyclin D1 in differentiating thyroid hyperplasia from papillary thyroid carcinoma
Maha E. Salama, Wael S. Ibrahim
Egyptian Journal of Pathology.2016; 36(1): 39. CrossRef - Clinical Analysis of Elderly Thyroid Cancer Patients Following Thyroidect
Keun Hee Lee, Hak Hoon Jun, Jong Woo Kim, Seung Ki Kim, Jin Hyung Heo
Korean Journal of Endocrine Surgery.2016; 16(4): 89. CrossRef - A Closer Look at Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
Won Bae Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2015; 30(1): 1. CrossRef - Korea's Thyroid-Cancer “Epidemic” — Screening and Overdiagnosis
Hyeong Sik Ahn, Hyun Jung Kim, H. Gilbert Welch
New England Journal of Medicine.2014; 371(19): 1765. CrossRef - Standardized Thyroid Cancer Mortality in Korea between 1985 and 2010
Yun Mi Choi, Tae Yong Kim, Eun Kyung Jang, Hyemi Kwon, Min Ji Jeon, Won Gu Kim, Young Kee Shong, Won Bae Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2014; 29(4): 530. CrossRef - The Association Between the Socioeconomic Status and Thyroid Cancer Prevalence; Based on the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2010-2011
Seong-Woo Choi, So-Yeon Ryu, Mi-ah Han, Jong Park
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2013; 28(12): 1734. CrossRef - Burden of cancer in Korea during 2000–2020
Jae-Hyun Park, Kwang-Sig Lee, Kyu-Sik Choi
Cancer Epidemiology.2013; 37(4): 353. CrossRef - Changes in the Clinicopathological Characteristics and Outcomes of Thyroid Cancer in Korea over the Past Four Decades
Bo Youn Cho, Hoon Sung Choi, Young Joo Park, Jung Ah Lim, Hwa Young Ahn, Eun Kyung Lee, Kyung Won Kim, Ka Hee Yi, June-Key Chung, Yeo-Kyu Youn, Nam Han Cho, Do Joon Park, Chang-Soon Koh
Thyroid.2013; 23(7): 797. CrossRef - Diagnostic value of decreased expression of CD56 protein in papillary carcinoma of the thyroid gland
Won Young Park, Seong Muk Jeong, Jung Hee Lee, Hyun Jeong Kang, Dong Hun Sin, Kyung Un Choi, Do Youn Park, Gi Yeong Huh, Mee Young Sol, Chang Hun Lee
Basic and Applied Pathology.2009; 2(2): 63. CrossRef
- Effects of Wnt-1 on the Growth and Apoptosis of FRTL-5 Cells.
-
Jung Min Kim, Tae Yong Kim, Young Kee Shong, Yoon Soo Rhee, Eun Jung Park, Hyun Chung Choi, Won Bae Kim
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 2007;22(1):35-44. Published online February 1, 2007
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2007.22.1.35
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- BACKGROUND
Wnt proteins are major signaling molecules involved in embryonic induction, generation of cell polarity and the cell fate decision. A central player in the Wnt signaling pathways is beta-catenin. Several studies have suggested that the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway may be involved in the physiologic/pathologic control of thyroid cell growth and function. METHODS: We investigated the effect of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) on the expression of Wnt proteins in FRTL-5 cells. To evaluate the effect of Wnt-1 on FRTL-5 cells growth, we isolated a stable cell line that overexpressed Wnt-1 (W1), and a vector-transfected cell clone (V3) was used as a control. We investigated the differences in the cellular growth rate, the cell cycle and cell apoptosis in the W1 and V3 cell lines. RESULTS: TSH caused a significant increase in the Wnt-1 level and a pronounced decrease in both the active and total beta-catenin levels in the FRTL-5 cells. The growth rate, the percentage of cells in the S/G2/M phase and the c-myc level were significantly higher in the W1 cells compared with the V3 cells. There was no change in the beta-catenin level and the cyclin D1 level in the W1 cells compared with the V3 cells. The cellular apoptosis induced by actinomycin-D seemed to be significantly decreased because the level of bcl-2 was increased in the W1 cells compared with the V3 cells. CONCLUSION: The FRTL-5 cells expressed Wnt-1 protein, and TSH increased the Wnt-1 expression, and it paradoxically decreased beta-catenin in the FRTL-5 cells. Overexpression of Wnt-1 in the FRTL-5 cells increased cell growth and it decreased apoptosis. Growth stimulation by Wnt-1 overexpression was not mediated by beta-catenin (the canonical Wnt pathway), but seemed to be mediated by activation of the Wnt/Ca2+ pathway, which involves an increased c-myc level. Suppression of apoptosis with Wnt-1 overexpression was due to the increased bcl-2 level.
- Retraction: Clinical Characteristics of Poorly Differentiated Carcinoma of the Thyroid and Comparison of Survival to Tall Cell and Columnar Cell Variants of the Papillary Carcinoma.
-
Tae Sik Jung, Jae Hoon Chung, Young Lyun Oh, Tae Yong Kim, Young Kee Shong, Won Bae Kim, Kyung Won Kim, Young Joo Park, Bo Youn Cho
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 2006;21(6):589. Published online December 1, 2006
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2006.21.6.589
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- No abstract available.
- Prevalence of Ultrasonographically-Detected Thyroid Nodules in Adults without Previous History of Thyroid Disease.
-
Ji Hye Suk, Tae Yong Kim, Mi Kyung Kim, Won Bae Kim, Hong Kyu Kim, Seong Hoon Jeon, Young Kee Shong
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 2006;21(5):389-393. Published online October 1, 2006
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2006.21.5.389
-
-
1,965
View
-
25
Download
-
11
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- BACKGROUND
The prevalence of palpable thyroid nodules in the general population is about 5%, and is 3~5 times higher in women than in men. However, much higher prevalence, up to 50%, was reported from autopsy data. Recently, the use of high resolution ultrasonography for routine check-up has resulted in much more detection of non-palpable thyroid nodules. We studied the prevalence of thyroid nodules in healthy adults without history of thyroid disease, and compared the prevalence in relation to palpability, age and gender. METHODS: The prevalence of thyroid nodules was studied in adults aged from 20 to 79 years who had visited the health promotion center at Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea, from Jan 2002 to Dec 2003. Subjects with previous thyroid disease were excluded. 7,440 subjects (6,168 female, 1,272 men) were included in this study. Thyroid palpation was performed and followed by ultrasonography using a 12-MHz real-time scanner. RESULTS: Thyroid nodules were detected in 3,040 of the 7,440 subjects (41%). Palpable nodules were present in 213 (3%), and non-palpable, but ultrasonographically detected thyroid nodules were present in 2,827 (38%). Thyroid nodules were present in 2,602 women (42.2%) and 370 men (29%). Among them, 159 women (2.6%) and 54 men (4.2%) had palpable thyroid nodules and 2,443 women (39.6%) and 316 men (24.8%) had non-palpable but ultrasonographically detected nodules. A significant linear trend was found between age and the prevalence of thyroid nodules. CONCLUSIONS: The prevalence of ultrasonographically detected thyroid nodules in adults with no previous history of thyroid disease was 41%. The prevalence of palpable nodules and non-palpable, but ultrasonographically detected nodules were 3% and 38%, respectively. Thyroid nodules were detected in 42.2% of women and 29% of men, showing that thyroid nodules are very common in healthy adults, even in men.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - The Prevalence of Thyroid Nodules and the Morphological Analysis of Malignant Nodules on Ultrasonography
An Hyun, Ji Tae-jeong, Lee Hyo-young, Im In-chul
Journal of Radiological Science and Technology.2019; 42(3): 201. CrossRef - Prevalence of thyroid nodules and their associated clinical parameters: a large-scale, multicenter-based health checkup study
Jae Hoon Moon, Min Kyung Hyun, Ja Youn Lee, Jung Im Shim, Tae Hyuk Kim, Hoon Sung Choi, Hwa Young Ahn, Kyung Won Kim, Do Joon Park, Young Joo Park, Ka Hee Yi
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2018; 33(4): 753. CrossRef - Prevalence and Annual Incidence of Thyroid Disease in Korea from 2006 to 2015: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study
Hyemi Kwon, Jin-hyung Jung, Kyung-Do Han, Yong-Gyu Park, Jung-Hwan Cho, Da Young Lee, Ji Min Han, Se Eun Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2018; 33(2): 260. CrossRef - An Iodine Database for Common Korean Foods and the Association between Iodine Intake and Thyroid Disease in Korean Adults
Mi-Rhan Han, Dal Lae Ju, Young Joo Park, Hee-Young Paik, YoonJu Song
International Journal of Thyroidology.2015; 8(2): 170. CrossRef - Management of Thyroid Nodules and Cancers Arising in the Elderly
Eunyoung Kim, June Young Choi, Kyu Eun Lee
Journal of Korean Thyroid Association.2012; 5(2): 99. CrossRef - Screening of Thyroid Cancer and Management of Thyroid Incidentaloma
Jung Jin Cho
Korean Journal of Family Medicine.2010; 31(2): 87. CrossRef - Postoperative Findings of the Cytological Diagnosis of Follicular Neoplasm or Hürthle Cell Neoplasm and the Risk of Malignancy
Ji Hye Yim, Eui Young Kim, Won Gu Kim, Tae Yong Kim, Gyungyup Gong, Suck Joon Hong, Won Bae Kim, Young Kee Shong
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2010; 25(4): 316. CrossRef - Prevalence of Thyroid Nodules Detected by Ultrasonography in Adults for Health Check-up and Analysis of Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology
Jae Hoon Chung
Journal of Korean Endocrine Society.2008; 23(6): 391. CrossRef - Prevalence of Thyroid Nodules Detected by Ultrasonography in Adults for Health Check-Ups and Analysis of Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology
Won Jun Kim, Joo Hyong Kim, Dong Won Park, Chang Beom Lee, Yong Soo Park, Dong Sum Kim, Woong Hwan Choi, Tae Wha Kim, You Hern Ahn
Journal of Korean Endocrine Society.2008; 23(6): 413. CrossRef - Trends Analysis of Characteristics of Thyroid Cancer Patients in One Medical Center
Seung Hun Lee, Tae Yong Kim, Jin-Sook Ryu, Gyungyub Gong, Won Bae Kim, Seong Chul Kim, Suck Joon Hong, Young Kee Shong
Journal of Korean Endocrine Society.2008; 23(1): 35. CrossRef - Prevalence of Thyroid Nodules Detected by Ultrasonography in Adult Men Attending Health Check-ups
Jung Hyun Kim, Sang Jun Park, Sang Eok Kim, Kwang Hee Lee, Il Kwon Cho, Sun Ik Jang, Jin Kwan Lee, Keum Soo Seo, Hyuck Po Kwon, Sung Chang Chung
Journal of Korean Endocrine Society.2007; 22(2): 112. CrossRef
- Clinical Characteristics of Poorly Differentiated Carcinoma of the Thyroid and Comparison of Its Survival to the Tall Cell and Columnar Cell Variants of Papillary Carcinoma.
-
Tae Sik Jung, Jae Hoon Chung, Young Lyun Oh, Tae Yong Kim, Young Kee Shong, Won Bae Kim, Kyung Won Kim, Young Joo Park, Bo Youn Cho
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 2006;21(2):132-141. Published online April 1, 2006
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2006.21.2.132
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- BACKGROUND
Poorly differentiated carcinoma (PDC) of the thyroid includes tall and columnar cell variants (TCV) of the papillary carcinoma as well as the thyroid carcinoma with trabecular, insular and solid (TIS) growth patterns. There have been a few clinical studies on the PDC of the thyroid. We evaluated the clinical characteristics and the outcome of the PDC. METHODS: We investigated the clinicopathologic features of the thyroid carcinoma with TIS growth patterns (n = 46) and TCV of the papillary carcinoma (n = 14). We investigated the clinical features of ten patients diagnosed as PDC of the thyroid who had been undergone thyroidectomy for well differentiated carcinoma previously and compared these outcome with those of patients primarily diagnosed as PDC of the thyroid (n = 60). RESULTS: The clinical course of the thyroid carcinoma with TIS growth patterns was slightly more aggressive than that of TCV of the papillary carcinoma. However, disease-specific survivals of both cancers were not significantly different. Disease-specific survival was independently correlated with the presence of distant metastasis at diagnosis and high dose radioiodine therapy. The clinical features and outcome of the patients with PDC detected at recurred sites after operation for well-differentiated carcinoma were more aggressive than those diagnosed as PDC of the thyroid. CONCLUSION: The prognosis of the thyroid carcinoma with TIS growth patterns and TCV of the papillary carcinoma were similar. The PDC which was detected after thyroidectomy for well-differentiated carcinoma had worse prognosis than primarily diagnosed as PDC of the thyroid.
- Role of 5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide-1-beta-D-ribofuranoside in the Growth Regulation of Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer Cells Lines.
-
Ja Young Song, Tae Yong Kim, Won Bae Kim, Young Kee Shong, Yoon Soo Rhee, Ji Hye Suck, Suck Joon Hong
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 2006;21(2):125-131. Published online April 1, 2006
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2008.21.2.125
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- BACKGROUND
Anaplastic thyroid carcinoma is one of the most aggressive human cancers with a median survival of only 6 months. Local surgical tumor debulking combined with radio-chemotherapy is generally used to treat this malady, but the low success rate has prompted the search for new therapeutic targets. We used 5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide-1-beta-D-ribofuranoside (AICAR) as an AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) activator to induce growth suppression and apoptosis in the anaplastic thyroid carcinoma cells. METHODS: We investigated the effect of AICAR on the proliferation of thyroid cancer cell lines (ARO, WRO and FRO) by performing methyl-thiazoletetrazolium bromide assay. We wanted to see the effect of AICAR on the apoptosis and cell cycle of the thyroid cancer cells, and we wanted to determine the mechanism of these changes. RESULTS: The proliferation of all thyroid cancer cell lines was significantly inhibited by administration of AICAR. FRO was the most susceptible cell line to AICAR treatment and so further studies were then performed with this cell line. The suppressive effect of AICAR on cell proliferation was related with phosphorylation of AMPK and the increased apoptosis. Also, cell cycle analysis revealed that progression to the G2-M phase was arrested (S-phase arrest) by AICAR treatment. S-phase arrest was associated with the increased protein expression of p21. CONCLUSION: In the anaplastic thyroid cancer cell lines, AICAR inhibited proliferation due to the arrest in the S-phase; this was accompanied with the increased expression of p21. Overall, AMPK activation by AICAR or any other pharmacological agent could be a tempting potential target for thyroid cancer therapy.
- Diagnosis of Impalpable Thyroid Nodule Detected by High-resolution Ultrasonography.
-
Tae Yong Kim, Won Bae Kim, Young Kee Shong
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 2005;20(3):200-203. Published online June 1, 2005
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2005.20.3.200
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- No abstract available.
- Thyroid Hormone and Cardiovascular Disease.
-
Young Kee Shong, Won Bae Kim, Tae Young Kim
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 2004;19(6):606-615. Published online December 1, 2004
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- No abstract available.
- Role of Pexoxisome Proliferator Activated Receptor Gamma in Growth Regulation of Thyroid Cancer Cells.
-
Tae Yong Kim, Ja Young Song, Young Kee Shong, Won Bae Kim
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 2004;19(5):511-521. Published online October 1, 2004
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- BACKGROUND
There is currently no effective option for the treatment of poorly differentiated thyroid carcinomas, so further studies are needed to evaluate new therapeutics. Thiazolinedione, an agonist of peroxisome proliferator activated receptor gamma (PPAR ), is known to suppress the growth of various tumor cell lines. This study was conducted to see if PPAR is involved in growth regulation of poorly differentiated thyroid cancer cells. SUBJECT AND METHODS: Thyroid cancer cell lines with a low degree differentiation, such as ARO and FRO cells were used, and their expression of PPAR mRNA checked. The effects of known agonists (rosiglitazone and 15-deoxy-delta12,14-prostglandin (15d-PGJ2)) and antagonists for PPAR (bisphenol A diglycidyl ether (BADGE)) on the growth of thyroid cancer cell lines expressing PPAR were evaluated by various methods, such as the methylthiazoletetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay, cell counts, and [3H]thymidine uptake. RESULTS: The expressions of PPAR were higher in ARO and FRO cells than in those of normal thyroid. Form the results of the MTT assay, the survival of ARO and FRO cells were found to decrease after administration of rosiglitazone or 15d-PGJ2. However, no change was observed after administration of BADGE. When the effect of rosiglitazone was evaluated by cell counting, there was significant decrease in number of ARO and FRO cells, but no change was observed after administration of 15d-PGJ2. Similar results were obtained using [3H]thymidine uptake. Thus, rosiglitazone treatment significantly decreased the [3H]thymidine uptake, whereas 15d-PGJ2 showed no significant effect. CONCLUSION: PPAR agonists (rosiglitazone and 15dPG-J2) suppressed the survival of ARO and FRO cells, undifferentiated thyroid cancer cell lines, with increased expressions of PPAR . However, the cell count and [3H] thymidine uptake were affected by rosiglitazone, but not by 15dPG-J2. This might suggest the antiproliferative effects of rosiglitazone are independent of PPAR ; and therefore, mediated by another unknown mechanism
- Effect of Estrogen on H2O2 Induced Apoptosis of FRTL-5 Cells.
-
Won Bae Kim, Tae Yong Kim, Ja Young Song, Young Kee Shong
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 2004;19(4):320-331. Published online August 1, 2004
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- BACKGROUND
Understanding the pathways and controlling mechanisms of thyrocyte apoptosis is important for the elucidation of the pathogenesis of goiter or thyroid cancer. A system for evaluating apoptosis, in FRTL-5 cells, triggered by hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), a highly likely apoptogenic signal in physiologic condition, was be set up to see the effects of TSH and estrogen on H2O2-induced apoptosis. METHOD: DNA laddering was used in the optimization process or the conditions of the set-up of system for the evaluation of apoptosis in the FRTL-5 cells. To quantify the apoptosis under the optimized conditions, histone-bound DNA fragments in the cytoplasm were measured by ELISA. RESULTS: 1) The optimized conditions for induction of apoptosis in the FRTL-5 cells by H2O2 were; observation of DNA laddering 18~24 hrs after the addition of 0.3 mM H2O2 to cells maintained in TSH-free, low serum containing media (5H1 or 5H0 media) for 48 hrs. 2) Exposure of the FRTL-5 cells to TSH (1 mU/L) for more than 48 hrs (6H0 media). before the addition of H2O2 significantly decreased the degree of apoptosis, compared to cells maintained under TSH-free conditions (0.98+/-0.21 vs. 2.27 0.11 arbitrary unit, p<0.05), whereas exposure for 24 hrs. did not. 3) Exposure of the FRTL-5 cells to high dose 17- estradiol (1-100 M) significantly decreased the degree of H2O2-induced apoptosis in a dose dependent manner. The addition of serum (1%) blunted the effects of estrogen on H2O2-induced apoptosis, and TSH totally abrogated the estrogen effect.Physiologic doses of estrogen (10~100 nM) showed no suppressive effects on H2O2-induced apoptosis in FRTL-5 cells. CONCLUSION: A system for evaluating apoptosis in FRTL-5 cells triggered by hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), a highly likely apoptogenic signal in physiologic condition, was set up, and found for the first time that high dose estrogen suppressed the H2O2-induced apoptosis in FRTL-5 cells
- Search for "Proximal Histidine" of Thyroperoxidase Using Site Directed Mutagenesis.
-
Won Bae Kim, Young Kee Shong
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 2003;18(4):371-378. Published online August 1, 2003
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- BACKGROUND
Thyroperoxidase (TPO), a transmembrane heme containing glycoprotein, catalyzes iodide organification and thyroid hormone synthesis. It is a single peptide making a loop with more than one disulfide bond. The tertiary conformational structure is essential for its enzymatic activity and immunogenicity. The proximal histidine is thought to play a major role in enzymatic activity since it is linked to the iron center of the heme. The crystal structure of TPO has not yet been reported, but some have suggested histidine 407 be a putative proximal histidine based on comparison of a.a. sequence for TPO and that for myeloperoxidase. METHODS: The putative histidine 407 and nearby histidine 414 were mutated to arginine to verify their role as the proximal histidine. Using site directed mutagenesis of wild type, human TPO cDNA, mutants H407R and H414R were made. Mutant cDNAs were transiently transfected into COS-7 cells, and the TPO enzyme activities were measured by guaiacol assay. Four cysteine residues around the putative proximal histidines were mutated to serine and their enzymatic activities were measured to check if they were involved in the formation of intra-molecular disulfide bonds. RESULTS: TPO protein expression of H407R- and H414R- transfected cells was confirmed by Western blot, using Hashimoto's IgG as primary antibody. Both the mutants H407R and H414R showed significant peroxidase enzymatic activity, although lower than those of the wild type. None of the cysteine mutants, C375S, C389S, C598S, and C655S, were detected by Hashimoto's IgG ordisplayed any enzymatic activity. CONCLUSION: These data suggest that neither histidine 407 nor histidine 414 functions as the "proximal histidine" in human TPO. All the cysteine residues checked (375, 389, 598, 655) might be involved in the formation of disulfide bonds in TPO molecules, but this hypothesis could not be confirmed. A further search for the other putative histidine residues using the same strategy is needed to define the structure-function relationship in the human TPO molecule.
- Effect of LiCl on Iodine Kinetics in Thyroid Cancer Cell Lines Transduced by Recombinant Adenovirus Containing Sodium Iodide Symporter(NIS) Gene.
-
Won Bae Kim, Ja Young Song, Sung Min Han, Jeong Seok Yeo, Heui ran Lee, Young Kee Shong, Dae Hyuk Moon
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 2003;18(2):166-176. Published online April 1, 2003
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- BACKGROUND
Lithium is known to increase the retention of iodide in the thyroid gland, or in well differentiated thyroid cancer tissue. The effects of lithium on the function of the sodium iodide symporter (NIS) protein, especially when the lithium is increased in the retention of iodide in NIS-producing cells, the effect of lithium, on the kinetics of undifferentiated thyroid cancer cells transduced by a recombinant adenovirus containing the NIS gene, were checked. METHOD: Human NIS cDNA was inserted into pAxCAwt, a recombinant adenoviral cosmid vector, where the E1 & E2 genes have been deleted, making Rad-hNIS, which was propagated in 293 cells. The iodide uptake was evaluated by the 125I uptake assay in the undifferentiated thyroid cancer cells, ARO, FRO and NPA, following the infection with Rad-hNIS (1 or 10 MOI) in the presence, or absence, of LiCl at optimized concentrations. The iodide efflux was evaluated by the 125I efflux assay, for 1 hour, in the same cells expressing the NIS in the presence, or absence, of LiCl. Similar experiments were performed in the normal thyroid cell line, FRTL-5, cultured in 6H5 media. RESULTS: LiCl, at concentrations over 1.0mM, caused a significant decrease in the cell viability, as evaluated by trypan blue dye exclusion, in a dose dependent manner. When infected with Rad-hNIS, the iodide uptake was not affected by the LiCl in the ARO or NPA cells. However, LiCl(0.1and 1.0mM) increased the iodide uptake by 50 to 100%(vs. control) in the Rad-hNIS transduced FRO cells. In the Rad-hNIS transduced FRO cells, the iodide was released rapidly from the cells, with only 20.7+/-4.8% of the iodide uptake remaining at 1 hour, which was no different in the presence of LiCl (24.5+/-7.9%). The iodide efflux was not affected by the LiCl in the FRTL-5 cells cultured in the presence of TSH. CONCLUSION: These results suggest that the lithium-induced iodide retention in the thyroid gland, or in well differentiated thyroid cancer tissue, is not caused by the effect of the lithium on the NIS function, or the function of proteins or channels, involved in iodide transport via cell membranes. Although the iodide uptake can be markedly increased by the expression of NIS, with the transduction of Rad-hNIS, in undifferentiated thyroid cancer cells, the iodide taken up is rapidly released from the cells. A method for inducing the iodide retention in the cell should be elucidated in order to render the NIS gene therapy effective.
- Serum Thyroglobulin Levels Predicting Recurrence and Distant Metastasis after Surgery in Patients with Differentiated Thyroid Cancer.
-
Kyoung Soo Kim, Jin Sook Ryu, Suck Joon Hong, Won Bae Kim, Young Kee Shong
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 2003;18(2):153-165. Published online April 1, 2003
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- BACKGROUND
Reports on serum thyroglobulin(Tg) levels being used to predict recurrence or distant metastasis during the follow-up of patients with differentiated thyroid cancer(DTC) has been inconsistent. In addition, there have been few reports that attempt to define the cut-off value of Tg for recurrence or distant metastasis obtained by a receiver operating characteristic(ROC) curve. As well, there are differences in opinions on what the value should be on the first serum Tg level measured just before radioactive iodine(RAI) ablation(Tg-RAI), during thyroxine administration (Tg-on), and after thyroxine withdrawal(Tg-off) during the follow-up. Reports on the positive predictive values(PPVs) and negative predictive values(NPVs) of these Tg values are rare. METHODS: A total of 205 patients(42 males, 163 females) with DTC were studied. All patients had undergone total or near-total thyroidectomy. After surgery and RAI ablation, annual thyroxine withdrawal 131I-whole body scan(WBS) with Tg measurements was performed. The mean duration of follow-up was 5.0 (1.4~7.4) years. The most sensitive and specific Tg values(cut-off values) for tumor recurrence and/or distant metastasis were selected by using ROC curves. We also calculated the PPVs and NPVs for recurrence and/or distant metastasis using two-by-two tables. RESULTS: Cut-off values of Tg-RAI, Tg-on, and Tg-off for recurrence were 11.8, 1.4, and 3.3ng/mL, respectively. For these values, the sensitivities were 85.4, 82.2, and 93.3%, with the specificitiesat 89.2, 92.4, and 88.0%. PPVs were 71.9, 77.1, and 77.0% while NPVs were 95.0, 94,4, and 97.8%. The cut-off values for distant metastasis were 27.4, 2.5, and 7.9ng/mL, respectively. For these cut-off values, the sensitivities were 86.7, 87.5, and 92.3%, with the specificities being 86.2, 90.8, and 80.2%. PPVs were 34.2, 46.7, and 25.0% and NPVs were 98.7, 98.8, and 99.3%. CONCLUSION: All three serum Tg levels were sensitive and specific markers for recurrence and distant metastasis. Their PPVs were low in contrast to the high NPVs. In comparison with Tg-on, Tg-off showed higher sensitivity and NPV as well as lower specificity and PPV. Therefore, in the case of higher Tg-on during the follow-up period, efforts to find recurrence and distant metastasis,such as 131I-WBS, should be done. In addition, regular measurement of Tg-off or Tg after stimulation with recombinant human TSH is recommended as a screening test.
- Completion Thyroidectomy in Patient with Differentiated Thyroid Cancer Who Initially Underwent Ipsilateral Operation.
-
Eun Sook Kim, Jung Min Koh, Won Bae Kim, Suck Joon Hong, Young Kee Shong
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 2002;17(5):657-663. Published online October 1, 2002
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- BACKGROUND
In some instances, thyroid cancer may be diagnosed only after resection of a putative or suspected benign nodule. In these cases a complete thyroidectomy is usually recommended to prevent recurrence. We analyzed the frequency of malignancy in the contralateral lobe after a complete thyroidectomy, and assessed the factors that may predict the presence of a malignancy, which might necessitate a complete thyroidectomy. METHODS: Between 1995 and 2001, 65 patients, who initially underwent a lobectomy and isthmectomy, but were finally diagnosed with differentiated thyroid carcinoma, underwent complete thyroidectomies. Their mean age was 39.8 +/- 12.4 years, ranging, 14 to 71 years. After initial surgery, 45 proved to have follicular carcinomas, 18 papillary carcinomas, 1 medullary and 1 insular carcinoma. The mean tumor size was 4.0 +/- 1.8 cm, ranging from 0.3 to 8.5 cm. After a complete thyroidectomy, the presence of a tumor the at contralateral lobe was assessed according to clinical parameters and the pathological findings in the ipsilateral lobe. RESULTS: The first surgeries revealed tumor multifocality in 27 cases, perithyroidal tumor extension in 4 and lymph node metastasis in 1. On completion of the thyroidectomy, 22 of the 65 patients had a malignancy in the contralateral lobe. Age, sex, size or the pathological primary tumor type, were not associated with the presence of additional tumors at the contralateral lobe. Tumor multifocality at the first surgery was the only significant variable to predict the presence of a tumor in the contralateral lobe. CONCLUSION: When thyroid cancer is diagnosed after ipsilateral surgery, the only predictive factor for the presence of a contralateral tumor was multifocality. We believe that a complete thyroidectomy is mandatory in these cases.
- Thyroid Nodule.
-
Won Bae Kim, Young Kee Shong
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 2002;17(4):445-459. Published online August 1, 2002
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- No abstract available.
- TSH Receptor Antibodies: Recent Update and Clinical Applications.
-
Won Bae Kim, Young Kee Shong
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 2002;17(1):10-19. Published online February 1, 2002
-
-
-
 PDF PDF
- Clinical Features of Well Differentiated Thyroid Carcinomas in Pregnant Women.
-
Seong Jin Lee, Suk Joon Hong, Pyi Ryang Lee, Young Kee Shong
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 2001;16(1):140-147. Published online February 1, 2001
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- BACKGROUND
In differentiated thyroid carcinomas (DTC), it has been reported that pregnancy may accelerate the course of the disease. But recent evidences suggested that the prognosis of DTC during pregnancy was similar to that of DTC in non-pregnant women of the same age. Also the optimal timing for the treatment is still controversial. We evaluated the clinical features of DTC in pregnant women. METHOD: We reviewed the histories of patients in whom the DTC was diagnosed before or during the pregnancy between 1994 and 1999. DTC were diagnosed by fine needle aspiration and the patients were treated by thyroid surgery. RESULTS: Six women who had a mean age of 30 years (27-34 years) were identified. The mean follow-up duration was 41 months (13-70 months). All patients had noticed a lump in their necks. In three patients, the nodules increased in size during pregnancy. A fine needle aspiration revealed a suspected malignancy in five patients and a postoperative biopsy confirmed the malignancy in one patient who had a preoperative cytologic diagnosis of nodular hyperplasia. All tumors were well differentiated and ranged in size from 1 to 6.5 cm. Radioactive iodine ablation and thyroid hormone suppression treatment were administered in five patients except in one case of papillary microcarcinoma. One patient had residual tumors in the right cervical lymph nodes and both lungs. She underwent repeated surgery and radioactive iodine therapy. CONCLUSION: This reports suggest that the DTC which is associated with pregnancy may have a similar prognosis to that of non-pregnant women and that the treatment of DTC in pregnant women may be safely delayed until after delivery in most patients. The treatment should not be delayed for more than a year.
- Clinical Significance of Measuring Thyrotropin Recepter Antibody.
-
Young Kee Shong, Bo Youn Cho
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 1999;14(4):609-619. Published online January 1, 2001
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- No abstract available.
- Thallium-291 Whole Body Scintigraphy in Postoperative Follow-up of Differentiated Thyroid Carcinoma.
-
Eun Sook Kim, Hong Kyu Kim, Sung Jin Lee, Jin Sook Ryu, Dae Hyuk Moon, Young Kee Shong
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 1999;14(1):63-70. Published online January 1, 2001
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- BACKGROUND
The advantages of thallium (Tl)-201 whole body scan in follow-up of patients with thyroid carcinoma include no need to discontinue thyroid hormone replacement, a shorter period of time between injection and imaging, a lower radiation dose, and preservation of affinity for subsequent therapeutic dose of 131I. To evaluate the reliability of whole body scintigraphy using Tl-201 in postoperative follow-up of thyroid carcinoma, this procedure was performed in patients after total thyroidectomy for thyroid carcinoma. The results were compared with those of 131I scintigraphy. METHODS: One hundred nineteen cases (119 patients) with a median age of 43 years (range, 20 85 years) were included in the study. After optimal endogenous thyroid-stimulating hormone stimulation (>50 mIU/mL), 131I (4 mCi) scan and Tl 201 (3 mCi) scan were simultaneously performed. Concomitantly serum thyroglobulin and anti-thyroglobulin antibody levels were checked. If abnormal findings on any of the scintigraphic methods or high levels of thyroglobulin (> 10 ng/mL) were detected, high dose (150~200mCi) 131I was administered as therapy and then whole body scans were performed repeatedly after the therapy. The presence or absence of thyroid cancer was established by pathologic, radiologic, and/or high dose 131I scan findings. RESULTS: In 12 patients, ll-201 scan revealed positive accumulations which were not found on 131I scan, of whom 9 had elevated thyroglobulin levels. In these cases, 5 cases were interpreted to have normal thyroid remnant and 7 cases showed pathologic findings (1 lung, 2 lymph node, 1 bone, and 2 lung and lymph node metastasis, and 1 false positive accumulation of thallium). Metastasis were confirmed histologically in 2 and radiologically in 5 cases. Negative Tl-201 scans, despite of positive 131I scans, occurred in 20 patients, of whom 6 had abnormal thyroglobulin levels. Seventeen cases were interpreted to have thyroid remnant, 2 cases were diagnosed to have thyroid carcinoma metastasis (1 lung, 1 lung and lymph node), and 1 case was not confumed. CONCLUSION: These results suggest that 131I scan is superior to 11-201 scan for detection of residual or metastatic differentiated thyroid carcinoma. However, the use of combined modalities may provide a higher diagnostic yield. TI-201 scan can be useful especially in cases in which 'I scan is negative despite of abnormal thyroglobulin levels.
- The Role of Low-dose ACTH Stimulation Test in the Diagnosis of Adrenal Insufficiency.
-
Chul Hee Kim, Ghi Su Kim, Hong Kyu Kim, Joong Yeol Park, Young Kee Shong, Ki Up Lee, Il Min Ahn, Sung Kwan Hong
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 1997;12(2):222-229. Published online January 1, 2001
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- BACKGROUND
Rapid adrenocorticotropin (ACTH) stimulation test using 250ug of ACTH (1-24) has been used as a standard test in the initial assessment of adrenal function. However, it has recently been suggested that a rnaximal cortisol response can be achieved with a much lower ACTH dose, and reducing the dose might further enhance the sensitivity of the test in the detection of mild adrenal insufficiency. This study was performed to evaluate the role of low-dose (lug) ACTH stimulation test in the assessment of adrenal function and the diagnosis of subtle adrenal insufficiency. METHODS: Twenty-two subjects with suspected adrenal insufficiency due to long-term corticosteroid use were included in this study. The correlations between clinical features and the serum cortisol responses to low dose (lug) and high dose (250 ug) ACTH stimulation were evaluated. RESULTS: In high dose test, 10 (67%) out of 15 subjects with clinical features of adrenal insufficiency showed decreased serum cortisol response (peak cortisol level <18 ug/dL), but 5 (33%) subjects showed normal response (peak cortisol level > 18ug/dL). On the other hand, 14 (93%) subjects with clinical features of adrenal insufficiency showed decreased serum cortisol response in low dose test, while only one showed normal response. In 7 subjects without clinical features of adrenal insufficiency, 5 subject (71%) showed normal response, and 2 subjects (29%) showed decreased response in both low and high dose tests. CONCLUSION: These results suggest that the 1-ug low dose ACTH stimulation test might be more sensitive than conventional 250-ug test in the detection of mild adrenal insufficiency. Further studies are needed to determine the optimal dose of ACTH and the criteria for normal response to ACTH stimulation.
- Piruitray Thyrotropin-Secreting Tumors in Korean.
-
Chul Hee Kim, Ghi Su Kim, Hong Kyu Kim, Joong Yeol Park, Young Kee Shong, Sang Bum Hong, Jung Min Ko, Chang Jin Kim
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 1997;12(2):165-175. Published online January 1, 2001
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- BACKGROUND
Thyrotropin-secreting pituitary adenoma is an uncommon disease and about 150 cases has been reported in the world literature. In Korea, only seven cases were reported as yet. The authors recently experienced four cases of TSH secreting pituitary tumor and analyzed the clinical characteristics and treatment outcomes of TSH-secreting tumors in Korean. METHODS: We analyzed clinical records of the four cases who had been recently treated at Asan Medical Center and the Korean literature which deals with the previously reported seven cases of TSH-secreting pituitary tumor. RESULTS: The average age at diagnosis was 37 years (ranging from 11 to 55 years). Four were men and seven were women. After the detection of hyperthyroidism, TSH-secreting pituitary adenoma was diagnosed 3.6 years later on the average. Ten patients presented with hyperthyroidism, but one had primary hypothyroidism. Typical features of acromegaly were observed in two patients. Visual disturbance was present in three cases, and galactorrhea was present in one case. Serum TSH concentrations ranged from 1.5 to 42.5uIU/mL showing mildly elevated or unsup-pressed TSH levels despite of elevated serum thyroid hormone concentrations. Among six cases in whom a-subunit level was measured, five showed elevated a-subunit level and a-subunit/TSH molar ratio. Two of 11 cases had microadenoma and the remainder had macroadeno#ma. Immunohisto-cheical studies were done in eight cases and revealed that three were positive for TSH only and five patients were positive for multiple hormones. Eight patients underwent transsphenoidal pituitary surgery and seven (88%) of them were cured. External irradiation or octreotide was used as adjunctive treatment in three cases. After treatment, TSH levels decreased in all six patients studied, hyperthyroidism was eliminated in all eight patients studied and visual disturbance was improved in two patients. CONCLUSION: Clinical characteristics of TSH-secreting pituitary adenoma in Koreans were similar with world literature, but were more common in women, had less visual disturbance and better surgical results. Diagnosis was commonly delayed for several years. TSH-secreting pituitary adenoma may be diagnosed more frequently and earlier with widespread use of sensitive TSH assay and early and proper diagnosis would lead proper treatments with improved outcome.
- Clinical Features of Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Type I in Koreans.
-
Chul Hee Kim, Ghi Su Kim, Hong Kyu Kim, Joong Yeol Park, Young Kee Shong, Ki Up Lee
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 1996;11(2):163-174. Published online November 7, 2019
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Background
Multiple endocrine neoplasia type I(MEN I) is a rare, eomplex, and potentially lethal disease. In Korean, only five anecdotal cases were reported as yet. The authors rescently experienced four cases of MEN I, and analysed the clinieal characteristics of MEN I in Koreans. Methods: The authors evaluated nine cases of MEN I, retrospectively. Four cases were analysed by clinical records in patients admitted to Asan Medical Center and five cases were reviewed by previously reported Korean literature from 1986 to 1995. Results: The average age was 39 years(ranged from 33 to 59 years). Eight of the nine patients had hyperparathyroidism documented by elevated serum calcium and PTH level with or without evidence of parathyroid mass. Initial presenting manifestations were symptomatic urinary stone, hypoglycernia due to insulinoma, hypogonadism, acromegaly, or peptic ulcer. Eight of nine patients had pancreatic islet cell tumors, and three of them were be malignant by radiologic and/or pathologic findings. The pancreatic tumors produced various hormones, such as gastrin, insulin, glucagon, or combination of them. Six of the nine cases had pituitary lesion. The most cornmon pituitary tumor was prolactinoma and the remaining was GH or GH and TSH producing tumor. In addition to the major components of MEN I, four had adrenocortical hyperplasia or adenoma and two had carcinoid tumor. There was only one familial case. Conclusion: The clinical charateristics of MEN I in Korean are mostly not different from the previous reports except older age at diagnosis, more comrnon adrenal involvement(44%) and gastrointestinal carcinoid tumor(22%). Although only one case was familial, more cases could be found if careful screening were done for the family members of the MBN I patients. In addition, screening and close follow up for endocrine pancreatic tumors are required for MEN I patients without detectable pancreatic lesion becau~se the malignant potential of pancreatic tumors has beeome an increasing concem for the prognosis of MEN I.
- Autoantigenic Role of Variant Thyroperoxidase.
-
Young Kee Shong, Dae Hyuk Moon, Ghi Su Kim
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 1996;11(1):61-67. Published online November 7, 2019
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Background
Thyroperoxidase(TPO) is one of the most important autoantigens in autoimmune thyroid disorders and autoantibody to TPO is found in almost every patients with various autoimmune thyroid diseases. Human TPO was already cloned and the completed nucleotide sequences are well known. In human thyroid tissues, several variants mRNA's of TPO are found in addition to the wild type. Especially the variants lacking exon 10(TPOΔexon10) and exon 16(TPOΔ exon16) are found in very large amount in both normal and Graves thyroid tissues. The significance of these variants TPO mRNAs are largely unknown. The authors tried to investigate the autoantigenic role of these variant TPO. Methods : To produce variant TPO cDNAs, oligonucleotide directed mutagenesis was performed using cDNA for wild type human TPO as template. The produced variants cDNAs were transfected into Cos-7 cells and variants TPO proteins were tested against patients sera showing high titers of anti-TPO antibody. Results: Seven of 12 Graves sera reacted with TPOΔexon 10 and 8 Graves sera with TPOΔ exonl6. Eight of 15 Hashimoto sera reacted TPOΔexon16 and 9 with TPOΔexon16. The reactivity with variants TPO was not related to clinical findings. Conclusion: These two variant TPOs, that is TPOexon10 and TPOΔexon16, could act as an autoantigen if they were translated in vivo, and could play a role in autoimmune thyroid disease. Their exact role in the pathogenesis of autoimmune thyroid disorders are to be clarified.
- Clinical Significance of Routine Measurement of Serum Calcitonin in Korean Patients with Thyroid Nodules as a Screening test of Sporadic Thyroid Medullary Carcinoma.
-
Young Kee Shong, Cheol Soo Choi, Hye Young Park, Bo Youn Cho
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 1996;11(1):11-17. Published online November 7, 2019
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Background
: It is not easy to diagnose sporadic medullary thyroid carcinoma(MTC) before surgery and this might lead the patient reoperation and/or lowered chance of definite cure. Methods : The prevalence of sporadic MTC in Korean was studied in patients with thyroid nodules. A prospective study of 1048 consecutive patients with thyroid nodules was performed. In all patients, measurements of basal serum calcitonin, thyroid hormones, TSH, anti-thyroglobulin antibody and anti-thyroperoxidase antibody were undertaken along with technetium-99m thyroid scintigraphy and fine needle aspiration cytology. In patients with elevated basal calcitonin levels, calcium stimulated calcitonin level was determined. Results: Two patient had markedly elevated calcitonin levels(over 3,200 pg/mL and 1,763 pg/ mL) and another one slightly elevated calcitoni#n(71.9 pg/mL). Fine needle aspiration cytology was suggestive of MTC in one and nodular hyperplasia in the other two. They underwent surgery and histological examination revealed MTC in those two with markedly elevated calcitonin levels. The patient with slightly elevated calcitonin, who was on the maintenance hemodialysis due to chronic renal failure, had nodular hyperplasia. Conclusion: MTC was found in 0.19% of patients with thyroid nodules, which was not different with the previously reported prevalence in Europe. Routine measurements of serum calcitonin might be of value to detect sporadic MTC; however, the cost-effectiveness of routine measurement of serum calcitonin is not clear, considering the relatively low prevalence of MTC in Koreans.
- A Korean Pedigree of Paget Bone Disease.
-
Young Kee Shong, Joong Yeol Park, Ki Up Lee, Ghi Su Kim, Suhn Hee Kim, Jae Kun Cho, You Sook Cho, Hong Ja Kim, Myung Jin Shin
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 1995;10(4):451-455. Published online November 7, 2019
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Paget bone disease(PBD) is usually focal, but can be wide spread disorder of the skeletal remodeling characterized by greatly increased osteoclast size and activity. It has extremely variable prevalence worldwide, being common in England and northern European countries and areas populated by their descendants, but strikingly uncommon in Asia, the middle east, Africa and Scandinavia. It's occurrence also shows familial clustering, some postulates autosomal dominant inheritance. Many studies have shown that paramyxoviruses may play a critical role in the etiology of this disorder. However, the precise etiology of PBD remains unknown.We describe a kindred with PBD in 3 successive generations. The propositus, a 55-year-old man, has panostotic PBD and giant cell reparative granuloma of pagets disease involving his head, mandible, abdomen and ileum, rare tumorous complication of Paget's disease. Bowed limbs were first noticed at age 25 years, and progressed for 20 years. Giant cell reparative granuloma began manifesting at age 45 years, and responded dramatically to high-dose dexamethasone therapy. His pretreatment biochemical finding were remarkable for elevated serum ALP, 765(normal 66-220 u/L) and osteocalcin, 154(normal 6.3-30.7 mg/ml), but normal serum calcium, phosphorous, 250HD and PTH. A nondecalcified iliac crest specimen demonstrated classic histopathologic 25OHD and PTH. A nondecalcified iliac crest specimen demonstrated classic histopathologic changes of PBD on light microscopy. His decreased father had a similar degree of bony deformities beginning at age 20 years, but had not been examined. His two asymptomatic daughters, 20 and 24-year-old, were both found to be affected with widespread PBD by bone scan, radiographic study, and their serum ALP levels, 939 and 435U/L, respectively. This is the first report of familial occurance of PBD and a case of giant cell reparative granuloma of Paget's disease in Korea, where PBD is very rare.
- Thyroid Stimulating Antibody Assay with Chinese Hamster Ovary Cells Expressing Human Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH) Receptor; Optimization of Assay Condition.
-
Bo Youn Cho, Hong Kyu Lee, Young Kee Shong, Chang Soon Koh, Ka Hee Yi, Yeon Sahng Oh, Won Bae Kim
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 1995;10(4):333-346. Published online November 7, 2019
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- We investigated the optimal condition of thyroid stimulating antibody(TSAb) assay using Chinese hamster ovary cells transfected with cDNA of human TSH receptor(TSHr-CHO) stably expressing functional TSH receptors. The extracellular cAMP responses of TSHr-CHO cells to the stimulation of bTSH or Graves' IgG were observed in three different incubation media. Stimulation indices of extracellular cAMP were higher when sucrose containing NaCl-free isotonic Hank's balanced salt solution(HBSS)(media A)was used as incubation media than those of NaCl-free hypotonic HBSS(media B) or those of NaCl containing isotonic HBSS(media C). The incubation of TSHr-CHO cells in media B caused marked increase in the basal cAMP level without concomittant fold-increase in the stimulated cAMP level at various doses of bTSH and Graves' IgG. Decreasing the stimulation indices of extracellular cAMP, use of media B failed to detect TSAb activities in two TSAb-positive Graves' IgG tested. In case of media C, extracellular cAMP responses are poor at 0.001 and 0.1U/L of bTSH and at all doses of Graves' IgG tested(0.5, 1, 5g/L). The incubation of TSHr-CHO cells in media B caused significant increase in the number of trypan blue-stained, nonviable cells(5.7+-1.5, 7.6+-1.9 and 8.5+-1.6% at 1, 2 and 3h of incubation, respectively; p<0.01) comparing to those incubated in media A or media C(about 2-3% in both media). Those decrease in the viability of TSHr-CHO cells when incubated in hypotonic incubation media may explain the decrease in the stimulation index of extracellular cAMP with the use of media B in contrast to the case of FRTL-5 cells. TSAb assay of 87 consecutive fresh Graves' patients with TSHr-CHO cells using media A detected TSAb activities in 90%(78 patients) of them, and moreover TSAb activities showed significant positive correlation with the pre-treatment serum T_3 and free T_4 levels of those patients. We conclude that TSAb assay with TSHr-CHO cells is a sensitive and physiologically relevant assay system to measure TSAb activities merely through measurements of extracellular cAMP provided that the cells are incubated in NaCl-free isotonic incubation media.
- Measurement of Thyrotropin Receptor Antibody.
-
Young Kee Shong
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 1995;10(4):329-332. Published online November 7, 2019
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- No abstract available.
- A Case of Nesidioblastosis in Adult with Hyperinsulinemic Hypoglycemia.
-
Young Kee Shong, Hong Kyu Kim, Young Joo Min, Joong Yeol Park, Sung Kwan Hong, Ki Up Lee, Duck Jong Han, Ho Jeong Lee, Ghi Su Kim, Gyung Yub Gong
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 1994;10(3):273-277. Published online November 6, 2019
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Nesidioblastosis is a primarily childhood disease which is often associated with hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia. It is very rarely found in adults. Only a few well documented cases are found in the world interature. The authors have recently experienced a case of nesidioblastosis in an adult. A 55-year-old man was admitted due to repeated episodes of reversible loss of consciousness. Hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia was documented. Under the presumptive diagnosis of insulinoma, localization procedures were done but no definite tumor was found. Only suspicious gradient in insulin concentration was found around the head of pancreas by percutaneous transhepatic portal venous sampling. Exploratory laparotomy was performed and Whipple's operation was done. Seventy percent of proximal pancreas was removed. Histomorphometric study of the resected specimen revealed uneven graded hyperplasia of the islet cells with the most profuse hyperplasia in the head region and progressive decrease in the degree of hyperplasia to the body and tail. The patient remains euglycemia until 6 months after operation since immediate postoperative period and can tolerate 24 hour fasting without any medication.
- Clinical Significance of Thyrotropin Measurement as a Screening Test in Ambulatory Patients.
-
Young Kee Shong, Hong Kyu Kim, Ghi Su Kim, Dae Hyuk Moon
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 1994;10(3):191-199. Published online November 6, 2019
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- The objective of this study is to determine the clinical significance of thyrotropin(TSH) measurement as a screening test in ambulatory patients. One hundred and nintynine patients with abnormal TSH levels detected at routine examinations were studied. The patients were examined and histories about the recent medications and nonthyroidal illness were taken. Additional thyroid tests were done including measuments of total T_3, free T_4, antithyroid autoantibodies, thyroid scan and radioiodine uptake. Of the total 199 patients, 107(54.7%) had thyroid diseases. 49 out of 101 patients with subnormal TSH had thyroid diseases, and the remainder had supressed TSH due to medications, associated nonthyroidal illness, and normal variations. 58 out of 99 patients with elevated TSH had thyroid diseases. Of those 47 patients whose TSH level was below 0.05 mIU/L, functional sensitivity of TSH assay in our laboratory, 37 had thyroid diseases. Of those 19 patients whose TSH level was above 7.0mIU/L, two times of upper normal limit, all had thyroid iseases.Simultaneous measurement of free T_4 disclosed 50(25.1%) out of total 199 patients with abnormal TSH levels had abnormal free T_4 values which is regarded as evidence of clinical thyroid dysfunction. In summary, a single measurement of TSH level alone seems to have high sensitivity but low specificity. Simultaneous measurement of free T_4 can reasonably compensate the low specificity of TSH measurement. In case of ambulatory patients without significant nonthyroidal illness, TSH values below functional sensitivity or above twice upper normal limit may predict thyroid disease and dysfunction with reasonable specificity.
- Nesidioblastosis in Adult with Hyperinsulinemic Hypoglycemia.
-
Young Kee Shong, Hong Kyu Kim, Young Joo Min, Joong Yeol Park, Sung Kwan Hong, Ki Up Lee, Duck Jong Han, Ho Jeong Lee, Gyung Yub Gong
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 1994;10(2):168-169. Published online November 6, 2019
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- No abstract available.
- Measurement of free T4.
-
Young Kee Shong
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 1994;10(2):95-97. Published online November 6, 2019
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- No abstract available.
- A Case of Primary Thyroid Lymphoma Involving Bone Marrow (Stage IVE) Assoeiated with Hashimoto's Thyroiditis.
-
Young Kee Shong, Joong Yeol Park, Ghi Su Kim, Jae Kun Cho, Yun Ho Chu, Wan Sik Eom, Sang Hee Kim, Hyun Sook Chi, Gyung Yub Gong, Ki Up Lee
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 1994;9(4):390-394. Published online November 6, 2019
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Primary lymphoma of the thyroid is a relatively rare malignant tumor of the thyroid. It is known to be frequently associated with Hashimoto's thyroiditis. In Korea, a few cases of primary lymphoma of the thyroid have been reported and most of these cases were in the stage I E or II E. Recently, we experienced a case of the primary thyroid lymphoma, stage IV E associated with Hashimoto's thyroiditis in a 70-year-old woman who presented with dysphagia and dyspnea due to rapidly enlarging neck mass.She was treated with combination chemotherapy(cyclophosphamide, adriamycin, vincristine and methylprednisolone) and local radiotherapy and achieved partial response with resolution of dysphagia and dyspnea.
- Thyroperoxidase in Autoimmune Thyroid Disorders.
-
Young Kee Shong
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 1994;9(4):277-283. Published online November 6, 2019
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- No abstract available.
- Cushing's Disease Due to ACTH Producing Pituitary Carcinoma.
-
Young Kee Shong, Joong Yeol Park, Ghi Su Kim, Won Kyoung Cho, Jung Kyo Lee, Ghee Young Choe, Mun Ho Lee, Ki Up Lee
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 1994;9(2):136-140. Published online November 6, 2019
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Primary carcinoma of the pituitary is only rarely reported. About half of the reported cases are nonfunctional. It is generally agreed that the presence of distant metastasis is required to clearly establish the diagnosis of pituitary carcinoma. We have experienced a case of ACTH-producing pituitary carcinoma causing Cushing's syndrome which could be diagnosed by histologic features only without evidence of distant metastasis. A 35-year-old female with Cushingoid appearance was diagnosed as Cushing's disease after biochemical and neuroradiological evaluation. Near total removal of the pituitary tumor was performed. By histopathologic examination, the tumor revealed evidences of histological malignancy such as prominent nuclear pleomorphism, frequent mitoses and extensive tumor necrosis. Pseudosarcomatous components were also noted. By immunohistochemical studies, the tumor cells expressed ACTH. However, there was no evidence of distant metastasis at the initial operation. She was diagnosed as having ACTH producing pituitary carcinoma by histologic feature only. One month later, she complained progressive nausea and vomiting, and follow-up brain MRI revealed regrowing pituitary mass. She was reoperated and near total tumor bulk was removed again followed by radiotherapy with 5580 rads. Four month after the second operation, she developed generalized tonic clonic seizure. Brain CT showed multiple enhancing nodules on left temporal and frontal lobes, and around falx cerebri. She refused further treatment and was managed only with anticonvalsants. About month after discharge she died at home.
- Sporadic Nonfamilial Hypophosphatemic Osteomalacia.
-
Young Kee Shong, Joong Yeol Park, Ghi Su Kim, You Sook Cho, Goo Yeong Cho, Sang Wook Kim, Jung Sik Park, Ki Up Lee
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 1994;9(1):25-31. Published online November 6, 2019
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Chronic hypophosphatemia caused by decreased intestinal absorption or increased renal clearance, may lead to rickets or osteomalacia independently of other predisposing abnormalities. The conditions commonly associated with increased renal clearance of phosphate are X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets, tumor associated rickets/osteomalacia, RTA and Fanconi syndrome. Recently we experienced 3 men with adult-onset, histologically proven osteomalacia associated with increased renal clearance of phosphate. None of them had a family history of bone disease, tumors or other tubular defects. All of these had remarkable biochemical and clinical improvement with medical treatment such as 1, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D and phosphate supplementation. Although we did not find tumors yet, we could not rule out the possibility of tumor-associated osteomalcia since it often takes several years to make a diagnosis because of small size, benign nature and unusual location of tumors. Thus, careful long-term follow up for tumor occurrence will be maintained in these patients with sporadic nonfamilial hypophosphatemic osteomalacia.
- Tuberculous abscess of the thyroid.
-
Seon Mee Park, Young Kee Shong, Ki Up Lee, Ghi Su Kim, Munho Lee, Kun Choon Park
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 1992;7(2):149-152. Published online January 1, 2001
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- No abstract available.
- Autonomously functioning thyroid nodules.
-
Young Kee Shong, Ki Up Lee, Ghi Su Kim, Munho Lee
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 1992;7(2):121-126. Published online January 1, 2001
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- No abstract available.
- Serum lipids and apolipoproteins in subclinical and overt hypothyro- idism and their changes with thyroxine therapy.
-
Young Kee Shong, Jin Sook Ryu, Ki Up Lee, Ghi Su Kim, Munho Lee
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 1992;7(1):31-38. Published online January 1, 2001
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- No abstract available.
- Changes in diurnal variation of thyrotropin in severe acutenonthyroidal illness.
-
Young Kee Shong, Jin Sook Ryu, Ki Up Lee, Sang Sig Cheong, Youn Suck Koh, Myung Hae Lee
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 1991;6(4):342-347. Published online January 1, 2001
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- No abstract available.
- Biochemical liver function tests in patients with Graves' disease.
-
Young Hwa Chung, Young Kee Shong
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 1991;6(1):45-50. Published online January 1, 2001
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- No abstract available.
- Simultaneous measurement of thyroid growth stimulating antibody and thyroid adenylate cyclase stimulating antibody using FRTL-5 cells in patients with Graves' disease.
-
Young Kee Shong, Dae Hyuk Moon, Ki Up Lee, Myung Hae Lee, Munho Lee, Bo Youn Cho, Chang Soon Koh
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 1991;6(1):17-24. Published online January 1, 2001
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- No abstract available.
- Mechanisms of action on blocking type-thyrotropin receptor antibody.
-
Bo Youn Cho, Dong Soo Lee, Ka Hee Yi, Hong Kyu Lee, Chang Soon Koh, Hun Ki Min, Young Kee Shong
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 1991;6(1):8-16. Published online January 1, 2001
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- No abstract available.
|